Rule by man often leads to governance driven by personal interests rather than the collective good, resulting in inconsistent policies and potential abuses of power. Such systems can undermine justice and limit citizen participation in decision-making processes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how rule by man impacts societies and what alternatives can offer more equitable governance.
Table of Comparison
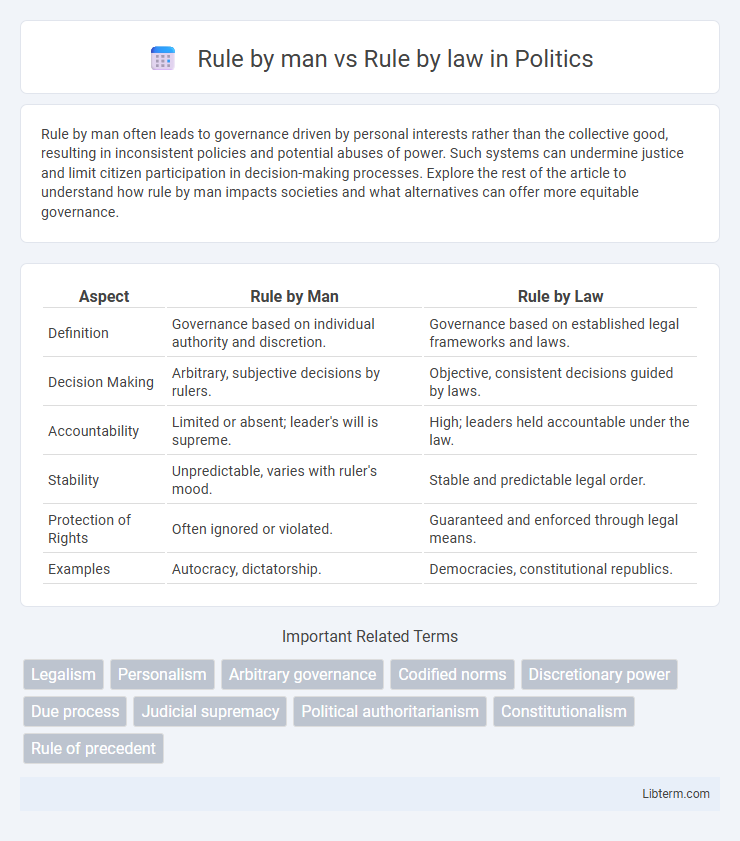
| Aspect | Rule by Man | Rule by Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance based on individual authority and discretion. | Governance based on established legal frameworks and laws. |
| Decision Making | Arbitrary, subjective decisions by rulers. | Objective, consistent decisions guided by laws. |
| Accountability | Limited or absent; leader's will is supreme. | High; leaders held accountable under the law. |
| Stability | Unpredictable, varies with ruler's mood. | Stable and predictable legal order. |
| Protection of Rights | Often ignored or violated. | Guaranteed and enforced through legal means. |
| Examples | Autocracy, dictatorship. | Democracies, constitutional republics. |
Introduction to Rule by Man and Rule by Law
Rule by Man refers to a system where decisions are made based on the whims and personal judgments of individual leaders, often lacking consistency and predictability. Rule by Law emphasizes governance through established legal frameworks and codified statutes that apply equally to all, ensuring accountability and fairness. The distinction highlights the contrast between arbitrary authority and structured legal order as foundations of political power.
Historical Origins of Governance Systems
The historical origins of governance systems reveal a clear distinction between rule by man and rule by law, with ancient monarchies epitomizing rule by man through concentrated, unchecked power in a sovereign individual. In contrast, the development of codified legal frameworks, such as Hammurabi's Code and Roman Law, marked the emergence of rule by law, emphasizing impartiality and consistency over arbitrary decisions. This evolution laid the foundation for modern constitutional and legal institutions, promoting accountability and limiting power through established statutes.
Defining Rule by Man: Key Characteristics
Rule by man emphasizes the subjective judgment and authority of individual rulers over established legal frameworks, often resulting in arbitrary decision-making and inconsistent enforcement. Key characteristics include the concentration of power in the hands of a single person or a small group, lack of transparency, and limited accountability mechanisms. This approach contrasts with rule by law, where laws are predefined, publicly accessible, and equally applied to all citizens, ensuring fairness and predictability.
Defining Rule by Law: Foundational Principles
Rule by law emphasizes governance through established, transparent legal frameworks that apply equally to all individuals and institutions, ensuring accountability and fairness. It is grounded in principles such as separation of powers, legal certainty, and protection of fundamental rights, preventing arbitrary use of authority. This foundational approach contrasts with rule by man, where decisions depend on the will or discretion of individuals rather than consistent legal standards.
Comparative Analysis: Authority and Accountability
Rule by man centralizes authority in individuals who govern based on personal discretion, often resulting in discretionary power with limited accountability mechanisms. Rule by law establishes authority through codified statutes, enforcing predictable governance and ensuring officials are accountable to established legal standards. This comparative framework highlights that rule by law promotes transparency and consistency, while rule by man risks arbitrary decisions and diminished checks on power.
Impact on Justice and Fairness
Rule by law ensures justice and fairness by applying consistent, transparent legal standards that hold all individuals accountable regardless of status, preventing arbitrary decisions. In contrast, rule by man often leads to biased judgments influenced by personal interests, undermining equal treatment and eroding public trust in the justice system. The stability of legal institutions and adherence to codified laws directly correlate with the reliability and impartiality of judicial outcomes.
Consequences for Civil Liberties and Human Rights
Rule by man often leads to arbitrary decisions and unchecked power, resulting in frequent violations of civil liberties and human rights. Rule by law provides a structured legal framework that safeguards individual rights and ensures accountability through transparent procedures. In systems governed by law, citizens are more likely to experience protection of freedoms such as speech, assembly, and due process.
Corruption and Abuse of Power
Rule by man often leads to corruption and abuse of power due to unchecked authority concentrated in individuals, resulting in arbitrary decisions and favoritism. Rule by law establishes a framework of clear, transparent rules that limit officials' discretion and enforce accountability, reducing opportunities for corruption. Legal institutions and independent judiciary serve as critical mechanisms to prevent the abuse of power and uphold fairness in governance.
Modern Case Studies: Examples in Practice
Rule by law in modern China exemplifies centralized control where legal frameworks enforce Communist Party authority, contrasting sharply with rule by man seen in authoritarian regimes like North Korea, where personal rulership overrides formal legal systems. In contrast, Western democracies such as Germany emphasize rule by law, ensuring transparent governance and judicial independence. These case studies highlight that rule by law fosters accountability and stability, whereas rule by man often results in arbitrary power and human rights abuses.
The Future of Governance: Striking a Balance
The future of governance hinges on balancing rule by man, characterized by discretionary power, with rule by law, which enforces predictable and transparent legal frameworks. Effective governance models integrate human judgment while ensuring adherence to established legal norms to prevent authoritarianism and promote accountability. Emerging digital technologies and AI-driven decision-making tools offer innovative pathways to enhance this equilibrium, fostering adaptive yet principled governance systems.
Rule by man Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com