An incumbent holds a current position or office, often referring to someone already serving in a political role or a corporate job. Understanding the advantages and challenges faced by an incumbent can provide insight into election dynamics or business stability. Explore the rest of the article to learn how incumbency influences outcomes and what it means for your decisions.
Table of Comparison
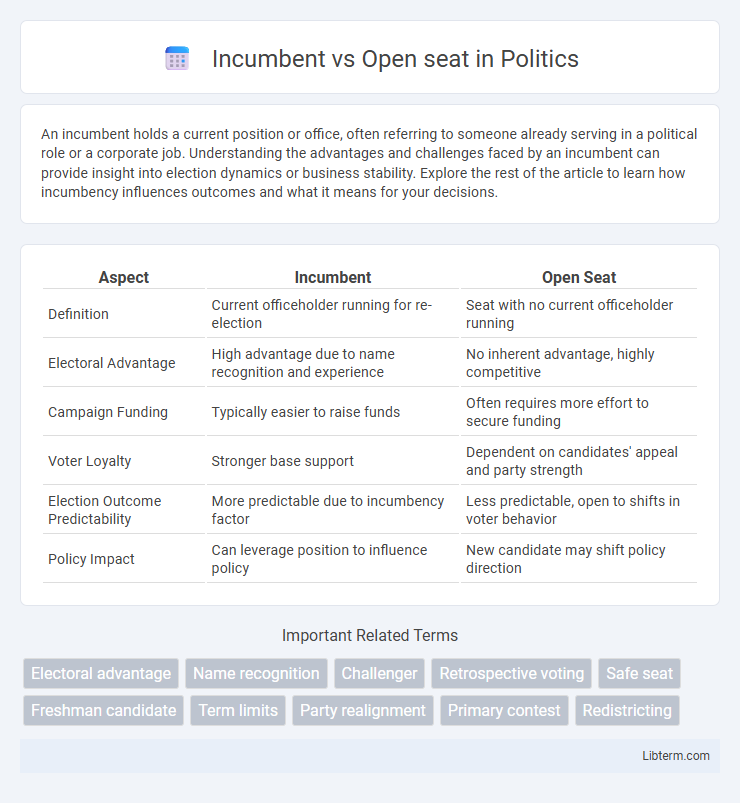
| Aspect | Incumbent | Open Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Current officeholder running for re-election | Seat with no current officeholder running |
| Electoral Advantage | High advantage due to name recognition and experience | No inherent advantage, highly competitive |
| Campaign Funding | Typically easier to raise funds | Often requires more effort to secure funding |
| Voter Loyalty | Stronger base support | Dependent on candidates' appeal and party strength |
| Election Outcome Predictability | More predictable due to incumbency factor | Less predictable, open to shifts in voter behavior |
| Policy Impact | Can leverage position to influence policy | New candidate may shift policy direction |
What is an Incumbent Seat?
An incumbent seat refers to an electoral position currently held by a sitting officeholder seeking re-election. These seats typically offer advantages such as name recognition, established voter base, and easier access to campaign resources. Election outcomes for incumbent seats often differ significantly from open seats due to the inherent benefits enjoyed by the incumbent candidate.
Defining an Open Seat in Elections
An open seat in elections refers to a political office where the incumbent is not seeking re-election, resulting in no candidate having the advantage of incumbency. This scenario often leads to more competitive races as both major parties view the seat as more winnable due to the lack of an established officeholder. Open seats typically attract a higher number of candidates, increasing voter engagement and campaign activity.
Key Differences: Incumbent vs Open Seat
Incumbent seats involve existing officeholders running for re-election, often benefiting from name recognition, established voter base, and campaign experience, which typically provides a competitive advantage. Open seats lack an incumbent candidate, leading to more unpredictable races with higher competition as candidates do not face the challenges of unseating an established officeholder. Voter turnout and campaign dynamics differ substantially between incumbent contests, where loyalty plays a role, and open seats, which tend to attract diverse candidates and increased political interest.
Advantages of Incumbents in Elections
Incumbents benefit from established name recognition, which significantly boosts voter trust and recall during elections. They often have easier access to campaign finance due to established donor networks and political connections. Incumbents can leverage their legislative achievements and constituent services as tangible proof of effectiveness, giving them a compelling advantage over challengers in both primary and general elections.
Challenges Faced by Open Seat Candidates
Open seat candidates face significant challenges such as building name recognition from scratch and securing sufficient campaign funding without the established support networks incumbents possess. They must effectively communicate their policies and vision to a wide electorate while overcoming voter loyalty to previous officeholders. Additionally, these candidates often encounter intense competition and scrutiny, making strategic campaigning and media presence critical for success.
Voter Behavior: Incumbent vs Open Seat Races
Voter behavior differs significantly between incumbent and open seat races, with incumbents often benefiting from name recognition, established political networks, and perceived experience, leading to higher voter loyalty and turnout. Open seat races typically generate more competitive campaigns and increased voter engagement, as the absence of an incumbent creates uncertainty and opportunities for new candidates to appeal to undecided or swing voters. Research shows turnout tends to be higher in open seat elections due to intensified media coverage and voter interest in potential shifts in political power.
Campaign Strategies for Incumbents and Open Seats
Incumbents leverage name recognition, established voter bases, and proven track records to target key demographics and maximize turnout through personalized outreach and issue advocacy. Campaign strategies for open seats emphasize building candidate visibility, articulating clear policy distinctions, and mobilizing grassroots support to fill the absence of an established contender. Data-driven voter targeting and strategic resource allocation are crucial in both scenarios to optimize campaign effectiveness and electoral success.
Historical Trends in Incumbent and Open Seat Outcomes
Historical trends indicate that incumbents in electoral races consistently enjoy higher reelection rates, often surpassing 80%, due to established name recognition and campaign infrastructure. Open seats, lacking an incumbent, typically result in more competitive contests with increased variability in party control, reflecting electoral volatility. Analysis of past election cycles reveals that open seat races can significantly shift legislative balances, making them critical focal points during strategic campaign planning.
Impact on Party Dynamics and Political Shifts
Incumbent seats generally offer stability for political parties due to the advantages of name recognition and established voter bases, reinforcing existing party dominance. Open seats, lacking an incumbent, often spark competitive races that increase the potential for party turnover and significant shifts in political power. These contests can lead to realignments within party dynamics by encouraging new candidates and altering voter alliances.
Conclusion: The Importance of Seat Status in Elections
Seat status plays a crucial role in election outcomes, as incumbent candidates typically benefit from name recognition, established voter bases, and greater access to campaign resources. Open seats often lead to more competitive races, attracting a higher number of candidates and increased voter engagement due to the absence of an established officeholder. Understanding the dynamics of incumbent versus open seats enables political strategists to allocate resources effectively and predict electoral volatility.
Incumbent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com