Lobbying organizations play a critical role in shaping public policy by representing the interests of businesses, industries, or advocacy groups to lawmakers and government officials. These entities use research, strategic communication, and relationship-building to influence legislation and regulatory decisions in favor of their clients or causes. Explore this article to understand how lobbying organizations operate and impact your industry or community.
Table of Comparison
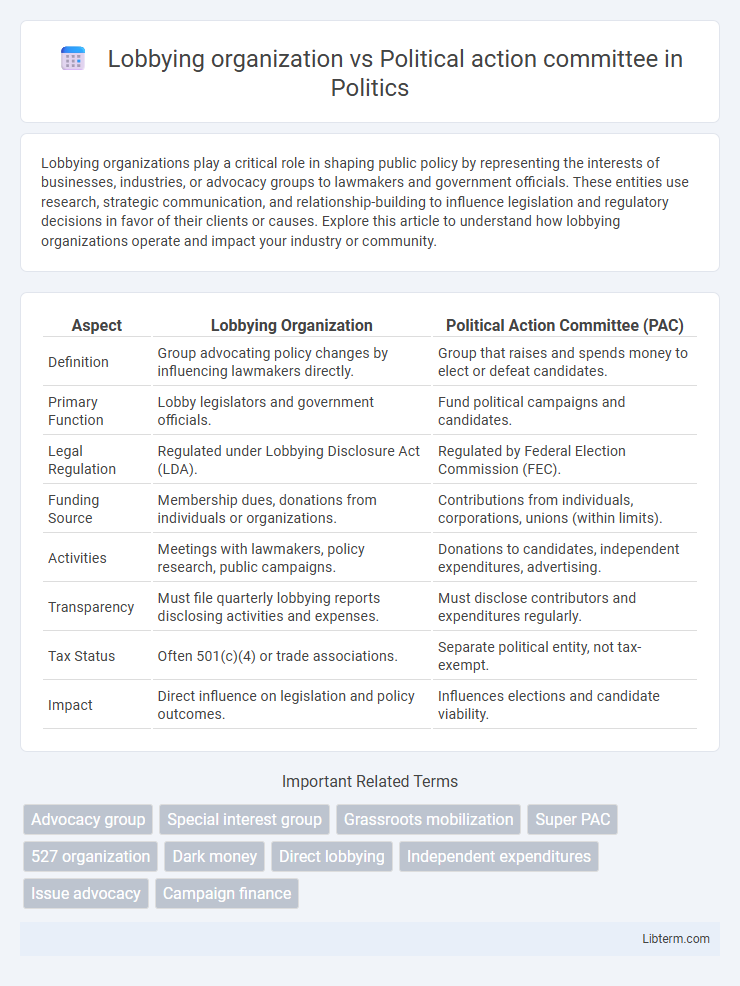
| Aspect | Lobbying Organization | Political Action Committee (PAC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group advocating policy changes by influencing lawmakers directly. | Group that raises and spends money to elect or defeat candidates. |
| Primary Function | Lobby legislators and government officials. | Fund political campaigns and candidates. |
| Legal Regulation | Regulated under Lobbying Disclosure Act (LDA). | Regulated by Federal Election Commission (FEC). |
| Funding Source | Membership dues, donations from individuals or organizations. | Contributions from individuals, corporations, unions (within limits). |
| Activities | Meetings with lawmakers, policy research, public campaigns. | Donations to candidates, independent expenditures, advertising. |
| Transparency | Must file quarterly lobbying reports disclosing activities and expenses. | Must disclose contributors and expenditures regularly. |
| Tax Status | Often 501(c)(4) or trade associations. | Separate political entity, not tax-exempt. |
| Impact | Direct influence on legislation and policy outcomes. | Influences elections and candidate viability. |
Understanding Lobbying Organizations
Lobbying organizations primarily focus on influencing legislation and policy through direct interaction with lawmakers and government officials, leveraging expert knowledge and relationship-building strategies. Political action committees (PACs) concentrate on raising and distributing funds to support political candidates and campaigns that align with their interests. Understanding lobbying organizations requires recognizing their role in advocacy and policy shaping without directly funding electoral candidates.
Defining Political Action Committees (PACs)
Political Action Committees (PACs) are organizations that collect and pool campaign contributions from members or donors to support or oppose political candidates, legislation, or ballot initiatives. Unlike lobbying organizations that directly influence policy through advocacy and communication with lawmakers, PACs primarily focus on financing electoral campaigns to gain political influence. PACs must adhere to strict Federal Election Commission (FEC) regulations governing contribution limits and disclosure requirements to ensure transparency in political funding.
Key Functions of Lobbying Organizations
Lobbying organizations primarily influence legislation and government policy by directly interacting with lawmakers and regulators to advocate for specific interests or causes. They conduct research, draft policy proposals, and mobilize public opinion to shape legislative outcomes without directly contributing to political campaigns. Unlike Political Action Committees (PACs), which focus on fundraising and supporting candidates' campaigns financially, lobbying organizations emphasize strategic advocacy and policy development to achieve their goals.
Core Activities of Political Action Committees
Political Action Committees (PACs) primarily focus on raising and distributing funds to support political candidates, campaigns, and legislation that align with their objectives. Unlike lobbying organizations that directly influence lawmakers through advocacy and policy recommendations, PACs concentrate on financial contributions to influence election outcomes and political agendas. Core activities include fundraising, financial reporting to the Federal Election Commission (FEC), and strategic allocation of contributions to candidates or parties that further their interests.
Legal and Regulatory Differences
Lobbying organizations primarily influence legislation and policy by directly interacting with government officials, whereas Political Action Committees (PACs) focus on raising and distributing funds to support political candidates or campaigns. Legally, lobbying organizations must register under the Lobbying Disclosure Act and report expenditures and activities related to influencing legislation, while PACs are regulated by the Federal Election Commission (FEC) with strict contribution limits and reporting requirements on fundraising and expenditures. Regulatory frameworks ensure transparency in lobbying activities and campaign financing, with distinct compliance standards to prevent conflicts of interest and maintain the integrity of the political process.
Funding Sources and Financial Influence
Lobbying organizations primarily receive funding from corporations, trade associations, and interest groups seeking to influence legislation through direct advocacy and relationship-building with lawmakers. Political action committees (PACs) aggregate contributions from individual donors, corporate entities, and unions to finance electoral campaigns and support political candidates aligned with their interests. The significant flow of funds into PACs allows for substantial financial influence in elections, while lobbying organizations leverage monetary resources to shape policy through persistent engagement and strategic communication.
Impact on Legislation and Elections
Lobbying organizations influence legislation by directly engaging with lawmakers to advocate for specific policies, using expertise and relationship-building to shape legislative outcomes. Political action committees (PACs) impact elections by raising and spending funds to support or oppose candidates, thereby influencing the electoral success of legislators who align with their interests. Both tools play critical roles in the legislative process, with lobbying organizations focusing on policy development and PACs targeting candidate election and re-election efforts.
Transparency and Disclosure Requirements
Lobbying organizations must register with the government and submit regular reports detailing their activities, expenditures, and clients to ensure transparency and public accountability. Political action committees (PACs) are required to disclose the sources of their contributions and expenditures to the Federal Election Commission, providing insight into their funding and political influence. Both entities face stringent transparency and disclosure mandates designed to prevent corruption and increase public trust in the political process.
Prominent Examples of Each Group
Prominent lobbying organizations such as the American Medical Association (AMA) and the National Rifle Association (NRA) leverage direct advocacy to influence legislation and public policy on healthcare and gun rights respectively. Major Political Action Committees (PACs) like EMILY's List, which supports pro-choice Democratic women candidates, and the National Association of Realtors PAC, which champions real estate industry interests, focus on fundraising and political contributions to sway election outcomes. Both entities operate within the political ecosystem but use distinct methods: lobbying organizations emphasize policy persuasion, while PACs concentrate on electoral support.
Choosing the Right Advocacy Approach
Choosing the right advocacy approach depends on the goals and resources available; lobbying organizations directly influence legislation through sustained efforts targeting policymakers, whereas political action committees (PACs) focus on funding candidates and campaigns to gain political influence. Lobbying offers a structured method to shape specific policy outcomes by engaging with legislators and regulatory agencies. PACs provide financial support to align elected officials with the organization's agenda, making them effective for broader political strategy and election-focused advocacy.
Lobbying organization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com