Engaging in regular question time sessions enhances critical thinking and encourages deeper understanding. Your active participation helps clarify complex topics and fosters a collaborative learning environment. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for making the most of question time.
Table of Comparison
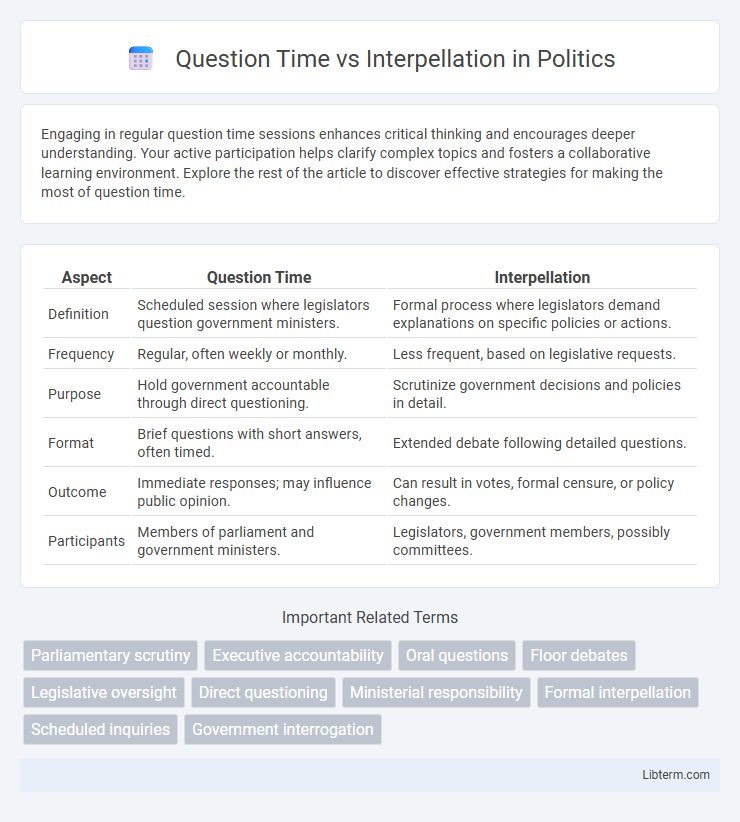
| Aspect | Question Time | Interpellation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled session where legislators question government ministers. | Formal process where legislators demand explanations on specific policies or actions. |
| Frequency | Regular, often weekly or monthly. | Less frequent, based on legislative requests. |
| Purpose | Hold government accountable through direct questioning. | Scrutinize government decisions and policies in detail. |
| Format | Brief questions with short answers, often timed. | Extended debate following detailed questions. |
| Outcome | Immediate responses; may influence public opinion. | Can result in votes, formal censure, or policy changes. |
| Participants | Members of parliament and government ministers. | Legislators, government members, possibly committees. |
Definition of Question Time
Question Time is a parliamentary procedure allowing legislators to pose direct questions to government ministers, ensuring transparency and accountability in governance. It typically occurs at scheduled intervals, enabling members to seek immediate responses on policy matters or administrative actions. This mechanism contrasts with interpellation, which usually involves formal, written questions requiring detailed ministerial replies over extended periods.
Definition of Interpellation
Interpellation is a formal parliamentary procedure where legislators submit questions or requests to government officials, compelling them to provide detailed explanations or justify policies. Unlike Question Time, which often involves brief and spontaneous inquiries, interpellations demand comprehensive responses and may lead to debates or votes on the issue addressed. This mechanism ensures governmental accountability by allowing elected representatives to scrutinize executive actions in a structured manner.
Historical Origins of Parliamentary Questioning
Parliamentary questioning traces its roots to early English parliaments in the 13th century, where members sought accountability from the monarchy. Question Time evolved as a formalized session in the UK Parliament during the 19th century, institutionalizing government scrutiny. Interpellation, originating in continental European parliaments, particularly in Eastern Europe during the 19th and 20th centuries, serves as a formal mechanism for legislators to demand detailed explanations from government officials.
Key Objectives of Question Time
Question Time aims to hold the executive accountable by enabling parliament members to query government ministers on policies and decisions, ensuring transparency and responsiveness. It prioritizes real-time scrutiny and public accountability through direct questioning and immediate answers. This process strengthens democratic oversight by facilitating open dialogue between the legislature and the executive.
Principal Purposes of Interpellation
Interpellation primarily serves as a formal mechanism in parliamentary systems to hold the government accountable by requiring ministers to provide detailed explanations on specific policy issues or actions. It enables legislators to scrutinize government decisions, demand transparency, and influence policy-making through direct questioning. Unlike Question Time, which often involves brief inquiries, interpellation involves structured debates that allow thorough examination of government conduct.
Procedural Differences Between Question Time and Interpellation
Question Time in parliamentary procedure involves brief, targeted inquiries directed at government ministers, with limited time for responses and strict adherence to pre-set questions. Interpellation allows for more detailed questioning, where members formally summon ministers to explain policies or actions, often resulting in extended debates and comprehensive discussions. The procedural emphasis in Question Time is on rapid accountability, while interpellation prioritizes in-depth scrutiny and ministerial explanation.
Roles of Government and Opposition
Question Time provides a structured opportunity for the Opposition to hold the Government accountable by asking direct questions about policy and administration. Interpellation allows the Opposition to formally challenge government ministers on specific issues, compelling detailed explanations and fostering transparency. Both mechanisms reinforce the roles of the Government in decision-making and the Opposition in scrutiny and oversight within parliamentary systems.
Impact on Political Accountability
Question Time serves as a regular parliamentary procedure allowing legislators to directly question government ministers, fostering transparency and immediate political accountability. Interpellation enables a formal, in-depth examination of government policies by requiring ministers to respond to specific allegations or issues, promoting detailed scrutiny. Both mechanisms enhance political accountability by ensuring executive actions are subject to legislative oversight and public awareness.
Global Examples of Question Time and Interpellation
Question Time, prominently practiced in the United Kingdom's House of Commons, allows Members of Parliament to directly question government ministers on policy and administration, enhancing transparency and accountability. In contrast, Interpellation is widely used in parliamentary systems such as Finland and South Korea, where legislators formally summon ministers to explain specific governmental actions, often followed by a debate or vote of confidence. Both mechanisms serve to uphold democratic oversight, with Question Time emphasizing spontaneous inquiry and Interpellation focusing on formalized scrutiny.
Comparative Effectiveness in Democratic Systems
Question Time offers real-time accountability by enabling legislators to directly interrogate government officials, fostering transparency and immediate public scrutiny. Interpellation allows for structured, formal debates on specific policies, providing detailed examination and documented responses that deepen legislative oversight. Comparative effectiveness depends on system design; Question Time suits fast-paced democracies requiring swift checks, while Interpellation excels in enhancing comprehensive policy evaluation and long-term accountability.
Question Time Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com