Voter suppression tactics undermine democratic processes by restricting access to the ballot through measures like strict ID laws, limited polling locations, and purging voter rolls. These actions disproportionately affect marginalized communities, reducing their political influence and eroding trust in elections. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these barriers impact Your right to vote and what can be done to ensure fair participation.
Table of Comparison
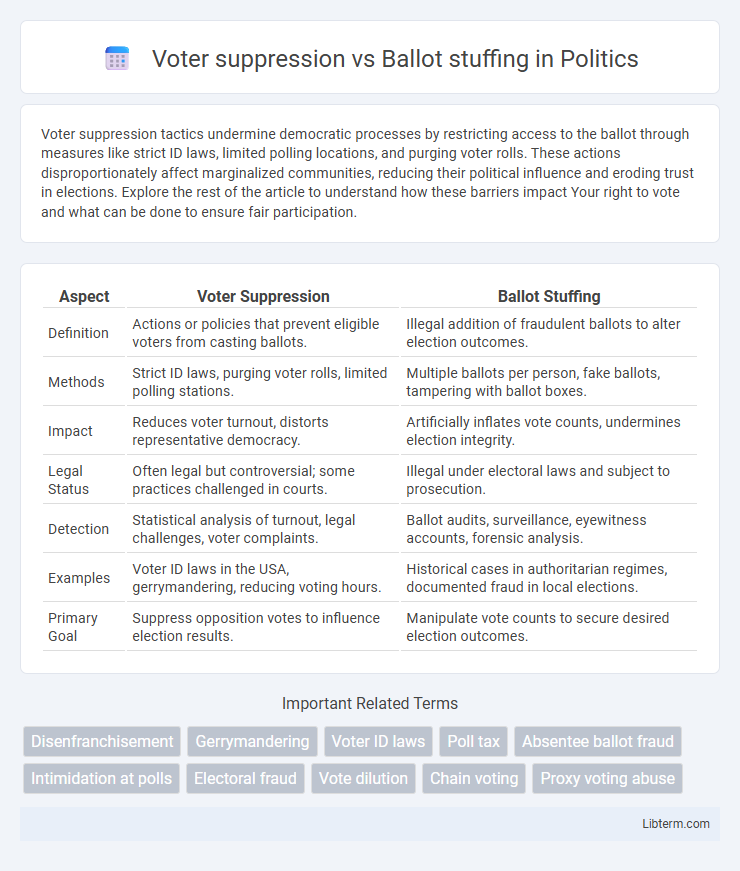
| Aspect | Voter Suppression | Ballot Stuffing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actions or policies that prevent eligible voters from casting ballots. | Illegal addition of fraudulent ballots to alter election outcomes. |
| Methods | Strict ID laws, purging voter rolls, limited polling stations. | Multiple ballots per person, fake ballots, tampering with ballot boxes. |
| Impact | Reduces voter turnout, distorts representative democracy. | Artificially inflates vote counts, undermines election integrity. |
| Legal Status | Often legal but controversial; some practices challenged in courts. | Illegal under electoral laws and subject to prosecution. |
| Detection | Statistical analysis of turnout, legal challenges, voter complaints. | Ballot audits, surveillance, eyewitness accounts, forensic analysis. |
| Examples | Voter ID laws in the USA, gerrymandering, reducing voting hours. | Historical cases in authoritarian regimes, documented fraud in local elections. |
| Primary Goal | Suppress opposition votes to influence election results. | Manipulate vote counts to secure desired election outcomes. |
Understanding Voter Suppression: Definition and Tactics
Voter suppression refers to strategies and tactics aimed at discouraging or preventing eligible voters from casting their ballots, including strict voter ID laws, purging voter rolls, limiting polling locations, and misinformation campaigns. These measures disproportionately impact marginalized groups, reducing electoral participation and undermining democratic representation. Unlike ballot stuffing, which involves illegal vote manipulation by adding fraudulent ballots, voter suppression systematically restricts voter access to influence election outcomes.
Ballot Stuffing Explained: Methods and Impact
Ballot stuffing involves illegally adding multiple fraudulent votes to manipulate election outcomes, commonly executed through methods such as submitting fake ballots, tampering with voting machines, or coercing officials to alter vote counts. This practice undermines democratic integrity by inflating vote totals and skewing election results, often leading to disputed legitimacy and legal challenges. The impact of ballot stuffing erodes public trust in electoral systems and can alter the distribution of political power.
Historical Context: Voter Suppression in Elections
Voter suppression has historically targeted marginalized groups to restrict their political power, with tactics such as literacy tests, poll taxes, and intimidation widespread during the Jim Crow era in the United States. In contrast, ballot stuffing, involving the fraudulent addition of votes, often aimed to artificially inflate support for certain candidates or parties, but voter suppression played a more systematic role in undermining democratic participation. The Voting Rights Act of 1965 marked a significant turning point, legally challenging many suppression methods and promoting greater electoral equity.
Notorious Cases of Ballot Stuffing Worldwide
Notorious cases of ballot stuffing have marred elections worldwide, such as the 2007 Kenyan general election where widespread fraudulent voting inflations were reported, and the 2011 Russian parliamentary elections, which faced accusations of mass ballot stuffing to favor the ruling party. In Pakistan's 2013 general elections, multiple instances of ballot stuffing were documented, undermining the electoral process and leading to widespread protests. These cases highlight the critical challenges in ensuring electoral integrity and the need for robust monitoring and transparent procedures.
Key Differences Between Voter Suppression and Ballot Stuffing
Voter suppression involves tactics such as strict ID laws, limited polling locations, and misinformation aimed at preventing eligible voters from casting ballots, thereby reducing voter turnout. Ballot stuffing refers to the illegal practice of submitting multiple or fraudulent votes to inflate vote counts, directly manipulating election results. The key difference lies in voter suppression restricting legitimate votes, while ballot stuffing adds illegitimate votes, both undermining election integrity in distinct ways.
Legal Frameworks Addressing Electoral Fraud
Legal frameworks addressing electoral fraud delineate clear prohibitions against both voter suppression and ballot stuffing to ensure election integrity. Statutes such as the Voting Rights Act and the Help America Vote Act enforce protections against discriminatory practices that limit voter access while criminalizing fraudulent ballot submissions and tampering. Robust enforcement mechanisms and judicial oversight are vital to detecting violations and upholding transparency in democratic processes.
Technological Advances: New Frontiers for Election Integrity
Technological advances have reshaped election integrity, with voter suppression now leveraging digital tools such as data analytics for targeted misinformation campaigns and restrictive online voting policies that hinder access. Ballot stuffing has evolved through electronic vote manipulation techniques, including hacking voting machines and exploiting software vulnerabilities to alter results. Emerging technologies like blockchain and biometric verification offer promising solutions to enhance transparency and secure the electoral process against these modern threats.
Real-World Consequences: Democracy at Risk
Voter suppression tactics, such as strict ID laws and limited polling locations, reduce electoral participation by disenfranchising marginalized groups, thereby undermining the principle of fair representation. Ballot stuffing, involving the illegal addition of fraudulent votes, distorts election outcomes and erodes public trust in democratic institutions. Both practices result in compromised legitimacy of elected officials, weakening democratic governance and increasing political instability.
Countermeasures and Prevention Strategies
Effective countermeasures against voter suppression include implementing robust voter ID laws, expanding access to mail-in and early voting, and deploying nonpartisan voter education campaigns to ensure accurate information. Ballot stuffing prevention strategies emphasize secure chain-of-custody protocols, enhanced voter verification systems, and advanced auditing techniques such as risk-limiting audits to detect and deter fraudulent activities. Technology-driven solutions combined with strict legal enforcement play a critical role in preserving election integrity and promoting transparent democratic processes.
Strengthening Confidence in the Electoral Process
Voter suppression tactics such as restrictive ID laws and limited polling locations undermine electoral integrity by disenfranchising eligible voters, while ballot stuffing--illegally adding fraudulent ballots--distorts election outcomes. Strengthening confidence in the electoral process requires robust safeguards including transparent audit protocols, secure voting technology, and comprehensive voter education initiatives. Implementing bipartisan oversight and real-time election monitoring further ensures accountability and public trust in democratic institutions.
Voter suppression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com