Participatory democracy empowers citizens to actively engage in decision-making processes, enhancing transparency and accountability within governance. By involving You directly in policy development, it fosters a deeper connection between the government and its people. Explore how this democratic approach transforms communities and influences political systems in the full article.
Table of Comparison
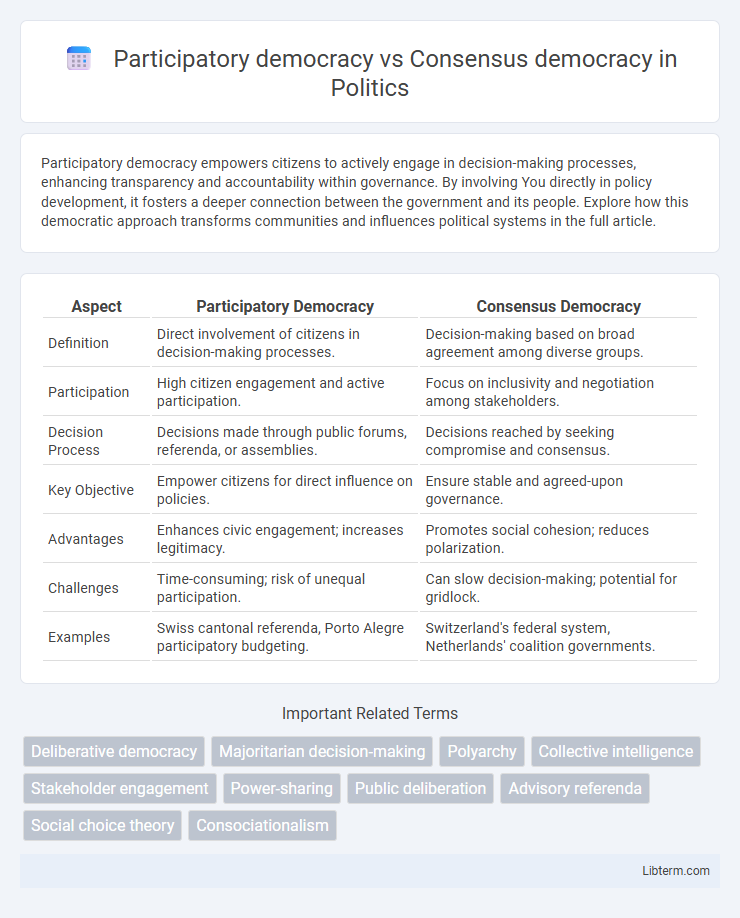
| Aspect | Participatory Democracy | Consensus Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct involvement of citizens in decision-making processes. | Decision-making based on broad agreement among diverse groups. |
| Participation | High citizen engagement and active participation. | Focus on inclusivity and negotiation among stakeholders. |
| Decision Process | Decisions made through public forums, referenda, or assemblies. | Decisions reached by seeking compromise and consensus. |
| Key Objective | Empower citizens for direct influence on policies. | Ensure stable and agreed-upon governance. |
| Advantages | Enhances civic engagement; increases legitimacy. | Promotes social cohesion; reduces polarization. |
| Challenges | Time-consuming; risk of unequal participation. | Can slow decision-making; potential for gridlock. |
| Examples | Swiss cantonal referenda, Porto Alegre participatory budgeting. | Switzerland's federal system, Netherlands' coalition governments. |
Introduction to Participatory and Consensus Democracy
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct involvement of citizens in decision-making processes, enhancing transparency and accountability through active public engagement. Consensus democracy seeks collective agreement among diverse groups, prioritizing inclusive dialogue and negotiated compromise to ensure broad representation. Both models aim to strengthen democratic legitimacy but differ in their mechanisms for citizen participation and policy formation.
Defining Participatory Democracy
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct involvement of citizens in decision-making processes, empowering individuals to influence policies beyond just voting. It fosters active civic engagement, promoting transparency and accountability in governance through mechanisms such as public assemblies, referendums, and citizen councils. This democratic model contrasts with consensus democracy, which prioritizes agreement among elected representatives to ensure broad support and stability in policymaking.
Understanding Consensus Democracy
Consensus democracy emphasizes broad agreement and inclusivity among diverse political groups to ensure stable and representative governance. It relies on power-sharing, negotiation, and compromise, often involving multiple parties and minority rights protection, contrasting with participatory democracy's focus on direct citizen involvement. Understanding consensus democracy highlights its role in fostering cooperation and preventing majoritarian dominance through institutional mechanisms like coalition governments and proportional representation.
Key Principles of Participatory Democracy
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct citizen involvement in decision-making processes, empowering individuals to influence policies through active engagement rather than relying solely on elected representatives. Key principles include inclusiveness, where all members of society have equal opportunity to participate; deliberation, fostering open discussion and debate to reach informed decisions; and empowerment, ensuring citizens have the resources and capacities needed to effect change. This contrasts with consensus democracy, which prioritizes agreement among political elites and institutional power-sharing to maintain stability and cooperation within diverse societies.
Core Features of Consensus Democracy
Consensus democracy emphasizes power-sharing, broad representation, and inclusive decision-making to achieve agreement among diverse groups. It features mechanisms such as proportional representation, coalition governments, and multiple veto points that ensure minority voices are protected and no single group dominates. This model prioritizes negotiation and compromise, fostering stability and preventing the tyranny of the majority.
Comparative Decision-Making Processes
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct involvement of citizens in decision-making, allowing broad public input and fostering deliberative engagement at various levels. Consensus democracy prioritizes agreement among diverse political actors, seeking negotiated compromises to achieve widespread acceptance of policies. While participatory models enhance inclusiveness and grassroots influence, consensus systems emphasize institutional mechanisms like coalition-building to balance interests and maintain political stability.
Benefits of Participatory Democracy
Participatory democracy enhances civic engagement by enabling citizens to directly influence decision-making processes, leading to increased political accountability and transparency. It fosters stronger community bonds as individuals collaborate to address shared concerns, promoting social cohesion and collective responsibility. Moreover, this democratic model often results in policies that better reflect diverse interests and local needs, improving governance effectiveness and public satisfaction.
Advantages of Consensus Democracy
Consensus democracy enhances political stability by incorporating diverse viewpoints from multiple parties, reducing polarization and fostering long-term cooperation. It promotes inclusive decision-making through broad-based participation, ensuring that minority interests are represented and reducing social conflict. This governance model improves policy quality by encouraging compromise and deliberation, leading to more balanced and sustainable outcomes.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Models
Participatory democracy faces challenges such as the potential for decision-making inefficiency due to mass involvement and the risk of unequal participation that marginalizes minority voices. Consensus democracy struggles with prolonged deliberation processes that may lead to decision paralysis and the difficulty of achieving unanimous agreement, which can suppress dissenting opinions. Both models are criticized for their complexity and the high demands they place on citizens and institutions to engage deeply and consistently in governance.
Choosing the Right Model for Effective Governance
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct citizen involvement in decision-making processes, enhancing transparency and accountability by allowing individuals to actively contribute to policy formulation. Consensus democracy prioritizes broad agreement among diverse political actors, fostering stability and inclusiveness through negotiated compromises and power-sharing arrangements. Choosing the right model depends on factors like political culture, social diversity, and institutional capacity, with participatory democracy suited for societies valuing grassroots engagement and consensus democracy ideal for managing pluralism in complex, multi-party systems.
Participatory democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com