Continuity ensures your business operations remain uninterrupted during unexpected events, minimizing downtime and financial losses. It involves strategic planning, risk assessment, and resource management to maintain critical functions effectively. Discover how to build a robust continuity plan by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
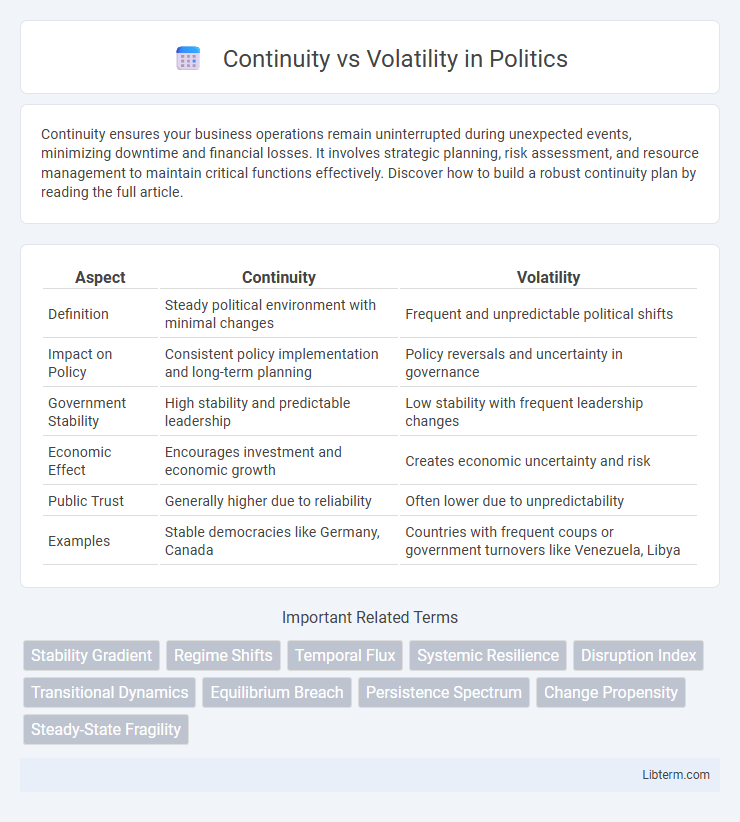
| Aspect | Continuity | Volatility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Steady political environment with minimal changes | Frequent and unpredictable political shifts |
| Impact on Policy | Consistent policy implementation and long-term planning | Policy reversals and uncertainty in governance |
| Government Stability | High stability and predictable leadership | Low stability with frequent leadership changes |
| Economic Effect | Encourages investment and economic growth | Creates economic uncertainty and risk |
| Public Trust | Generally higher due to reliability | Often lower due to unpredictability |
| Examples | Stable democracies like Germany, Canada | Countries with frequent coups or government turnovers like Venezuela, Libya |
Understanding Continuity and Volatility
Continuity in business refers to the ability to maintain consistent operations and performance levels over time, often supported by stable processes and predictable environments. Volatility describes the frequency and magnitude of unexpected changes or fluctuations impacting markets, prices, or organizational conditions. Understanding continuity and volatility enables companies to develop strategies for risk management, resilience, and sustainable growth by balancing stability with adaptability.
Historical Context: Continuity vs Volatility
Historical context reveals periods of continuity marked by stable political institutions and incremental social changes, contrasted sharply by volatile eras defined by rapid upheaval and transformative events such as revolutions or economic crises. Continuity often underpins the preservation of cultural norms and legal frameworks, while volatility accelerates shifts in power structures and societal values. Understanding this dynamic aids in analyzing how past societies responded to challenges and adapted over time.
Key Drivers of Continuity
Key drivers of continuity include stable market demand, consistent consumer behavior, and reliable supply chains that ensure smooth operations. Strong brand reputation and effective risk management strategies contribute significantly by maintaining trust and minimizing disruptions. Furthermore, continuous innovation and robust organizational culture provide resilience, enabling businesses to sustain growth despite changing external conditions.
Factors Leading to Volatility
Factors leading to volatility include economic instability, geopolitical tensions, fluctuating market demand, and sudden regulatory changes. High-frequency trading, investor sentiment shifts, and unexpected global events such as natural disasters or pandemics exacerbate market unpredictability. These elements disrupt continuity by causing rapid price swings and reduced market confidence.
Impact on Organizational Performance
Continuity in organizational operations fosters stability, enabling consistent output, employee confidence, and long-term strategic planning that enhances overall performance. Volatility introduces rapid, unpredictable changes that can disrupt workflows, reduce productivity, and increase operational risks, posing challenges to maintaining competitive advantage. Balancing continuity with adaptive capabilities allows organizations to sustain efficient performance while responding agilely to market fluctuations and external shocks.
Case Studies: Continuity in Action
Case studies on continuity illustrate how organizations maintain stability through consistent processes and long-term strategic planning, enabling resilience amid market fluctuations. For example, Toyota's implementation of lean manufacturing demonstrates operational continuity by reducing waste and ensuring quality, which sustains competitive advantage. Similarly, Procter & Gamble's commitment to continuous innovation balances market volatility with steady growth, showcasing continuity in action.
Case Studies: Volatility Unleashed
Case studies like the 2008 financial crisis demonstrate volatility unleashed through rapid market fluctuations and systemic failures, highlighting the fragility of economic continuity. The COVID-19 pandemic triggered unprecedented supply chain disruptions and stock market volatility, emphasizing challenges in maintaining operational stability. Firms embracing agile risk management frameworks successfully navigated these periods, showcasing the critical balance between continuity and volatility in dynamic environments.
Strategies to Balance Continuity and Volatility
Effective strategies to balance continuity and volatility include implementing flexible operational frameworks that adapt to market fluctuations while maintaining core business processes. Utilizing scenario planning and risk management tools enables organizations to anticipate potential disruptions and respond proactively without compromising long-term stability. Integrating agile methodologies with robust governance structures fosters innovation and resilience, ensuring sustained performance in dynamic environments.
Continuity vs Volatility in Decision Making
Decision making under continuity involves stable environments where past experiences reliably predict future outcomes, promoting consistent strategies and calculated risk-taking. In contrast, volatility introduces rapid, unpredictable changes that require adaptive decision making, flexibility, and real-time information processing to mitigate risks. Effective leaders balance continuity's predictability with volatility's uncertainty by developing dynamic decision frameworks that leverage historical data and emerging trends.
Future Trends in Managing Continuity and Volatility
Future trends in managing continuity and volatility emphasize advanced predictive analytics and adaptive risk management frameworks that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to forecast disruptions and optimize response strategies. Businesses are increasingly integrating real-time data monitoring with agile operational models to enhance resilience and sustain competitive advantage amid fluctuating market conditions. Embracing digital transformation and hybrid work environments further supports dynamic decision-making processes critical for navigating ongoing uncertainty and accelerating innovation.
Continuity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com