Electoral coalitions are strategic alliances formed between political parties to combine resources and increase their chances of winning elections. These coalitions enable parties to pool voter bases, share campaign costs, and present unified platforms that appeal to a broader electorate. Discover how forming an effective electoral coalition can shape political outcomes by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
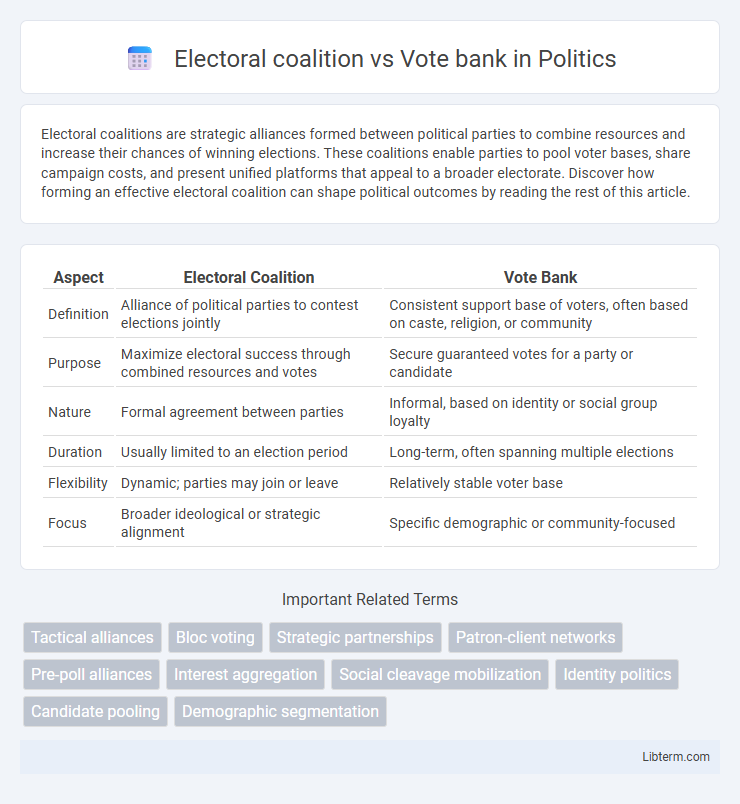
| Aspect | Electoral Coalition | Vote Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alliance of political parties to contest elections jointly | Consistent support base of voters, often based on caste, religion, or community |
| Purpose | Maximize electoral success through combined resources and votes | Secure guaranteed votes for a party or candidate |
| Nature | Formal agreement between parties | Informal, based on identity or social group loyalty |
| Duration | Usually limited to an election period | Long-term, often spanning multiple elections |
| Flexibility | Dynamic; parties may join or leave | Relatively stable voter base |
| Focus | Broader ideological or strategic alignment | Specific demographic or community-focused |
Introduction to Electoral Coalitions and Vote Banks
Electoral coalitions are strategic alliances between political parties designed to combine voter bases and increase the likelihood of winning elections. Vote banks refer to stable groups of voters who consistently support a particular party or candidate due to shared interests, identity, or social factors. Understanding the dynamics of electoral coalitions and vote banks is essential for analyzing electoral strategies and predicting election outcomes.
Definitions: Electoral Coalition vs. Vote Bank
An electoral coalition is a strategic alliance between political parties aiming to combine votes and resources to win elections, often formalized through agreements or understandings. A vote bank refers to a reliable group of voters who consistently support a particular party or candidate due to shared interests, identities, or benefits. While electoral coalitions are temporary and tactical, vote banks represent a stable, long-term source of electoral support.
Historical Context and Emergence
Electoral coalitions emerged historically as strategic alliances among political parties to consolidate votes and increase their chances of winning elections in multi-party democracies. Vote banks developed in socio-political landscapes where parties targeted specific communities or social groups to secure consistent electoral support based on identity, religion, caste, or ethnicity. The evolution of electoral coalitions contrasts with the persistence of vote bank politics, reflecting shifting voter alignments and tactical political collaborations over time.
Key Features of Electoral Coalitions
Electoral coalitions are strategic alliances among political parties formed to maximize vote share and increase chances of winning elections, often characterized by negotiated seat-sharing arrangements and common minimum programs. They differ from vote banks, which are stable support bases defined by demographic, ethnic, or religious identities, as coalitions are fluid and based on political pragmatism rather than fixed social groups. Key features of electoral coalitions include flexibility in party collaboration, shared campaign resources, and the ability to appeal to a broader electorate through combined voter bases.
Characteristics of Vote Banks
Vote banks are characterized by a fixed group of voters united by common interests such as caste, religion, ethnicity, or economic status, who consistently support a particular political party in elections. These groups rely heavily on identity politics and clientelism, often expecting tangible benefits or patronage in return for their loyalty. Unlike electoral coalitions, which are strategic alliances between parties to maximize vote share, vote banks represent a more stable and emotionally driven voter base rooted in social and cultural affiliations.
Advantages of Forming Electoral Coalitions
Forming electoral coalitions allows political parties to pool resources, voter bases, and campaign strengths, significantly enhancing their chances of winning seats in competitive elections. These alliances increase the representation of diverse interest groups, promoting broader policy consensus and stability in governance. Electoral coalitions also reduce vote splitting among ideologically similar parties, optimizing overall electoral outcomes and enabling collective bargaining power in legislative bodies.
Risks and Criticisms of Vote Bank Politics
Vote bank politics often leads to the marginalization of broader societal interests by prioritizing the narrow agendas of specific caste, religious, or ethnic groups, resulting in social fragmentation and communal tensions. This approach risks fostering corruption and clientelism as politicians may offer preferential treatment or resources to secure loyalty from loyal groups, undermining democratic fairness and policy effectiveness. Unlike electoral coalitions that form strategic alliances for governance, vote bank politics can hinder inclusive development and perpetuate divisive identity politics.
Impact on Democratic Processes
Electoral coalitions can enhance democratic processes by fostering political inclusivity and encouraging broader representation of diverse interests, leading to more stable governments and policy consensus. In contrast, vote banks often undermine democratic ideals by prioritizing identity politics and group loyalty over policy performance, resulting in polarization and reduced accountability. The dynamic between these two phenomena significantly influences voter engagement, political competition, and the overall quality of democracy.
Case Studies: Electoral Coalitions and Vote Banks in Practice
Electoral coalitions, such as the 2019 National Democratic Alliance in India, unify diverse political parties to maximize vote share across regions, contrasting with vote banks that represent consistent demographic support like the Bahujan Samaj Party's appeal to Dalit voters. Case studies reveal that coalitions leverage strategic alliances to broaden electoral reach, while vote banks depend on targeted identity politics to secure loyalty. Understanding these dynamics highlights how parties balance broad-based coalitions and focused demographic support to achieve electoral success.
Future Trends and Challenges
Electoral coalitions are expected to increase as political parties seek to pool resources and voter bases to overcome fragmented electorates, especially in multiparty democracies. Vote banks may face challenges due to growing voter awareness and digital campaigns that emphasize issue-based voting rather than identity politics. Future trends suggest a shift towards data-driven coalition strategies that target floating voters while minimizing reliance on traditional loyalty blocs.
Electoral coalition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com