Pluralism embraces diversity by recognizing and respecting multiple beliefs, values, and cultures within a society. It fosters dialogue, cooperation, and inclusivity, promoting social harmony amid differences. Explore the rest of this article to understand how pluralism can enrich your community experience.
Table of Comparison
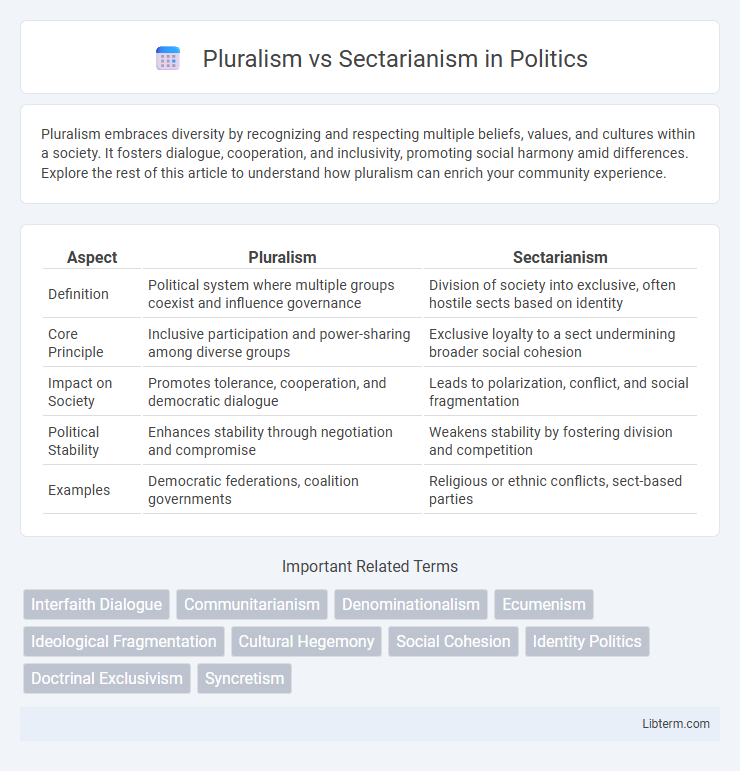
| Aspect | Pluralism | Sectarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political system where multiple groups coexist and influence governance | Division of society into exclusive, often hostile sects based on identity |
| Core Principle | Inclusive participation and power-sharing among diverse groups | Exclusive loyalty to a sect undermining broader social cohesion |
| Impact on Society | Promotes tolerance, cooperation, and democratic dialogue | Leads to polarization, conflict, and social fragmentation |
| Political Stability | Enhances stability through negotiation and compromise | Weakens stability by fostering division and competition |
| Examples | Democratic federations, coalition governments | Religious or ethnic conflicts, sect-based parties |
Understanding Pluralism: Definition and Core Principles
Pluralism is a social and political philosophy recognizing the coexistence of diverse groups, beliefs, and values within a society, emphasizing mutual respect and dialogue. Core principles of pluralism include inclusivity, tolerance, and the promotion of equal rights and opportunities for all cultural, religious, and ideological communities. Unlike sectarianism, which fosters division and exclusivity, pluralism encourages cooperation and peaceful coexistence among different identities and worldviews.
What is Sectarianism? Origins and Characteristics
Sectarianism is a rigid form of allegiance to a particular religious, ethnic, or political group that often leads to social division and conflict. Originating from historical struggles for power and identity, sectarianism is characterized by intolerance, exclusion, and antagonism between rival sects or factions within a larger community. This phenomenon frequently results in polarization, discrimination, and violence, undermining social cohesion and pluralistic values.
Historical Evolution of Pluralism and Sectarianism
The historical evolution of pluralism traces back to ancient civilizations where diverse religious, ethnic, and cultural groups coexisted under shared political systems, fostering tolerance and dialogue. In contrast, sectarianism emerged prominently during periods of political fragmentation and religious reformations, often resulting in exclusive identity formation and conflict between competing sects or factions. Over centuries, pluralism developed as a framework for managing diversity through inclusion and mutual recognition, while sectarianism has frequently been linked to social division and power struggles within societies.
Social Impact: Pluralism vs Sectarianism in Communities
Pluralism fosters social cohesion by encouraging diversity, inclusivity, and mutual respect among community members, which strengthens democratic values and reduces conflict. Sectarianism, in contrast, often leads to social fragmentation, exclusion, and tension, increasing the risk of violence and undermining social stability. Communities embracing pluralism experience enhanced collaboration and economic development, while sectarian divides frequently result in polarized societies with limited social mobility.
Political Implications: Governance in Pluralistic vs Sectarian Societies
Governance in pluralistic societies often emphasizes inclusive decision-making, power-sharing, and protection of minority rights to ensure political stability and prevent dominance by any single group. In contrast, sectarian societies tend to experience fragmented governance, where political power is allocated based on ethnic, religious, or sectarian identities, frequently leading to institutionalized discrimination and conflict. This division can undermine state cohesion, limit effective policy implementation, and foster cycles of political instability and violence.
Religious Dynamics: Tolerance vs Division
Religious pluralism fosters tolerance by encouraging coexistence and mutual respect among diverse faiths, promoting social harmony and shared values. Sectarianism, in contrast, intensifies division by prioritizing exclusive group identities and often leading to conflict and segregation within communities. The dynamic between pluralism and sectarianism significantly shapes societal stability and interfaith relations worldwide.
Economic Effects: Diversity and Sectarian Exclusion
Economic pluralism fosters innovation, market resilience, and inclusive growth by encouraging diverse participation across ethnic and religious groups. Sectarian exclusion limits access to resources, employment, and business opportunities, thereby hindering economic development and increasing inequality. Regions embracing pluralism typically experience higher economic productivity and social stability compared to those dominated by sectarian divisions.
Education and Identity Formation
Education plays a crucial role in fostering pluralism by promoting inclusive curricula that represent diverse cultures, religions, and perspectives, enabling students to develop multifaceted identities. Sectarianism often emerges when educational systems emphasize exclusive narratives, reinforcing in-group loyalties and marginalizing minority identities, which can lead to social fragmentation. Cultivating critical thinking and intercultural competence within schools helps counter sectarian divides and supports the formation of cohesive, yet diverse, communal identities.
Pluralism vs Sectarianism in Global Case Studies
Pluralism promotes inclusive governance and social cohesion by recognizing diverse cultural, religious, and ethnic identities within global societies, as exemplified by India's federal structure accommodating various religious communities. Sectarianism, in contrast, often fuels conflict and division, evident in the Middle East where Sunni-Shia tensions contribute to political instability in countries like Iraq and Lebanon. Effective pluralist models emphasize dialogue and legal protections for minority rights, reducing sectarian strife and fostering peaceful coexistence.
Building Inclusive Societies: Solutions and Future Directions
Building inclusive societies requires embracing pluralism by recognizing and valuing diverse cultural, religious, and ethnic identities while addressing sectarian divides through dialogue and equitable policies. Promoting education that fosters mutual respect and implementing legal frameworks that protect minority rights are critical solutions to reduce sectarian tensions. Future directions emphasize integrating digital platforms for cross-community communication and inclusive governance models to strengthen social cohesion and prevent exclusion.
Pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com