Tactical voting is a strategy where you cast your vote not for your preferred candidate, but for the one most likely to defeat a less desired contender. This approach can significantly impact election outcomes by consolidating support and preventing vote splitting among similar candidates. Explore the rest of the article to understand how tactical voting influences democratic processes and whether it's the right choice for your next election.
Table of Comparison
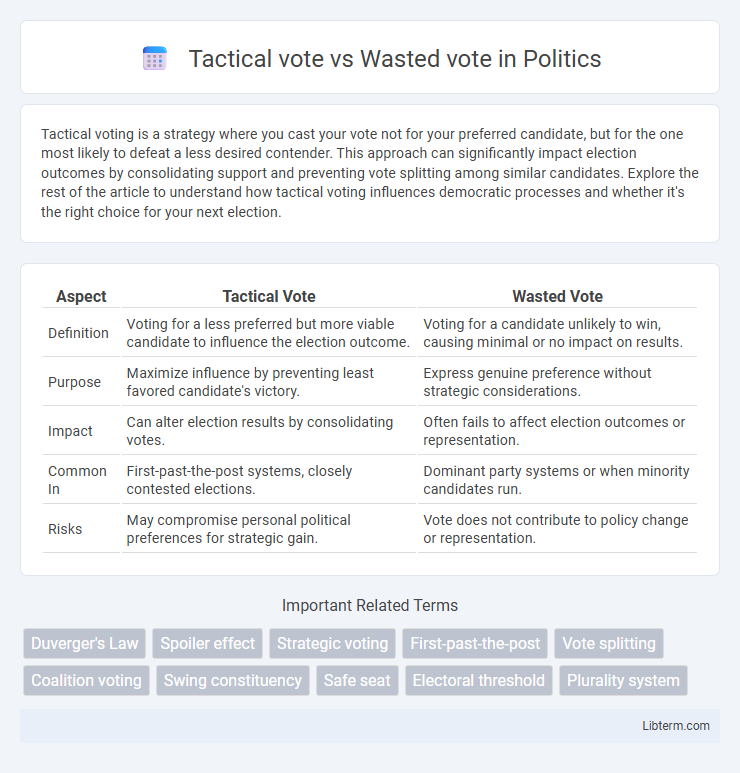
| Aspect | Tactical Vote | Wasted Vote |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting for a less preferred but more viable candidate to influence the election outcome. | Voting for a candidate unlikely to win, causing minimal or no impact on results. |
| Purpose | Maximize influence by preventing least favored candidate's victory. | Express genuine preference without strategic considerations. |
| Impact | Can alter election results by consolidating votes. | Often fails to affect election outcomes or representation. |
| Common In | First-past-the-post systems, closely contested elections. | Dominant party systems or when minority candidates run. |
| Risks | May compromise personal political preferences for strategic gain. | Vote does not contribute to policy change or representation. |
Understanding Tactical Voting
Tactical voting involves casting a ballot not for a preferred candidate but to prevent an undesirable outcome, often by supporting a more viable contender. Understanding tactical voting requires analyzing election systems, voter behavior, and strategic considerations to maximize influence. Unlike wasted votes, which fail to impact results, tactical votes aim to consolidate support and sway tight races effectively.
What Constitutes a Wasted Vote
A wasted vote occurs when a ballot does not contribute to electing a candidate, either because it is cast for a losing candidate or exceeds the number needed for victory. In first-past-the-post systems, votes for candidates with no realistic chance of winning often become wasted votes. Understanding the distribution of wasted votes helps explain why some voters engage in tactical voting to maximize the impact of their ballots.
Motivations Behind Tactical Voting
Tactical voting arises from voters' desire to influence election outcomes by supporting a less-preferred candidate with a better chance of winning, minimizing the risk of a wasted vote that fails to impact results. This behavior is motivated by strategic calculations, such as preventing an undesirable candidate's victory or maximizing the effectiveness of a vote within plurality or first-past-the-post electoral systems. Voters often weigh the trade-off between sincere preference and pragmatic choice to ensure their vote contributes to a more favorable electoral outcome.
Impact of Electoral Systems on Voting Strategies
Electoral systems significantly influence voting strategies by shaping perceptions of vote utility, where tactical voting often emerges in plurality or majoritarian systems to prevent wasted votes. In proportional representation systems, the likelihood of wasted votes decreases, encouraging voters to support preferred candidates without fear of vote loss. Strategic adaptation to system rules directly alters electoral outcomes, highlighting the profound impact of electoral frameworks on voter behavior.
Pros and Cons of Tactical Voting
Tactical voting can influence election outcomes by allowing voters to support a less preferred but more viable candidate, increasing the chances of defeating a less desirable opponent. It can prevent wasted votes in first-past-the-post systems but may undermine genuine voter preferences and reduce true representation. However, tactical voting risks perpetuating a two-party system and marginalizing smaller parties, limiting political diversity.
How Wasted Votes Influence Election Outcomes
Wasted votes, which are votes that do not contribute to a candidate's victory, significantly impact election outcomes by distorting true voter preferences and skewing representation. When a large number of votes are wasted on losing candidates or excess votes for safe winners, it can lead to disproportionate results, often favoring major parties and disadvantaging smaller or emerging ones. This phenomenon encourages tactical voting, where voters strategically select candidates with realistic chances to minimize wasted votes and influence election dynamics.
Case Studies: Tactical Voting in Recent Elections
Tactical voting played a decisive role in the 2019 UK General Election where voters strategically supported the Labour or Conservative candidates to prevent the opposing party from winning key constituencies. In the 2020 U.S. Presidential Election, some voters engaged in tactical voting by opting for moderate candidates in swing states to block more extreme rivals from securing electoral votes. Case studies from these elections demonstrate how tactical voting can significantly influence outcomes by concentrating votes on viable candidates rather than favored but less likely winners, minimizing wasted votes.
Reducing Wasted Votes: Possible Reforms
Implementing ranked-choice voting and proportional representation systems significantly reduces wasted votes by allowing voters to rank candidates or ensuring seats correspond closely to the percentage of votes received, respectively. These reforms encourage greater voter participation and more accurate representation of diverse political preferences. Electoral threshold adjustments and multi-member districts also contribute to minimizing wasted votes by broadening the impact of minority party support in legislative bodies.
Voter Psychology: Strategic Voting vs. Sincere Voting
Voter psychology reveals strategic voting, where individuals cast ballots for less-preferred but viable candidates to prevent undesirable outcomes, contrasting with sincere voting, where voters select their genuine favorite regardless of viability. Tactical voting often stems from the fear of wasted votes, driving voters to prioritize perceived effectiveness over personal preference. Understanding this dynamic highlights the tension between maximizing electoral influence and expressing true political identity.
The Future of Tactical and Wasted Votes in Democracy
Tactical voting strategically influences election outcomes by supporting candidates with better chances of winning, whereas wasted votes occur when votes do not contribute to electing any candidate. Advances in data analytics and real-time polling may reduce wasted votes by guiding voters toward more effective choices that reflect their preferences. The future of democracy hinges on enhancing voter education and leveraging technology to balance tactical voting benefits without undermining genuine representation.
Tactical vote Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com