A vote of no confidence is a formal parliamentary procedure used to express that a governing body or official no longer has the support or trust of its members. This action can lead to the resignation or removal of the leader or government, impacting political stability and decision-making. Discover how a vote of no confidence functions and its implications for Your political landscape in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
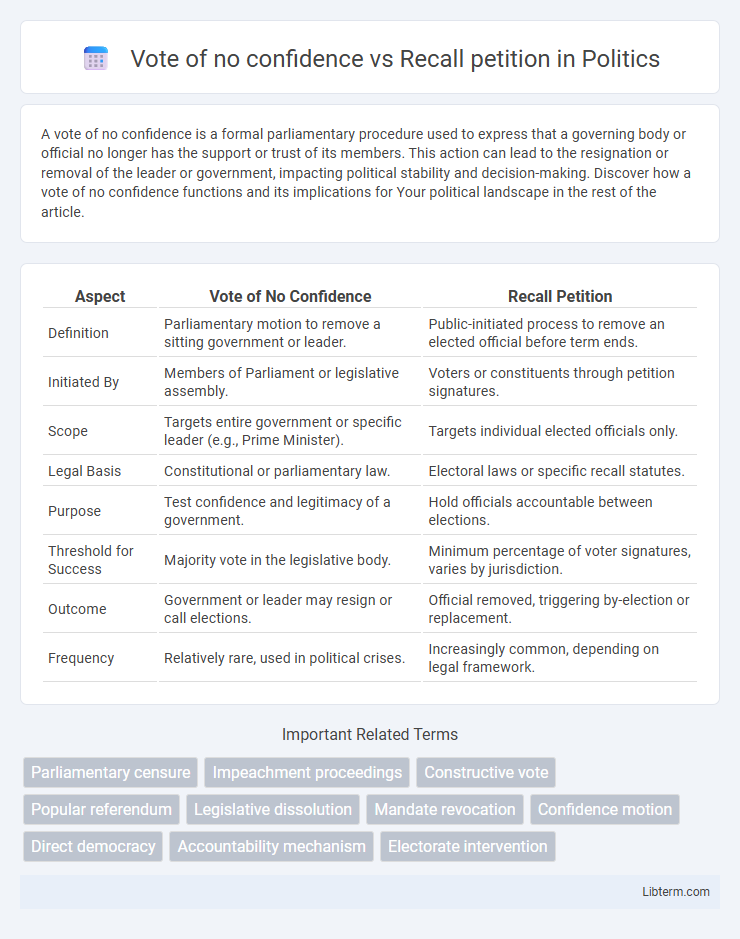
| Aspect | Vote of No Confidence | Recall Petition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Parliamentary motion to remove a sitting government or leader. | Public-initiated process to remove an elected official before term ends. |
| Initiated By | Members of Parliament or legislative assembly. | Voters or constituents through petition signatures. |
| Scope | Targets entire government or specific leader (e.g., Prime Minister). | Targets individual elected officials only. |
| Legal Basis | Constitutional or parliamentary law. | Electoral laws or specific recall statutes. |
| Purpose | Test confidence and legitimacy of a government. | Hold officials accountable between elections. |
| Threshold for Success | Majority vote in the legislative body. | Minimum percentage of voter signatures, varies by jurisdiction. |
| Outcome | Government or leader may resign or call elections. | Official removed, triggering by-election or replacement. |
| Frequency | Relatively rare, used in political crises. | Increasingly common, depending on legal framework. |
Understanding Vote of No Confidence
A Vote of No Confidence is a parliamentary procedure used to determine whether a sitting government or leader retains the support of the legislature, often leading to the government's resignation if lost. Unlike a Recall Petition, which is initiated by the electorate to remove an elected official before their term ends, a Vote of No Confidence is carried out by elected representatives within the legislative assembly. This mechanism ensures accountability within a parliamentary system and maintains the executive's legitimacy through legislative support.
Defining Recall Petition
A recall petition is a formal process enabling voters to remove an elected official from office before the end of their term through a direct vote, typically triggered by a specified number of citizen signatures. Unlike a vote of no confidence, which is a parliamentary procedure initiated by legislators to express lack of support for a government or leader, a recall petition empowers the general electorate to hold an individual accountable. This mechanism enhances democratic participation by providing a direct tool for constituents to enforce political accountability.
Key Differences Between Vote of No Confidence and Recall Petition
A vote of no confidence is a parliamentary procedure used to remove an incumbent government or leader by legislators, reflecting a loss of majority support within the assembly. In contrast, a recall petition is a grassroots mechanism that allows voters to initiate the removal of an elected official before the end of their term through a direct popular vote. The key differences lie in the initiators (legislators vs. electorate), the targeted officials (typically executives or entire governments vs. individual representatives), and the procedural requirements for triggering removal.
Process and Procedure: Vote of No Confidence
The vote of no confidence is a parliamentary procedure where elected representatives formally express their lack of support for a government or leader, typically requiring a majority vote within the legislative body. This process begins with the submission of a motion, followed by debates and a scheduled vote, often governed by specific legislative rules and timeframes. Unlike recall petitions, which rely on citizen initiatives to remove an official, the vote of no confidence is strictly a legislative mechanism aimed at holding the ruling administration accountable.
Process and Procedure: Recall Petition
A recall petition initiates a formal process allowing voters to remove an elected official before their term ends by collecting a required number of valid signatures within a specified time frame. The procedure involves submitting a written application to the electoral authority, followed by verification of signatures and scheduling a recall election upon meeting the threshold. This process empowers constituents to hold public officials accountable through direct democratic action, distinct from legislative votes of no confidence.
Legal Framework and Authority
The Vote of No Confidence operates within parliamentary systems, allowing legislators to withdraw support from a government or leader under constitutional or legislative rules, primarily governed by the country's constitution and parliamentary procedures. Recall Petitions function as a direct democratic tool enabling constituents to remove elected officials before the end of their term, with legal frameworks varying by jurisdiction but typically outlined in electoral or local government laws. Authority for a Vote of No Confidence usually rests with the legislative assembly, while Recall Petitions empower voters directly through established legal mechanisms.
Historical Examples and Case Studies
The Vote of No Confidence and Recall Petition serve as mechanisms for holding elected officials accountable, each with distinct historical applications and legal frameworks. Notably, the Vote of No Confidence has been pivotal in parliamentary systems such as the United Kingdom, where the 1979 vote led to the fall of the Labour government under James Callaghan, marking a significant political shift. Recall Petitions, exemplified by the 2018 case in Canada when the recall of MLA Paul Reitsma failed despite significant voter mobilization, highlight grassroots efforts to remove officials without dissolving the entire legislature, showcasing contrasting democratic enforcement tools.
Impact on Political Stability
Votes of no confidence directly challenge the sitting government's authority, often leading to its collapse and triggering early elections, which can cause significant political instability. Recall petitions empower citizens to remove individual elected officials before their term ends, potentially increasing accountability but rarely destabilizing the entire government structure. Both mechanisms influence political stability differently: votes of no confidence disrupt governance at the executive level, while recall petitions primarily affect local or legislative representation without systemic upheaval.
Advantages and Disadvantages
A Vote of No Confidence allows legislative bodies to remove an elected official or government without a public vote, providing swift political accountability and stability, but it can lead to political instability and frequent government changes. Recall Petitions enable constituents to directly remove elected officials through a public vote, promoting direct democracy and increasing voter control, yet the process is time-consuming, costly, and may be exploited for political vendettas. Both mechanisms serve as checks on power but vary in efficiency, democratic involvement, and potential for misuse.
When to Use: Vote of No Confidence vs Recall Petition
A vote of no confidence is typically used within legislative bodies to express that a government or leader no longer has the assembly's support, often leading to the dissolution of the government or resignation of the leader. A recall petition is employed by citizens to remove an elected official from office before the end of their term through a direct vote, usually triggered by dissatisfaction with their performance or conduct. The vote of no confidence is appropriate for parliamentary systems where the legislature can unseat the executive, whereas recall petitions apply in jurisdictions with provisions for direct voter intervention in executive or legislative representation.
Vote of no confidence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com