Single-party rule centralizes political power within one party, eliminating opposition and often restricting democratic processes. This governance model can lead to increased stability but may also undermine political freedoms and pluralism. Discover how single-party rule shapes societies and impacts your political environment by reading the full article.
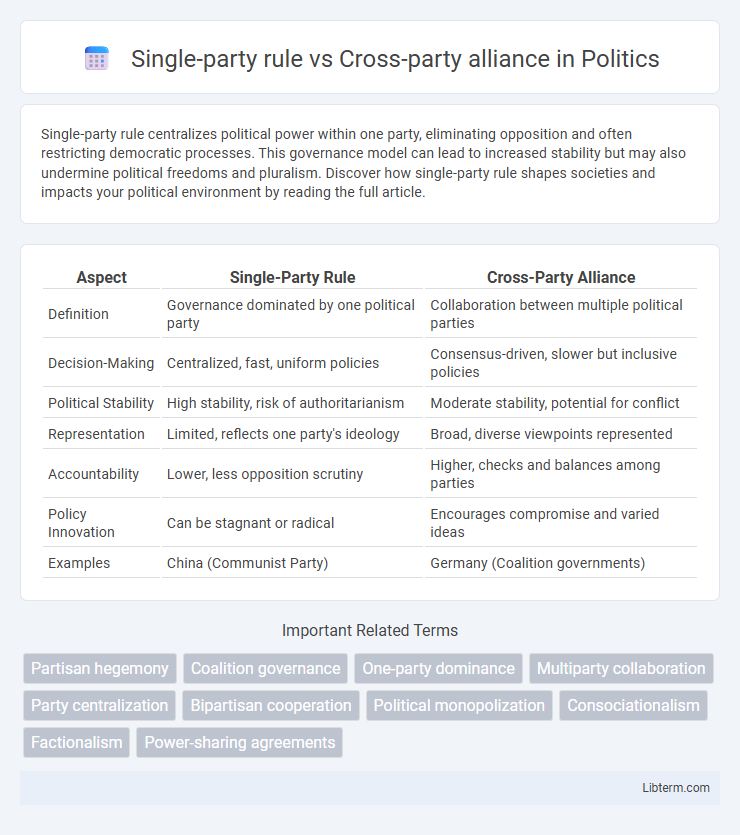
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Single-Party Rule | Cross-Party Alliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance dominated by one political party | Collaboration between multiple political parties |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, fast, uniform policies | Consensus-driven, slower but inclusive policies |
| Political Stability | High stability, risk of authoritarianism | Moderate stability, potential for conflict |
| Representation | Limited, reflects one party's ideology | Broad, diverse viewpoints represented |
| Accountability | Lower, less opposition scrutiny | Higher, checks and balances among parties |
| Policy Innovation | Can be stagnant or radical | Encourages compromise and varied ideas |
| Examples | China (Communist Party) | Germany (Coalition governments) |
Introduction to Political Governance Models
Single-party rule centralizes political power within one dominant party, enabling streamlined decision-making and policy implementation but often at the cost of limited political pluralism and opposition suppression. Cross-party alliances involve cooperation between multiple political parties to form a governing coalition, promoting diverse representation and shared policymaking responsibilities while potentially facing challenges in consensus building. Understanding these governance models is crucial for analyzing stability, accountability, and the dynamics of political power distribution within different governmental systems.
Defining Single-party Rule
Single-party rule is a political system where a single political party controls the government, excluding opposition parties from power. This form of governance centralizes decision-making authority and often limits political pluralism, impacting democratic processes and civil liberties. Unlike cross-party alliances, single-party rule lacks the collaborative negotiation that characterizes multi-party cooperation in policymaking.
Understanding Cross-party Alliances
Cross-party alliances involve collaboration between multiple political parties to achieve common goals that single-party rules may not effectively address alone. These alliances enhance policy-making by integrating diverse perspectives, leading to more comprehensive and balanced legislative outcomes. Understanding the dynamics of cross-party cooperation is crucial for promoting political stability and inclusive governance in multiparty systems.
Historical Examples of Single-party Governance
Single-party rule has been exemplified historically by regimes such as the Communist Party in the Soviet Union and the National Socialist German Workers' Party in Nazi Germany, where centralized authority maintained strict control over political and social institutions. These governments prioritized ideological uniformity, with limited political pluralism and suppression of opposition to sustain power. In contrast, cross-party alliances, like the coalition governments in post-World War II Europe, embraced political collaboration to promote stability and diverse representation.
Case Studies of Cross-party Alliances
Cross-party alliances have emerged as strategic mechanisms in diverse democracies, effectively enabling coalition governments that enhance political stability and policy continuity, as observed in Germany's coalition between the Christian Democratic Union and the Social Democratic Party. In contrast to single-party rule, where political dominance is centralized, these alliances facilitate power-sharing and broader representation, evident in the United Kingdom during the 2010 coalition between the Conservative Party and the Liberal Democrats. Such case studies highlight cross-party alliances as pivotal in managing fragmented parliaments, promoting consensus-driven governance, and mitigating partisan conflicts.
Advantages of Single-party Rule
Single-party rule ensures consistent policy implementation and decisiveness by eliminating conflicting interests and delays caused by coalition negotiations. Centralized power under a single party streamlines governance, enabling swift responses to economic challenges and national security issues. This system fosters political stability by minimizing fragmentation and maintaining unified leadership direction.
Benefits of Cross-party Collaboration
Cross-party collaboration fosters diverse perspectives that enhance policymaking quality and promote balanced solutions reflecting a broader citizen base. It mitigates political polarization by encouraging compromise and mutual understanding among parties, strengthening democratic stability and social cohesion. Cross-party alliances facilitate efficient governance by pooling resources and expertise, leading to more sustainable and widely accepted policies.
Challenges Faced by Single-party Systems
Single-party systems often face challenges such as limited political pluralism, which leads to reduced accountability and risks of authoritarian governance. The absence of competition can result in policy stagnation and corruption due to unchecked power. These systems struggle with legitimacy issues as public dissent remains suppressed, hindering democratic responsiveness and social cohesion.
Obstacles in Building Cross-party Alliances
Building cross-party alliances faces significant obstacles such as ideological differences, conflicting policy priorities, and mutual distrust among parties. These challenges hinder consensus-building and complicate negotiation processes, often resulting in stalled or ineffective collaborations. Overcoming entrenched partisan interests requires sustained dialogue, compromise, and mechanisms to align diverse party agendas into a cohesive platform.
Future Trends in Political Party Structures
Future trends in political party structures indicate a growing shift towards cross-party alliances driven by increasing voter demand for collaborative governance and policy innovation. Single-party rule faces challenges from fragmented electorates and the rise of coalition politics, which foster more inclusive decision-making processes. Technological advancements and social media also enhance transparency and accountability, encouraging parties to form strategic partnerships for broader representation and stability.
Single-party rule Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com