Populism often appeals to the concerns and frustrations of ordinary people by challenging established political elites and institutions. This political approach can significantly impact democratic processes and policy decisions by promoting a direct connection between leaders and their base. Discover how populism shapes modern governance and what it means for your political landscape in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
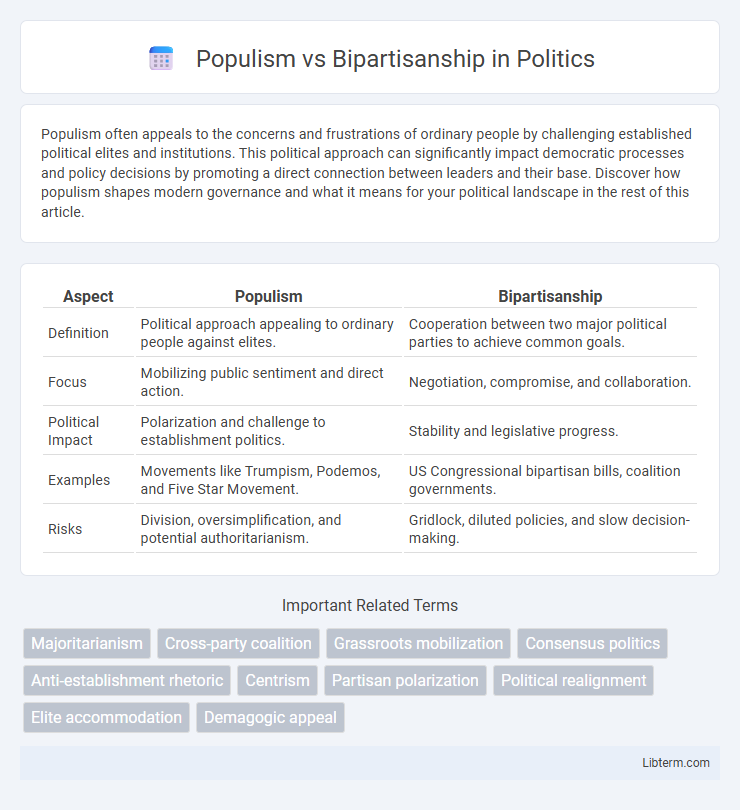
| Aspect | Populism | Bipartisanship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political approach appealing to ordinary people against elites. | Cooperation between two major political parties to achieve common goals. |
| Focus | Mobilizing public sentiment and direct action. | Negotiation, compromise, and collaboration. |
| Political Impact | Polarization and challenge to establishment politics. | Stability and legislative progress. |
| Examples | Movements like Trumpism, Podemos, and Five Star Movement. | US Congressional bipartisan bills, coalition governments. |
| Risks | Division, oversimplification, and potential authoritarianism. | Gridlock, diluted policies, and slow decision-making. |
Understanding Populism: Core Principles and Appeal
Populism centers on the core principle of representing the "common people" against perceived elites, emphasizing direct political engagement and often challenging established institutions. Its appeal lies in addressing widespread dissatisfaction by simplifying complex issues into a clear "us versus them" narrative, generating strong emotional resonance among voters. Populist movements leverage this connection to mobilize support through rhetoric that promises to restore power to ordinary citizens and disrupt traditional power structures.
The Essence of Bipartisanship in Modern Politics
Bipartisanship in modern politics embodies collaboration between major political parties to achieve common goals and address national challenges effectively. It prioritizes compromise and mutual understanding, enabling the passage of legislation that reflects a broader consensus rather than partisan interests. This approach strengthens democratic institutions by fostering stability, reducing polarization, and promoting inclusive governance.
Historical Evolution: Populism and Bipartisanship Compared
Populism surged in the late 19th century as a grassroots movement challenging established elites, emphasizing direct appeals to the common people, while bipartisanship has traditionally aimed at collaboration between major political parties to achieve legislative compromise. Historically, populism's episodic rise often disrupts bipartisanship by prioritizing polarized, culturally charged agendas over cross-party negotiation. The evolution of U.S. political dynamics reveals that populism tends to emerge during periods of social or economic anxiety, contrasting with bipartisanship, which flourished during eras emphasizing stability and consensus-building in governance.
Populism’s Impact on Political Discourse
Populism transforms political discourse by emphasizing direct appeals to the masses, often framing complex issues through simplistic, emotionally charged narratives that challenge traditional bipartisan cooperation. This approach can deepen political polarization by undermining mutual compromise and promoting an "us versus them" mentality between elites and ordinary citizens. Consequently, populism reshapes policy debates, prioritizing identity and sentiment over nuanced, cross-party dialogue.
Bipartisanship and Policy-Making Efficiency
Bipartisanship enhances policy-making efficiency by fostering collaboration between political parties, which leads to more stable and widely supported legislation. It reduces legislative gridlock and accelerates the passage of laws that address complex issues through compromise and mutual understanding. This cooperative approach ensures that policies are better vetted and more effective in addressing diverse stakeholder needs.
Populist Leaders vs. Bipartisan Statesmen
Populist leaders often appeal to widespread public sentiments by prioritizing popular demands and charismatic communication, frequently challenging established political norms and institutions. In contrast, bipartisan statesmen work to bridge ideological divides, fostering cooperation and compromise between parties to achieve sustainable policy solutions. The tension between populism and bipartisanship highlights divergent approaches to governance: immediate mass appeal versus long-term consensus building.
Societal Effects: Division versus Consensus
Populism often exacerbates societal division by framing political discourse as a struggle between "the people" and "the elite," intensifying polarization and eroding trust in institutions. In contrast, bipartisanship fosters consensus by encouraging collaboration across party lines, promoting policy stability and reducing social fragmentation. The societal effects of populism versus bipartisanship are evident in increased political unrest versus enhanced civic cohesion, respectively.
Media Influence: Shaping Populist and Bipartisan Narratives
Media influence plays a crucial role in shaping populist and bipartisan narratives by framing political discourse through selective coverage and sensationalism. Populist movements often leverage social media platforms to amplify messages that resonate emotionally with the public, while mainstream media tends to promote bipartisan dialogue by highlighting compromise and institutional stability. The contrasting media strategies significantly affect public perception, contributing to either polarization or consensus in political environments.
Challenges and Criticisms Facing Both Approaches
Populism often faces criticism for oversimplifying complex policy issues and fostering division by appealing to emotional, anti-establishment sentiments, which can undermine democratic institutions. Bipartisanship struggles with challenges such as gridlock and diluted policymaking, where compromise may lead to ineffective or incremental reforms that fail to address urgent problems. Both approaches encounter skepticism regarding their ability to sustainably unify diverse political groups while delivering tangible results in governance.
Future Outlook: Reconciling Populism with Bipartisanship
Reconciling populism with bipartisanship requires fostering inclusive political dialogues that address widespread public concerns while promoting collaborative governance. Emphasizing shared goals over partisan divides can create frameworks for policy-making that balance populist demands with pragmatic compromise. The future outlook hinges on integrating grassroots movements into institutional processes to sustain democratic stability and responsive leadership.
Populism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com