E-democracy transforms traditional political processes by leveraging digital tools to increase citizen participation, transparency, and accountability. This technological evolution enables You to engage in policymaking, voting, and public debate from anywhere with internet access. Discover how e-democracy reshapes governance and empowers your voice in the detailed article ahead.
Table of Comparison
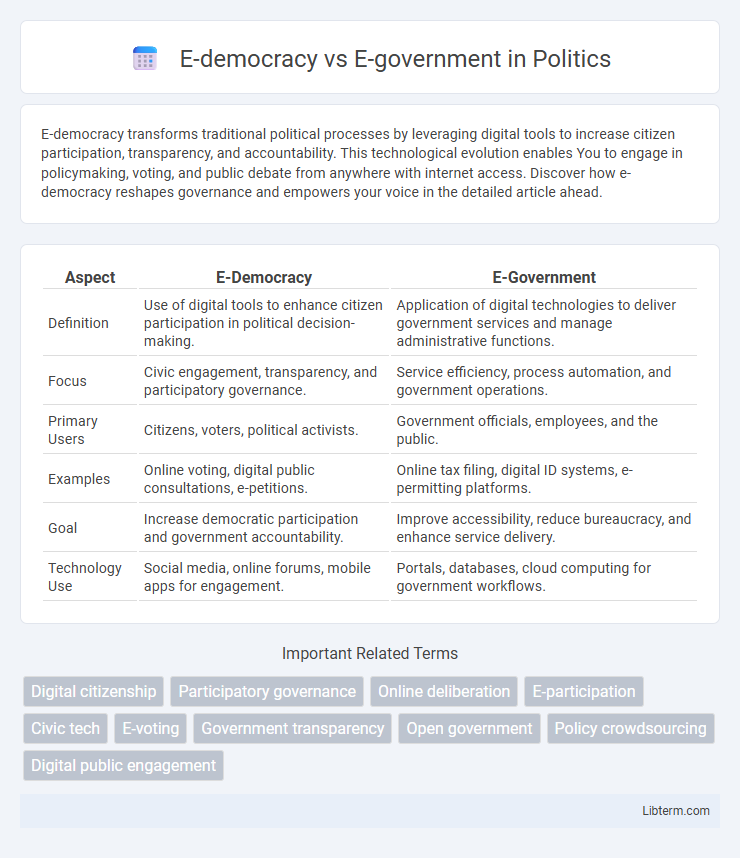
| Aspect | E-Democracy | E-Government |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of digital tools to enhance citizen participation in political decision-making. | Application of digital technologies to deliver government services and manage administrative functions. |
| Focus | Civic engagement, transparency, and participatory governance. | Service efficiency, process automation, and government operations. |
| Primary Users | Citizens, voters, political activists. | Government officials, employees, and the public. |
| Examples | Online voting, digital public consultations, e-petitions. | Online tax filing, digital ID systems, e-permitting platforms. |
| Goal | Increase democratic participation and government accountability. | Improve accessibility, reduce bureaucracy, and enhance service delivery. |
| Technology Use | Social media, online forums, mobile apps for engagement. | Portals, databases, cloud computing for government workflows. |
Introduction to E-Democracy and E-Government
E-Democracy leverages digital tools to enhance citizen participation, transparency, and public deliberation in governance processes, empowering individuals to influence decision-making directly. E-Government focuses on improving the efficiency and accessibility of government services through digital platforms, streamlining administrative operations and facilitating interaction between the state and citizens. Both frameworks integrate information and communication technologies (ICT) but differ in their primary goal: E-Democracy emphasizes participatory governance, while E-Government centers on service delivery and administrative efficiency.
Defining E-Democracy: Key Concepts
E-democracy centers on using digital technologies to enhance citizen participation, promote transparency, and foster direct engagement in democratic processes. It emphasizes tools like online voting, public consultations, and social media platforms to facilitate inclusive decision-making and accountability. Unlike e-government, which focuses on delivering public services efficiently through digital means, e-democracy prioritizes empowering citizens to influence policy and governance outcomes actively.
Understanding E-Government: Core Functions
E-Government primarily facilitates efficient public service delivery, online administrative processes, and transparent governance through digital platforms. Its core functions include electronic service provision, digital communication between government and citizens, and data-driven policy implementation. Enhanced accessibility and streamlined operations define the essential framework of modern e-government systems.
Primary Differences between E-Democracy and E-Government
E-democracy centers on citizen participation and engagement through digital platforms, enabling direct input in policy-making and decision processes, whereas e-government focuses on the administration, delivery, and management of public services via information and communication technologies (ICT). E-democracy prioritizes transparency, accountability, and public discourse to enhance democratic processes, while e-government emphasizes efficiency, convenience, and accessibility of government services for citizens. The primary difference lies in e-democracy fostering interactive citizen-government collaboration, whereas e-government streamlines internal government operations and service provision.
Historical Evolution of Digital Governance
The historical evolution of digital governance highlights distinct paths for e-democracy and e-government, where e-government emerged in the 1990s as a means to enhance public service delivery through digital platforms, while e-democracy developed to promote citizen engagement, transparency, and participatory decision-making using online tools. Early e-government initiatives focused on digitizing existing bureaucratic processes, whereas e-democracy integrated social media and interactive technologies to foster public dialogue and political participation. This evolution reflects shifting priorities from administrative efficiency to inclusive governance powered by advancements in internet accessibility and digital communication.
Benefits of E-Democracy in Modern Society
E-democracy empowers citizens by enhancing political participation through digital platforms, enabling real-time engagement and transparent decision-making processes. It fosters inclusivity by giving marginalized groups access to governmental discussions and voting mechanisms online, bridging geographical and socio-economic gaps. The increased accountability from digital feedback and monitoring tools strengthens trust in public institutions and promotes responsive governance.
Advantages of E-Government for Public Administration
E-Government enhances public administration by streamlining service delivery through digital platforms, reducing processing times, and increasing transparency in governmental operations. It facilitates efficient resource management and improves citizen engagement by providing easier access to information and services. Moreover, e-government systems promote accountability and reduce corruption by enabling real-time tracking and monitoring of administrative activities.
Challenges Facing E-Democracy and E-Government
E-democracy faces challenges including digital divide, low citizen engagement, and concerns over data privacy and misinformation. E-government struggles with issues such as cybersecurity vulnerabilities, lack of interoperability among government systems, and limited digital literacy among public servants and citizens. Both require robust infrastructure, transparent policies, and continuous technological adaptation to ensure secure, inclusive, and effective digital governance.
Case Studies: Global Implementations and Outcomes
E-democracy initiatives in countries like Estonia and South Korea highlight enhanced citizen engagement through digital voting platforms and participatory policymaking, leading to increased transparency and trust in governance. E-government implementations in Singapore and Denmark demonstrate streamlined public service delivery, improved efficiency, and cost reduction by integrating online portals for administrative tasks and digital identity systems. Comparative case studies reveal that while e-democracy fosters direct citizen interaction and policy influence, e-government focuses on optimizing bureaucratic processes, both contributing to modernized governance in diverse global contexts.
The Future of Digital Participation and Governance
E-democracy emphasizes citizen engagement through digital platforms, enabling more inclusive decision-making processes and real-time feedback loops. E-government focuses on efficient service delivery and transparent administration by integrating technology into public sector operations. The future of digital participation and governance lies in blending these approaches, leveraging AI-driven analytics and blockchain to enhance trust, accountability, and collaborative policymaking.
E-democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com