Labor unions play a crucial role in protecting workers' rights by negotiating fair wages, benefits, and safer working conditions. Understanding how labor unions operate can empower you to make informed decisions about your employment and workplace representation. Dive into the article to explore the impact of labor unions on today's workforce and your career.
Table of Comparison
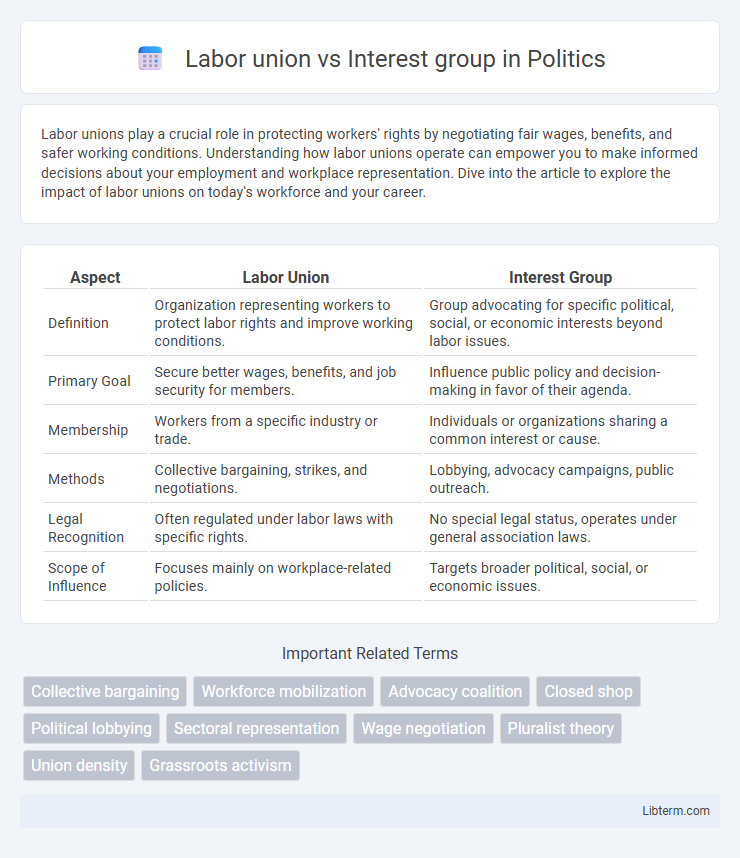
| Aspect | Labor Union | Interest Group |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organization representing workers to protect labor rights and improve working conditions. | Group advocating for specific political, social, or economic interests beyond labor issues. |
| Primary Goal | Secure better wages, benefits, and job security for members. | Influence public policy and decision-making in favor of their agenda. |
| Membership | Workers from a specific industry or trade. | Individuals or organizations sharing a common interest or cause. |
| Methods | Collective bargaining, strikes, and negotiations. | Lobbying, advocacy campaigns, public outreach. |
| Legal Recognition | Often regulated under labor laws with specific rights. | No special legal status, operates under general association laws. |
| Scope of Influence | Focuses mainly on workplace-related policies. | Targets broader political, social, or economic issues. |
Introduction to Labor Unions and Interest Groups
Labor unions are organizations formed to represent workers' collective interests, focusing primarily on improving wages, working conditions, and benefits through collective bargaining. Interest groups, broader in scope, advocate for specific political, social, or economic causes by influencing public policy and decision-making processes. Both entities wield significant influence but differ in membership composition, objectives, and methods of advocacy.
Core Definitions: Labor Unions vs Interest Groups
Labor unions are organized associations of workers formed to protect and advance their collective labor rights, wages, and working conditions. Interest groups represent a broader range of members aiming to influence public policy on specific issues without necessarily being tied to labor. Both entities engage in advocacy, but labor unions concentrate on employment-related concerns while interest groups address diverse social, political, or economic interests.
Historical Evolution of Labor Unions and Interest Groups
Labor unions emerged during the Industrial Revolution as organized groups advocating for workers' rights, fair wages, and improved working conditions, significantly shaping labor laws and policies. Interest groups developed more broadly to represent diverse societal concerns, lobbying for political influence across various sectors beyond labor issues. The historical evolution of labor unions and interest groups reflects a shift from narrowly focused worker advocacy to a complex system of political representation and policy influence.
Membership Structure and Organization
Labor unions consist exclusively of workers within a particular industry or company, organized to collectively bargain for wages and working conditions. Membership in labor unions is typically mandatory or heavily encouraged for employees in unionized workplaces, featuring a hierarchical structure with elected officers and representatives. Interest groups encompass a broader range of members united by shared concerns or goals, often including individuals, businesses, or other organizations, and they employ diverse organizational structures tailored to advocacy and lobbying efforts.
Goals and Objectives: Labor Unions vs Interest Groups
Labor unions primarily aim to protect and improve the wages, working conditions, and benefits of their members through collective bargaining and advocacy. Interest groups have broader goals, representing specific ideologies, industries, or causes by influencing public policy and legislation to advance their particular interests. While labor unions focus on employee rights and workplace issues, interest groups target a wider range of social, economic, or political objectives beyond labor concerns.
Methods of Influence and Advocacy
Labor unions primarily use collective bargaining, strikes, and workplace advocacy to influence labor laws, working conditions, and wage negotiations, positioning themselves as direct representatives of workers' interests. Interest groups employ lobbying, public campaigns, and political contributions to sway legislation and public opinion on specific issues, often engaging a wider range of stakeholders beyond a single workforce. Both utilize mobilization strategies, but labor unions emphasize member-driven actions while interest groups leverage broader advocacy coalitions and policy research.
Impact on Public Policy and Legislation
Labor unions directly influence public policy and legislation by advocating for workers' rights, collective bargaining laws, and labor standards, often leveraging strikes and collective actions to exert pressure on lawmakers. Interest groups encompass a broader array of causes beyond labor issues, using lobbying, political donations, and grassroots campaigns to shape policies across sectors like environment, healthcare, and business regulation. Both entities play pivotal roles in democratic governance, but labor unions uniquely represent the collective economic interests of workers, thereby profoundly impacting labor-related legislation and workplace regulations.
Challenges Faced by Labor Unions and Interest Groups
Labor unions face challenges such as declining membership rates, changes in labor laws, and employer resistance that hinder collective bargaining power. Interest groups often struggle with limited resources, public perception issues, and difficulties in influencing policymaking due to competing agendas. Both entities must navigate complex political landscapes and adapt strategies to maintain relevance and effectiveness.
Case Studies: Key Differences in Action
Labor unions primarily focus on collective bargaining for workers' wages, benefits, and working conditions, as demonstrated by the 2020 strikes by the United Auto Workers (UAW) which successfully secured better contracts for auto workers. Interest groups like the National Rifle Association (NRA) concentrate on broader political advocacy and influencing legislation related to gun rights without direct employer negotiations. The distinction in action is evident in how labor unions engage directly with employers for labor contracts, while interest groups operate by lobbying policymakers and shaping public opinion on specific issues.
Future Trends and the Evolving Role of Both Groups
Labor unions are increasingly adopting digital platforms to enhance member engagement and streamline collective bargaining processes, reflecting a shift toward technology-driven advocacy. Interest groups are expanding their influence through data analytics and targeted lobbying strategies to shape policy in emerging sectors like renewable energy and artificial intelligence. Both entities are evolving to address cross-sector collaborations, emphasizing adaptability to political and economic changes that will define their roles in future labor and policy landscapes.
Labor union Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com