A ballot is a tool used in elections to collect votes from participants, ensuring each individual's choice is securely recorded and counted. It can be physical, like a paper slip, or digital, depending on the voting system employed. Explore the rest of the article to understand how ballots impact the democratic process and your voting rights.
Table of Comparison
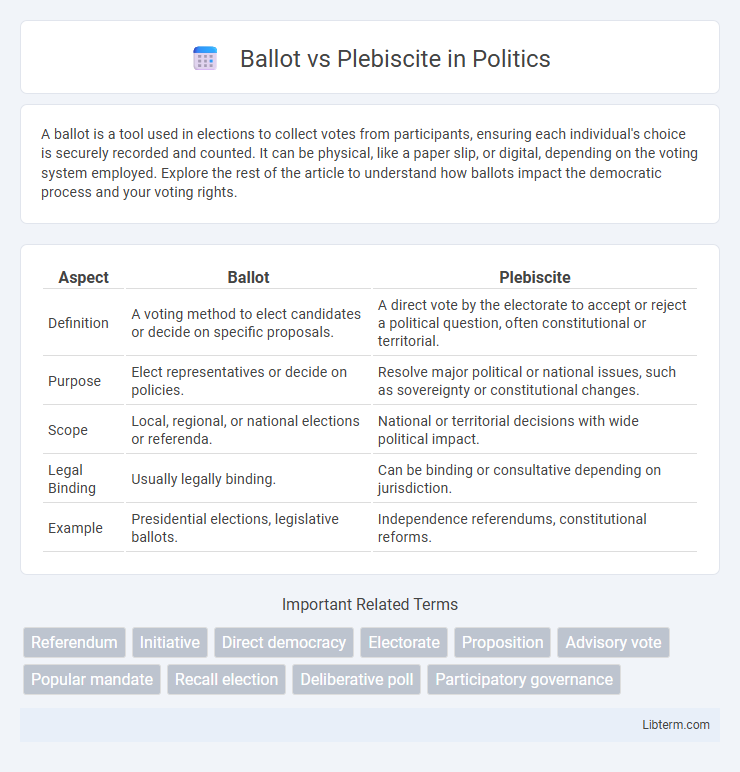
| Aspect | Ballot | Plebiscite |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A voting method to elect candidates or decide on specific proposals. | A direct vote by the electorate to accept or reject a political question, often constitutional or territorial. |
| Purpose | Elect representatives or decide on policies. | Resolve major political or national issues, such as sovereignty or constitutional changes. |
| Scope | Local, regional, or national elections or referenda. | National or territorial decisions with wide political impact. |
| Legal Binding | Usually legally binding. | Can be binding or consultative depending on jurisdiction. |
| Example | Presidential elections, legislative ballots. | Independence referendums, constitutional reforms. |
Understanding Ballots and Plebiscites
Ballots are formal voting tools used in elections to enable individuals to select candidates or decide on specific issues, ensuring confidentiality and accuracy in expressing voter preferences. Plebiscites are direct votes by the electorate on important public questions or constitutional matters, serving as a mechanism for governments to gauge public opinion or legitimize decisions. Understanding the distinct functions of ballots and plebiscites highlights their roles in democratic processes: ballots facilitate representative elections, while plebiscites allow for direct public decision-making on key policy issues.
Definitions: Ballot vs Plebiscite
A ballot is a method of voting in which individuals cast their votes anonymously to select candidates or decide on specific issues. A plebiscite is a direct vote by the electorate to approve or reject a particular proposal, often related to constitutional or territorial matters. While ballots are used in various elections, plebiscites specifically address fundamental policy or sovereignty questions.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Ballots originated in ancient Athens as a means to ensure secret voting, evolving over centuries into various forms of paper or electronic voting tools used in elections worldwide. Plebiscites date back to Roman times, where they functioned as direct votes by the citizenry on specific issues, often related to governance or constitutional matters. Both mechanisms have developed to support democratic decision-making, with ballots emphasizing individual voter secrecy and plebiscites focusing on collective public consent.
Key Differences Between Ballot and Plebiscite
A ballot refers to the method or device used for casting votes in an election, emphasizing individual voter choice, whereas a plebiscite is a direct vote by the electorate on a specific issue or policy. Ballots are commonly used in representative democracies for electing candidates or deciding referenda, while plebiscites serve to gauge public opinion on constitutional or national matters. The key difference lies in the scope and purpose: ballots focus on candidate selection or multiple-choice decisions, whereas plebiscites address a singular, binding question posed to all eligible voters.
Types of Issues Addressed
Ballots are primarily used for electing candidates and voting on a wide range of legislative and policy issues, such as local ordinances, referenda, and constitutional amendments. Plebiscites specifically address questions of national or regional importance, often relating to sovereignty, independence, or major constitutional changes. The scope of plebiscites is generally narrower but carries significant political weight compared to the broader range of issues manageable through ballots.
Legal Frameworks and Procedures
Ballots operate under strict legal frameworks established by electoral commissions, ensuring voter anonymity, standardized processes, and judicial oversight to validate election results. Plebiscites are governed by specific statutory laws or constitutional provisions that dictate the scope, question phrasing, and often require legislative approval before implementation. Both procedures involve official registration, regulated campaigning rules, and defined timelines to guarantee transparency and legitimacy within their respective legal environments.
Examples from Global Democracies
Ballots are widely used in global democracies for electing representatives, such as the United States presidential elections and the United Kingdom's parliamentary votes, where individual choices determine political leadership. Plebiscites, on the other hand, often address a single issue or constitutional matter, exemplified by the 2016 Brexit referendum in the UK and the 1995 Quebec sovereignty referendum in Canada. Both mechanisms play distinct roles in democratic governance by either selecting leaders or gauging public opinion on specific policy questions.
Impact on Governance and Public Policy
Ballots enable representative democracy by allowing citizens to elect officials who create and implement policies, ensuring governance is influenced indirectly through chosen leaders. Plebiscites provide direct input from the populace on specific policy issues, leading to immediate governmental action that reflects majority public opinion. This direct involvement can expedite policy changes but may also oversimplify complex governance matters.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Ballots offer anonymity and privacy, promoting free expression of voter preferences, but they can be costly and logistically complex to administer. Plebiscites provide a direct way for citizens to influence specific policy decisions, enhancing democratic participation, yet they may oversimplify complex issues and risk being influenced by temporary public opinion or misinformation. Both methods require careful consideration of context to balance representativeness, cost, and clarity in decision-making processes.
Choosing Between Ballot and Plebiscite
Choosing between a ballot and a plebiscite depends on the scope and formality of the decision-making process. A ballot is typically used for electing representatives or deciding specific issues in an organized electoral system, ensuring anonymity and structured voting procedures. A plebiscite, often a direct vote on significant constitutional or policy questions, serves as a tool for governments to seek public approval on critical matters, reflecting broader public consent rather than individual candidate selection.
Ballot Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com