Cultural diplomacy leverages the exchange of ideas, arts, and traditions to foster mutual understanding and strengthen international relationships. This approach enhances global cooperation by building trust and encouraging dialogue between diverse communities. Discover how cultural diplomacy can transform your perspective and impact global connections in the full article.
Table of Comparison
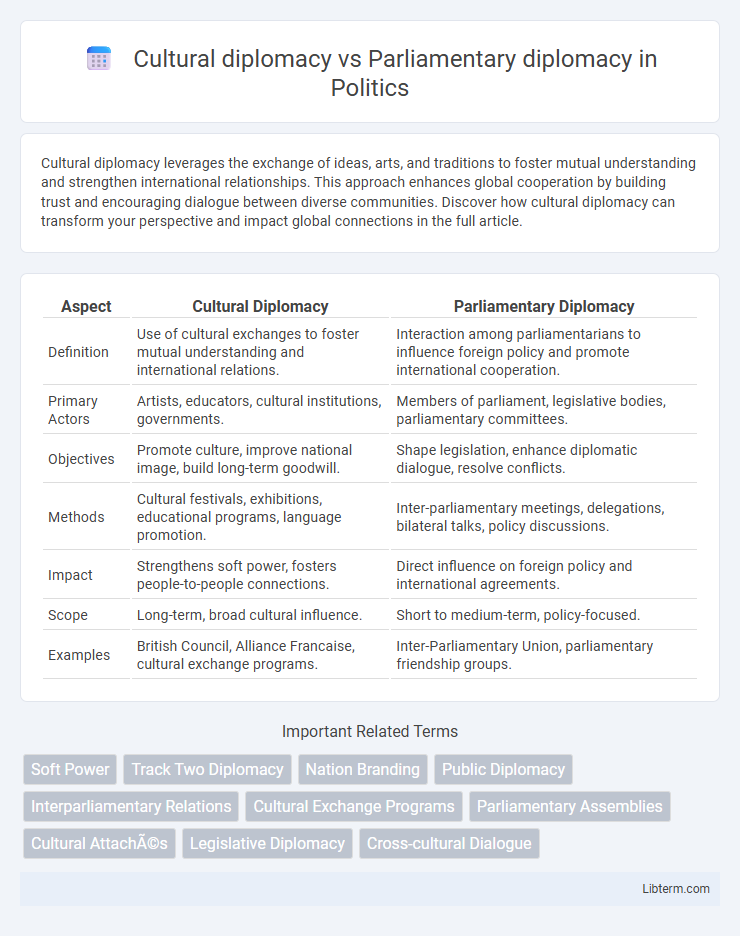
| Aspect | Cultural Diplomacy | Parliamentary Diplomacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of cultural exchanges to foster mutual understanding and international relations. | Interaction among parliamentarians to influence foreign policy and promote international cooperation. |
| Primary Actors | Artists, educators, cultural institutions, governments. | Members of parliament, legislative bodies, parliamentary committees. |
| Objectives | Promote culture, improve national image, build long-term goodwill. | Shape legislation, enhance diplomatic dialogue, resolve conflicts. |
| Methods | Cultural festivals, exhibitions, educational programs, language promotion. | Inter-parliamentary meetings, delegations, bilateral talks, policy discussions. |
| Impact | Strengthens soft power, fosters people-to-people connections. | Direct influence on foreign policy and international agreements. |
| Scope | Long-term, broad cultural influence. | Short to medium-term, policy-focused. |
| Examples | British Council, Alliance Francaise, cultural exchange programs. | Inter-Parliamentary Union, parliamentary friendship groups. |
Introduction to Cultural and Parliamentary Diplomacy
Cultural diplomacy leverages the exchange of arts, education, and traditions to strengthen international relationships and foster mutual understanding between nations. Parliamentary diplomacy involves dialogue and cooperation among legislative bodies to influence global governance, promote peace, and resolve conflicts through formal political channels. Both forms of diplomacy are essential tools in public diplomacy, complementing traditional state-to-state negotiations by engaging diverse stakeholders in international affairs.
Defining Cultural Diplomacy
Cultural diplomacy involves the exchange of ideas, values, traditions, and other aspects of culture to strengthen relationships and promote mutual understanding between countries. It uses art, music, education, and cultural events as tools to influence foreign publics and build long-term trust beyond political negotiations. Unlike parliamentary diplomacy, which centers on formal legislative dialogue and policy-making among elected officials, cultural diplomacy emphasizes people-to-people connections and soft power enhancement.
Understanding Parliamentary Diplomacy
Parliamentary diplomacy involves legislators engaging in dialogue and cooperation across national borders to promote peace, mutual understanding, and policy coordination. It differs from cultural diplomacy by emphasizing formal political processes, legislative collaboration, and conflict resolution through parliamentary channels. Key entities in parliamentary diplomacy include inter-parliamentary organizations such as the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), which facilitate structured international dialogue among lawmakers.
Historical Evolution of Both Approaches
Cultural diplomacy emerged during the early 20th century as nations sought to promote mutual understanding through the exchange of arts, education, and media, with programs like the U.S. Fulbright Program exemplifying its influence. Parliamentary diplomacy evolved from traditional state-centric diplomacy, gaining prominence in the 19th and 20th centuries as legislative bodies increasingly engaged in international dialogue, exemplified by the Inter-Parliamentary Union established in 1889. Both approaches have adapted to globalization by expanding from bilateral interactions to multilateral frameworks, influencing international relations through soft power and legislative cooperation.
Objectives and Strategies in Cultural Diplomacy
Cultural diplomacy aims to build mutual understanding and trust between nations through the exchange of ideas, arts, and traditions, fostering long-term relationships beyond formal political ties. Its strategies include organizing cultural festivals, educational exchanges, and promoting language learning to create positive perceptions and influence international public opinion. Unlike parliamentary diplomacy, which focuses on legislative dialogue and political negotiations, cultural diplomacy emphasizes soft power techniques to shape foreign policy indirectly by engaging civil society and cultural institutions.
Mechanisms and Roles in Parliamentary Diplomacy
Parliamentary diplomacy operates through formal mechanisms such as inter-parliamentary unions, bilateral legislative visits, and participation in international parliamentary assemblies, enabling lawmakers to engage directly in dialogue and cooperation across borders. Its roles include fostering mutual understanding, influencing foreign policy decisions, and promoting peace through legislative collaboration, often complementing traditional diplomatic efforts. Unlike cultural diplomacy, which emphasizes people-to-people exchanges and cultural promotion, parliamentary diplomacy leverages the authority and legislative functions of elected representatives to shape international relations.
Key Differences Between Cultural and Parliamentary Diplomacy
Cultural diplomacy promotes mutual understanding through the exchange of arts, education, and cultural heritage, emphasizing soft power to build long-term international relationships. Parliamentary diplomacy involves dialogue and negotiation among legislators to influence foreign policy and foster inter-parliamentary cooperation, focusing on formal political processes. The key difference lies in their methods: cultural diplomacy leverages cultural influence and public engagement, whereas parliamentary diplomacy operates within official legislative frameworks to shape diplomatic outcomes.
Synergies and Interactions Between Both Forms
Cultural diplomacy and parliamentary diplomacy often intersect through the promotion of mutual understanding and trust between nations, leveraging cultural exchanges alongside legislative dialogues. These synergies enhance diplomatic outcomes by combining soft power tools like cultural programs with formal parliamentary discussions, fostering deeper bilateral and multilateral cooperation. Interaction between both forms amplifies the impact of international relations by integrating people-to-people connections with policy-making processes, thus supporting sustainable peace and development.
Challenges Facing Cultural and Parliamentary Diplomacy
Cultural diplomacy faces challenges such as overcoming language barriers, managing cultural misunderstandings, and addressing the complexities of representing diverse cultural identities on a global stage. Parliamentary diplomacy struggles with political polarization, differing legislative procedures across countries, and the difficulty of achieving bipartisan consensus in international negotiations. Both forms of diplomacy must navigate issues related to credibility, communication, and the alignment of domestic and international political agendas.
Future Trends in International Diplomacy
Cultural diplomacy increasingly leverages digital platforms and virtual exchanges to foster cross-cultural understanding, enhancing soft power and global cooperation. Parliamentary diplomacy is evolving through multilateral legislative forums and inter-parliamentary networks, promoting transparency, dialogue, and conflict resolution among nations. Future trends suggest a hybrid approach integrating cultural initiatives with parliamentary engagement to address complex global challenges and strengthen international relations.
Cultural diplomacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com