Centralized governance consolidates decision-making authority within a single location or group, enhancing consistency and control across an organization. This approach streamlines policy implementation and reduces redundancy, improving operational efficiency. Discover how centralized governance can optimize your organizational structure by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
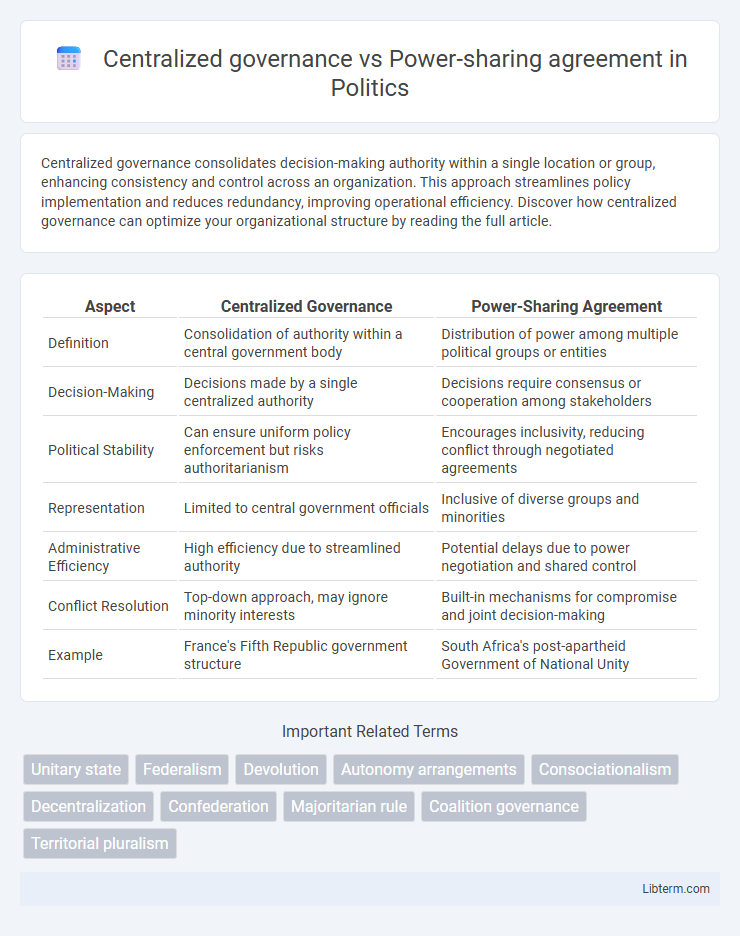
| Aspect | Centralized Governance | Power-Sharing Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consolidation of authority within a central government body | Distribution of power among multiple political groups or entities |
| Decision-Making | Decisions made by a single centralized authority | Decisions require consensus or cooperation among stakeholders |
| Political Stability | Can ensure uniform policy enforcement but risks authoritarianism | Encourages inclusivity, reducing conflict through negotiated agreements |
| Representation | Limited to central government officials | Inclusive of diverse groups and minorities |
| Administrative Efficiency | High efficiency due to streamlined authority | Potential delays due to power negotiation and shared control |
| Conflict Resolution | Top-down approach, may ignore minority interests | Built-in mechanisms for compromise and joint decision-making |
| Example | France's Fifth Republic government structure | South Africa's post-apartheid Government of National Unity |
Introduction to Governance Structures
Centralized governance concentrates decision-making authority within a single, central entity to ensure uniform policy implementation and streamlined administrative control. Power-sharing agreements distribute authority among multiple stakeholders or institutions, promoting inclusivity and balancing interests to prevent dominance by any one group. Understanding these governance structures is essential for analyzing political stability, institutional effectiveness, and conflict resolution mechanisms in diverse organizational or governmental contexts.
Defining Centralized Governance
Centralized governance consolidates authority within a single, central body responsible for decision-making, policy enforcement, and resource distribution across an entire organization or state. This model ensures uniformity, streamlined management, and rapid implementation of directives but may reduce local autonomy and adaptability. In contrast, power-sharing agreements distribute decision-making authority among multiple stakeholders or regions to promote inclusivity and balance competing interests.
Understanding Power-Sharing Agreements
Power-sharing agreements distribute political authority among diverse groups to foster inclusive governance and prevent dominance by a single faction, contrasting with centralized governance where power is concentrated in one entity. These agreements often emerge in divided societies to ensure representation of ethnic, religious, or political minorities, promoting stability and reducing conflict. Effective power-sharing requires clear frameworks for decision-making, resource allocation, and conflict resolution to balance competing interests and maintain national unity.
Key Differences Between the Two Systems
Centralized governance consolidates decision-making authority within a single, central body, leading to uniform policies and streamlined administration, whereas power-sharing agreements distribute authority among multiple groups to ensure representation and prevent domination. Centralized systems typically emphasize efficiency and control, while power-sharing structures prioritize inclusivity and conflict resolution. The key differences lie in authority distribution, decision-making processes, and mechanisms for managing diversity and political stability.
Advantages of Centralized Governance
Centralized governance streamlines decision-making processes by concentrating authority within a single, cohesive structure, resulting in faster implementation and uniform policies across the organization or state. It enhances accountability by clearly defining leadership roles and responsibilities, minimizing conflicts stemming from power distribution. Centralized systems often achieve greater efficiency in resource allocation and crisis management due to their unified control and coordinated strategy execution.
Benefits of Power-Sharing Agreements
Power-sharing agreements enhance political stability by promoting inclusivity and reducing conflict among diverse groups, fostering equitable representation and cooperation. These agreements encourage consensus-building, which strengthens democratic governance and facilitates long-term peace. By distributing power across multiple stakeholders, they prevent dominance by any single entity, ensuring balanced decision-making and respect for minority rights.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Model
Centralized governance often faces challenges such as limited local autonomy, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and slower responsiveness to regional needs, leading to criticisms of overconcentration of power and reduced citizen participation. Power-sharing agreements struggle with complexities in decision-making, potential gridlocks, and sustaining long-term cooperation among diverse groups, which critics argue can entrench divisions and hamper effective governance. Both models encounter difficulties balancing authority distribution, with centralized structures risking authoritarian tendencies while power-sharing frameworks may compromise policy coherence and stability.
Case Studies: Real-world Examples
Centralized governance in Singapore demonstrates strong national unity and efficient policy implementation, while India's power-sharing agreement showcases the accommodation of diverse ethnic and regional interests through coalition governments. Rwanda's post-genocide power-sharing arrangement has been instrumental in stabilizing the country and fostering reconciliation among conflicting groups. In contrast, China's centralized governance model enables rapid economic development but limits regional autonomy and political pluralism.
Impact on Political Stability and Inclusion
Centralized governance often leads to streamlined decision-making but may marginalize minority groups, reducing political inclusion and increasing the risk of instability through dissent. Power-sharing agreements enhance political stability by promoting inclusivity and representation of diverse groups, which can mitigate conflicts in divided societies. However, such agreements may slow decision-making processes and sometimes entrench ethnic or sectarian divisions, potentially affecting long-term governance efficiency.
Choosing the Right Governance Model
Choosing the right governance model depends on the organizational structure and stakeholder needs; centralized governance consolidates decision-making authority, ensuring uniform policies and streamlined processes, ideal for maintaining control and consistency. Power-sharing agreements distribute authority among diverse groups, promoting collaboration, inclusivity, and balanced representation, which is effective in pluralistic environments. Evaluating factors like decision speed, accountability, and stakeholder influence guides the selection between centralized and power-sharing governance frameworks.
Centralized governance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com