Democratic transparency ensures that government actions and decisions are open to public scrutiny, fostering accountability and trust between citizens and their leaders. It empowers citizens with access to information, enabling informed participation in the democratic process. Explore the rest of this article to understand how transparency shapes effective governance and your role in supporting it.
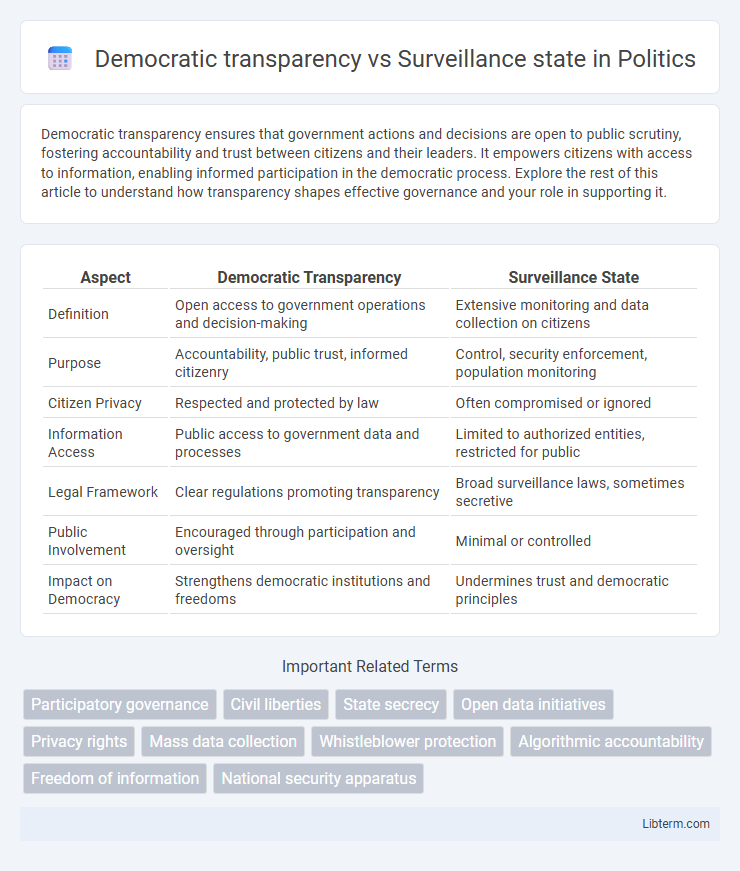
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Democratic Transparency | Surveillance State |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Open access to government operations and decision-making | Extensive monitoring and data collection on citizens |
| Purpose | Accountability, public trust, informed citizenry | Control, security enforcement, population monitoring |
| Citizen Privacy | Respected and protected by law | Often compromised or ignored |
| Information Access | Public access to government data and processes | Limited to authorized entities, restricted for public |
| Legal Framework | Clear regulations promoting transparency | Broad surveillance laws, sometimes secretive |
| Public Involvement | Encouraged through participation and oversight | Minimal or controlled |
| Impact on Democracy | Strengthens democratic institutions and freedoms | Undermines trust and democratic principles |
Understanding Democratic Transparency
Democratic transparency ensures that government actions and decisions are open and accessible to citizens, promoting accountability and public trust. It relies on mechanisms like freedom of information laws, open data portals, and transparent policymaking processes to empower citizens with knowledge. This openness contrasts with surveillance states, where secrecy and extensive monitoring undermine privacy and restrict informed public participation.
Defining the Surveillance State
The surveillance state is defined by the pervasive monitoring and collection of citizens' data by government agencies, often justified by national security or public order. This system relies on advanced technologies like facial recognition, mass data mining, and ubiquitous video surveillance to track individual behavior and communications. In contrast, democratic transparency emphasizes accountability, open government practices, and the protection of privacy rights, limiting state power to prevent unchecked surveillance.
Historical Evolution of Government Transparency
Government transparency has evolved significantly from early democratic ideals promoting open access to information to counterbalance authoritarian secrecy. Historical milestones such as the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) in 1966 institutionalized transparency by mandating public access to government records, reflecting growing demands for accountability. In contrast, the rise of the surveillance state, accelerated by digital technologies and post-9/11 security policies, has increasingly challenged these transparency principles by expanding covert government monitoring.
The Rise of Digital Surveillance Technologies
The rise of digital surveillance technologies has intensified the tension between democratic transparency and the surveillance state, as governments increasingly deploy advanced tools like facial recognition, AI-driven data analytics, and mass metadata collection to monitor citizens. These technologies enable unprecedented levels of surveillance, often without adequate legal safeguards or public accountability, undermining principles of privacy and democratic participation. Balancing national security interests with protecting civil liberties requires robust transparency frameworks and strict oversight to prevent abuse and preserve trust in democratic institutions.
Transparency as a Pillar of Accountability
Transparency serves as a fundamental pillar of accountability by ensuring that government actions are open to public scrutiny, thereby preventing abuses of power inherent in surveillance states. Democratic transparency mandates that institutions disclose information willingly, enabling citizens to make informed decisions and hold officials responsible for their conduct. By contrast, opaque surveillance practices undermine trust, as secrecy shields misconduct from detection and weakens the democratic oversight essential for safeguarding civil liberties.
Risks Posed by Expanding Surveillance Powers
Expanding surveillance powers in democratic societies risks eroding civil liberties and undermining the fundamental right to privacy, as unchecked data collection enables mass monitoring of citizens. The concentration of surveillance capabilities without robust oversight increases potential abuse by governments, including targeting political dissidents and marginalized groups. Persistent surveillance can create a chilling effect on free speech and democratic participation, threatening the accountability and transparency essential to vibrant democracies.
Privacy Rights in Democratic Societies
Privacy rights in democratic societies are fundamental to maintaining individual freedoms and preventing government overreach. Democratic transparency ensures that state actions are visible and accountable without compromising citizens' personal data, contrasting sharply with surveillance states where extensive monitoring erodes privacy protections. Balancing transparency with robust privacy laws is crucial to uphold public trust and safeguard civil liberties in democratic governance.
Balancing National Security and Civil Liberties
Democratic transparency ensures government accountability and public trust by openly sharing information and respecting citizens' privacy rights. Surveillance states prioritize extensive monitoring to prevent threats, often at the cost of civil liberties and individual freedoms. Balancing national security with civil liberties requires implementing oversight mechanisms, clear legal frameworks, and technology safeguards that protect both safety and democratic values.
Public Trust: Transparency vs Surveillance
Balancing democratic transparency with surveillance practices critically impacts public trust, as transparency fosters citizen confidence by ensuring government accountability and open access to information. In contrast, pervasive surveillance often erodes trust by creating perceptions of privacy invasion and authoritarian control, undermining the legitimacy of democratic institutions. Studies show that enhanced transparency mechanisms correlate with higher public approval and engagement, whereas excessive surveillance can lead to public skepticism and decreased civic participation.
Future Directions for Open Governance
Future directions for open governance emphasize enhancing democratic transparency through advanced digital platforms that promote citizen participation and real-time accountability. Embracing decentralized technologies like blockchain can prevent data monopolization by surveillance states, fostering secure and transparent public record-keeping. Integrating artificial intelligence in governance aims to balance efficient service delivery with privacy protection, minimizing risks of state overreach while empowering informed civic engagement.
Democratic transparency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com