General elections determine the leadership and policies that shape a nation's future by allowing citizens to vote for representatives in government. Understanding the electoral process, voter eligibility, and the significance of each vote is crucial for informed participation. Explore the article to learn how your vote impacts the democratic system and the key factors influencing election outcomes.
Table of Comparison
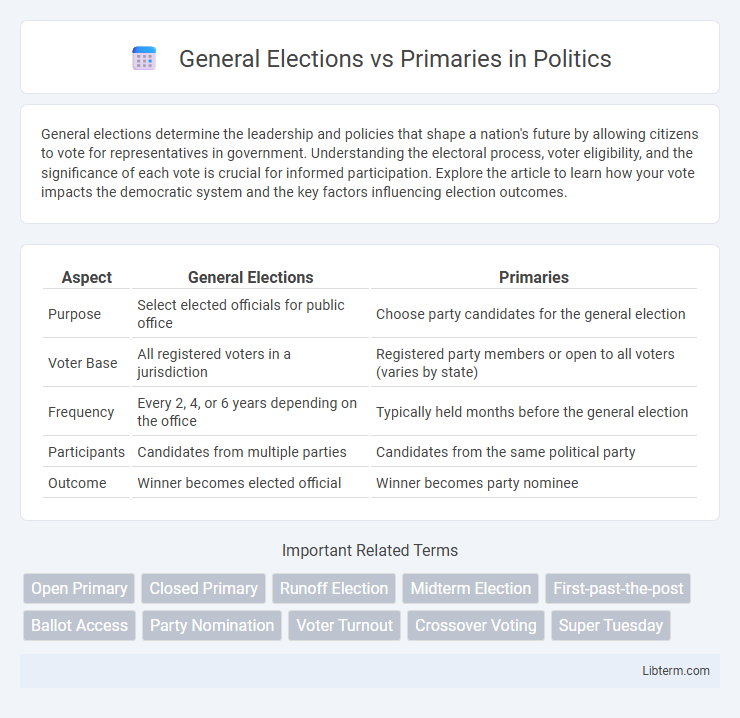
| Aspect | General Elections | Primaries |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Select elected officials for public office | Choose party candidates for the general election |
| Voter Base | All registered voters in a jurisdiction | Registered party members or open to all voters (varies by state) |
| Frequency | Every 2, 4, or 6 years depending on the office | Typically held months before the general election |
| Participants | Candidates from multiple parties | Candidates from the same political party |
| Outcome | Winner becomes elected official | Winner becomes party nominee |
Definition of General Elections
General elections determine the elected officials who will hold public office at local, state, or national levels, involving all registered voters within a jurisdiction. These elections finalize the selection process by choosing among candidates who have often advanced through primary elections or party nominations. Voter participation in general elections is critical for legitimizing governmental authority and shaping policy direction.
Definition of Primaries
Primaries are preliminary elections where political parties select their candidates for the General Elections, determining who will represent each party on the ballot. Unlike General Elections, which involve voters choosing among candidates from different parties, primaries limit voting to party members or registered affiliates depending on the state's rules. These intra-party contests play a crucial role in shaping the candidate lineup and setting the stage for the final electoral competition.
Key Differences Between General Elections and Primaries
General elections determine the final officeholder by pitting candidates from different political parties against each other, while primaries select a party's nominee through intra-party voting. Voter eligibility varies, with primaries often restricted to party members or registered affiliates, whereas general elections are open to all registered voters. The timing also differs: primaries occur earlier in the election cycle to narrow the candidate field, followed by general elections that finalize the winner.
Purpose and Significance of General Elections
General elections serve as the decisive democratic process where voters select officials to hold public office, impacting legislative and executive branches at various government levels. These elections determine the final allocation of political power, reflecting the electorate's overall preference among candidates from all parties. The purpose of general elections is to establish legitimate governance through broad participation, ensuring representatives are chosen based on majority support.
Purpose and Significance of Primaries
Primaries serve as the preliminary electoral process where political parties select their candidates for the general elections, ensuring voter participation in candidate nomination. These elections are significant because they empower party members to influence which candidates will represent their ideology, providing a democratic foundation within the party structure. By determining party nominees, primaries shape the competitive landscape of general elections and impact overall election outcomes.
Voter Participation in General Elections vs Primaries
Voter participation in general elections typically surpasses that of primaries due to higher public awareness and perceived stakes, as general elections determine final officeholders. Primary elections often see lower turnout because they involve party-specific contests, attracting mainly dedicated party members or activists. Factors influencing this disparity include voter eligibility restrictions, lack of media coverage, and varying levels of voter engagement with intra-party competition.
Election Process: General Elections Explained
General elections are the definitive voting events where registered voters select candidates for public office from those nominated in primaries or by parties. Unlike primaries that narrow down party candidates, general elections determine the final officeholders through a majority or plurality vote. This process is conducted nationwide on a fixed date, ensuring a structured and regulated democratic selection of government representatives.
Election Process: Primaries Explained
Primaries serve as preliminary elections where political parties select their candidates for the General Elections, functioning as an essential part of the candidate nomination process. Voters participate in choosing preferred candidates within a specific party, influencing which individuals appear on the General Election ballot. These elections can be open, closed, or semi-closed, varying by state regulations, impacting voter eligibility and participation in selecting party nominees.
Impact on Political Parties and Candidates
General elections determine the ultimate distribution of power among political parties by deciding which candidates secure public office, directly influencing party strength and policy direction. Primaries function as critical battlegrounds within parties, shaping candidate selection and ideological positioning that affect party unity and voter base appeal. The strategic outcomes of primaries often set the tone for general election competitiveness, impacting campaign resources, messaging, and candidate viability.
Importance of Both in the Democratic Process
General elections determine the final officeholders by allowing voters to choose among candidates from different parties, reflecting the public's ultimate political preference. Primaries serve as internal party elections that identify and select the strongest candidates, ensuring that parties present viable options to the electorate. Both stages are crucial for democratic legitimacy, voter engagement, and the overall transparency of the electoral system.
General Elections Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com