At-large voting allows all eligible voters within a jurisdiction to vote for candidates who will represent the entire area rather than subdivided districts. This system can influence election outcomes by encouraging candidates to address broader community issues and reducing the impact of localized voting blocs. Explore the article to understand how at-large voting shapes political representation and its advantages or disadvantages for your community.
Table of Comparison
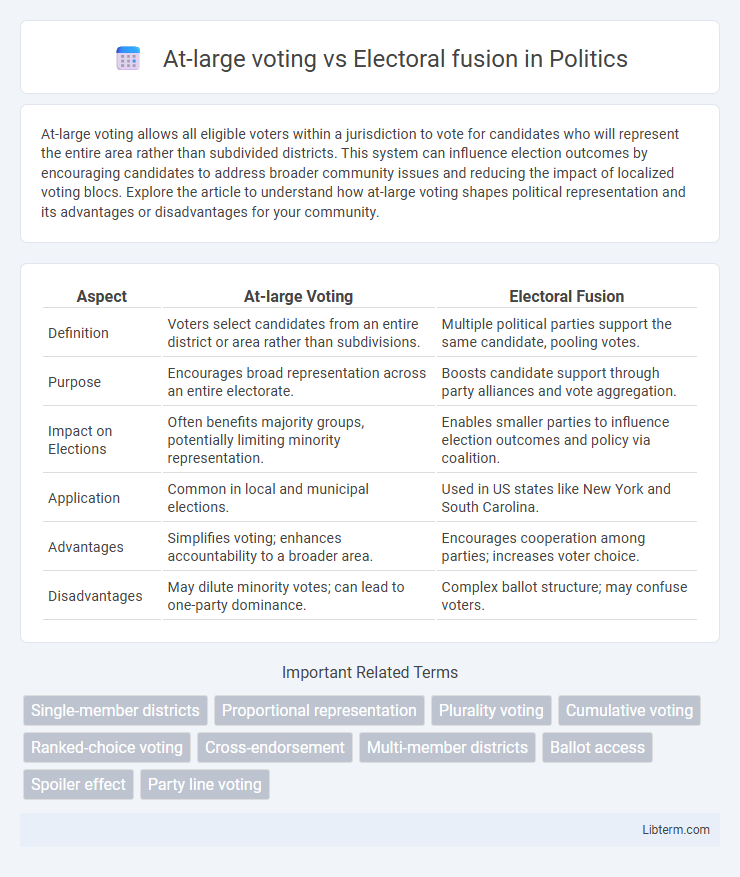
| Aspect | At-large Voting | Electoral Fusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voters select candidates from an entire district or area rather than subdivisions. | Multiple political parties support the same candidate, pooling votes. |
| Purpose | Encourages broad representation across an entire electorate. | Boosts candidate support through party alliances and vote aggregation. |
| Impact on Elections | Often benefits majority groups, potentially limiting minority representation. | Enables smaller parties to influence election outcomes and policy via coalition. |
| Application | Common in local and municipal elections. | Used in US states like New York and South Carolina. |
| Advantages | Simplifies voting; enhances accountability to a broader area. | Encourages cooperation among parties; increases voter choice. |
| Disadvantages | May dilute minority votes; can lead to one-party dominance. | Complex ballot structure; may confuse voters. |
Understanding At-large Voting Systems
At-large voting systems allow all voters in a jurisdiction to vote for multiple seats, often resulting in representation that reflects the majority's preferences while potentially marginalizing minority groups. This contrasts with electoral fusion, where multiple political parties endorse the same candidate to pool votes and increase electoral chances. Understanding the mechanics and impacts of at-large voting is essential for analyzing its effects on electoral fairness, minority representation, and political competition.
What is Electoral Fusion?
Electoral fusion is a voting system where multiple political parties support the same candidate, allowing that candidate to appear on the ballot under each party's line. Votes from all party lines are combined to determine the candidate's total vote count, enabling smaller parties to influence elections without acting as spoilers. This system contrasts with at-large voting, where candidates run citywide or districtwide and voters select multiple representatives, often diluting smaller parties' impact.
Core Differences Between At-large Voting and Electoral Fusion
At-large voting involves candidates being elected by the entire voting population of a jurisdiction rather than from districts, promoting broad representation but often diluting minority votes. Electoral fusion allows multiple political parties to endorse the same candidate, consolidating support and increasing the candidate's chances through combined party lines on the ballot. The core difference lies in at-large voting structuring the electorate's geographic representation, whereas electoral fusion focuses on strategic party alliances and ballot access.
Historical Context and Evolution
At-large voting, originating in the late 19th century, was widely used in U.S. municipal elections to elect multiple representatives from a single jurisdiction, often marginalizing minority voices and prompting civil rights challenges. Electoral fusion, emerging in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, allowed multiple political parties to support a common candidate, strengthening third-party influence and coalition-building in states like New York. Over time, at-large voting faced reform through district-based systems to enhance representation fairness, while electoral fusion experienced legal fluctuations but remains a strategic tool for minor parties to impact major-party outcomes.
Advantages of At-large Voting
At-large voting allows representatives to be elected by the entire electorate, promoting broader accountability and reducing the impact of localized special interests. This system enhances electoral equity by enabling minority voices to influence outcomes across the whole jurisdiction, rather than being confined to smaller districts. The simplicity of at-large voting can also improve voter engagement and simplify ballot design, contributing to higher participation rates.
Benefits of Electoral Fusion
Electoral fusion allows multiple political parties to endorse the same candidate, increasing voter choice and amplifying minority party influence without splitting the vote. This system encourages coalition-building and strategic cooperation among parties, enhancing overall democratic representation. Compared to at-large voting, electoral fusion better reflects diverse political preferences and promotes proportional representation.
Disadvantages and Criticisms of Each System
At-large voting often leads to the underrepresentation of minority groups and can result in the dominance of majority interests, reducing political diversity and marginalizing smaller communities. Electoral fusion faces criticism for potentially confusing voters due to multiple party endorsements for a single candidate and enabling strategic alliances that may obscure true candidate positions. Both systems can diminish electoral competitiveness by consolidating power among established parties or groups, limiting voter choice and reducing accountability.
Impact on Minority Representation
At-large voting systems often dilute minority representation by allowing majority groups to control all seats, reducing the electoral influence of minority populations. In contrast, electoral fusion enables minority parties or candidates to combine support from multiple political lines, increasing their chances of gaining representation. This cooperative strategy promotes more diverse and equitable political outcomes by amplifying minority voices within the electoral process.
Case Studies: Real-world Applications
At-large voting systems, widely used in municipal and school board elections, often result in majority group domination, as observed in New York City's school board elections where minority representation remains limited. Electoral fusion, allowing multiple parties to endorse the same candidate, is notably applied in New York State, enhancing minor party influence and voter choice while impacting coalition politics and election outcomes. Case studies from NYC highlight that electoral fusion can increase voter turnout and political plurality, contrasting with at-large voting's tendency toward reduced diversity in elected bodies.
Which System Best Supports Democratic Values?
At-large voting dilutes minority representation by allowing the majority to dominate all seats, undermining proportionality and political diversity essential to democratic fairness. Electoral fusion enables multiple parties to endorse a single candidate, promoting coalition-building and amplifying voter choice, thus enhancing political inclusivity and responsiveness. Therefore, electoral fusion better supports democratic values by fostering representation diversity and enabling broader voter influence.
At-large voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com