A referendum is a direct voting process allowing citizens to approve or reject specific policies or laws, empowering Your voice in democratic decision-making. This mechanism enhances political participation and ensures government accountability by reflecting the will of the people. Explore the rest of this article to understand how referendums impact societies and influence governance worldwide.
Table of Comparison
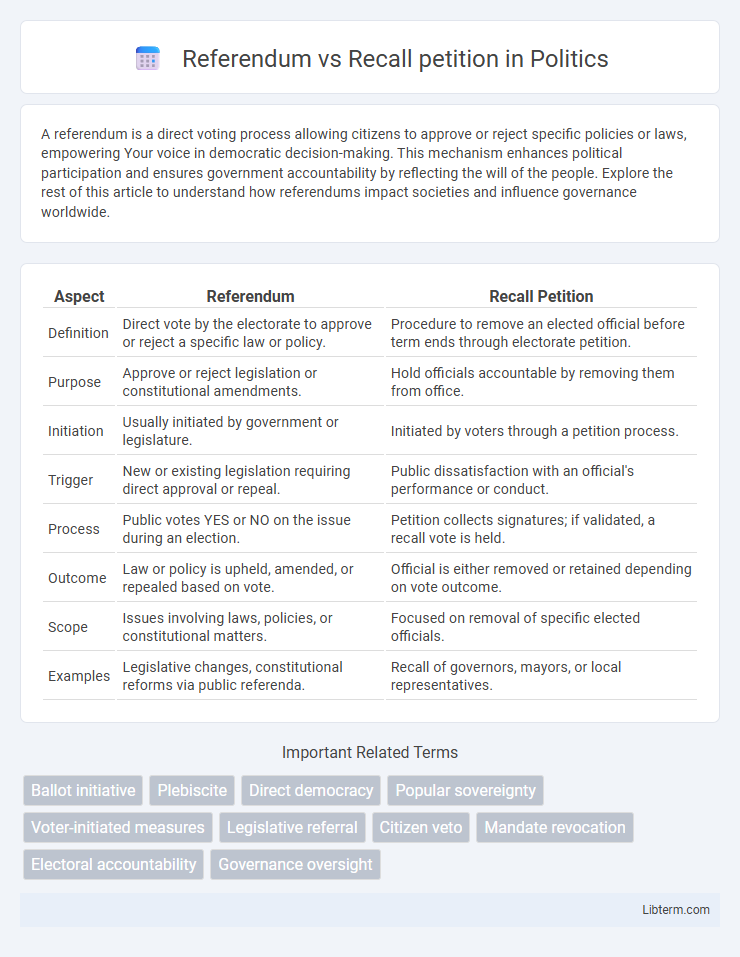
| Aspect | Referendum | Recall Petition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct vote by the electorate to approve or reject a specific law or policy. | Procedure to remove an elected official before term ends through electorate petition. |
| Purpose | Approve or reject legislation or constitutional amendments. | Hold officials accountable by removing them from office. |
| Initiation | Usually initiated by government or legislature. | Initiated by voters through a petition process. |
| Trigger | New or existing legislation requiring direct approval or repeal. | Public dissatisfaction with an official's performance or conduct. |
| Process | Public votes YES or NO on the issue during an election. | Petition collects signatures; if validated, a recall vote is held. |
| Outcome | Law or policy is upheld, amended, or repealed based on vote. | Official is either removed or retained depending on vote outcome. |
| Scope | Issues involving laws, policies, or constitutional matters. | Focused on removal of specific elected officials. |
| Examples | Legislative changes, constitutional reforms via public referenda. | Recall of governors, mayors, or local representatives. |
Understanding Referendum and Recall Petition
Referendum and recall petitions are essential democratic tools allowing citizens to influence government decisions directly. A referendum enables voters to approve or reject specific legislative acts or policies proposed by lawmakers, serving as a form of direct lawmaking. In contrast, a recall petition empowers citizens to remove an elected official from office before their term ends, ensuring accountability and responsiveness in public service.
Definitions: Referendum vs Recall Petition
A referendum is a direct voting process where citizens approve or reject a specific legislative measure or policy. A recall petition is a procedure that allows voters to remove an elected official from office before the end of their term by gathering sufficient signatures. Both mechanisms serve as tools for direct democracy but target different aspects of governance--referendum addresses laws, while recall concerns individual officeholders.
Historical Origins of Referendum and Recall
The historical origins of referendum trace back to ancient Greece and Switzerland, where direct citizen involvement in decision-making shaped democratic governance by allowing voters to approve or reject legislation. Recall petitions originated in early 20th-century United States progressive movements, designed to empower constituents to remove elected officials before their terms ended. Both mechanisms reflect evolving efforts to enhance political accountability and direct democracy.
Key Differences Between Referendum and Recall
Referendum allows voters to approve or reject specific legislative measures, serving as a direct form of democracy to enact or repeal laws, whereas recall petition enables voters to remove elected officials from office before their term ends. Referendums typically address policy issues or laws, while recall petitions target individual political representatives due to performance or misconduct concerns. The signature threshold for a referendum often depends on the number of votes cast in previous elections, while recall petitions require a certain percentage of voters from the official's constituency to initiate removal proceedings.
Legal Framework Governing Both Processes
The legal framework governing referendum and recall petitions varies significantly by jurisdiction but generally requires strict adherence to constitutional or statutory provisions that define eligibility, petition filing, signature verification, and timelines. Referendum laws typically establish procedures for citizens to approve or reject legislation passed by the government, requiring a certain percentage of voter signatures within a specified period. Recall petition regulations allow voters to remove elected officials before the end of their term through a documented process involving clear criteria, signature thresholds, and judicial oversight to ensure legality and prevent misuse.
Procedures and Steps Involved
Referendum and recall petitions involve distinct procedures to influence government decisions or remove elected officials. A referendum requires gathering a specified number of voter signatures to propose a new law or repeal existing legislation, followed by verification and placement on the election ballot. Recall petitions necessitate collecting signatures from a defined percentage of voters within a set timeframe, leading to a recall election to determine whether the official should be removed from office.
Roles of Citizens in Each Process
Citizens initiate a referendum petition by collecting signatures to propose new laws or repeal existing legislation, directly influencing legislative decisions through popular vote. In a recall petition, voters aim to remove an elected official from office before their term ends, demonstrating direct accountability mechanisms in governance. Both processes empower citizens to actively participate in democratic decision-making and hold public officials or laws responsible to community interests.
Notable Examples Worldwide
The 2016 Brexit referendum in the United Kingdom exemplifies a notable use of the referendum process to decide on EU membership, while California's 2003 recall petition against Governor Gray Davis stands as a prominent example of citizen-initiated recall in action. Switzerland, known for its frequent use of referendums, notably held the 2010 referendum on immigration quotas, directly shaping national policy. In contrast, Venezuela's 2004 recall referendum against President Hugo Chavez demonstrated the use of recall mechanisms within a politically charged environment.
Advantages and Drawbacks
Referendum petitions empower voters to approve or reject legislation, promoting direct democracy and ensuring government accountability, but may oversimplify complex issues and slow legislative processes. Recall petitions allow citizens to remove elected officials before term completion, enhancing political responsiveness and deterring misconduct, yet they can be costly, politically motivated, and disrupt governance stability. Both mechanisms strengthen participatory governance but require balanced safeguards to prevent misuse and maintain effective administration.
Implications for Democratic Governance
Referendum and recall petitions serve as critical tools of direct democracy, enabling citizens to influence government decisions and hold elected officials accountable outside regular election cycles. Referendums allow voters to approve or reject specific legislative measures, reinforcing public participation in policymaking and enhancing legitimacy. Recall petitions empower the electorate to remove underperforming or corrupt officials before their term ends, promoting political responsiveness but potentially introducing instability if overused.
Referendum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com