A coalition government forms when multiple political parties collaborate to create a majority administration, often resulting from no single party securing outright control. This system encourages compromise and power-sharing, aiming to balance diverse perspectives within governance. Explore the rest of this article to understand how coalition governments impact political stability and policy-making.
Table of Comparison
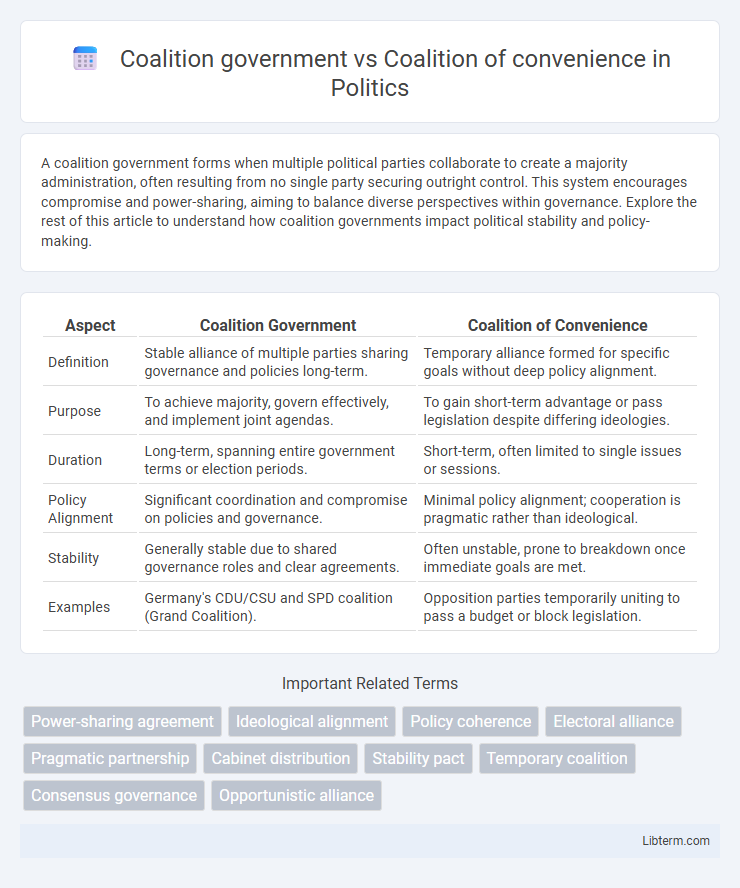
| Aspect | Coalition Government | Coalition of Convenience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stable alliance of multiple parties sharing governance and policies long-term. | Temporary alliance formed for specific goals without deep policy alignment. |
| Purpose | To achieve majority, govern effectively, and implement joint agendas. | To gain short-term advantage or pass legislation despite differing ideologies. |
| Duration | Long-term, spanning entire government terms or election periods. | Short-term, often limited to single issues or sessions. |
| Policy Alignment | Significant coordination and compromise on policies and governance. | Minimal policy alignment; cooperation is pragmatic rather than ideological. |
| Stability | Generally stable due to shared governance roles and clear agreements. | Often unstable, prone to breakdown once immediate goals are met. |
| Examples | Germany's CDU/CSU and SPD coalition (Grand Coalition). | Opposition parties temporarily uniting to pass a budget or block legislation. |
Defining Coalition Government
A coalition government is a formal alliance between multiple political parties that collaborate to form a majority and govern collectively, often sharing ministerial roles and policy agendas. This type of government is structured to ensure stability and represent diverse political interests within a parliamentary system. Unlike a coalition of convenience, which is a temporary and strategic partnership without deep policy integration, a coalition government requires sustained cooperation and compromise among its members.
Understanding Coalition of Convenience
A Coalition of Convenience forms when political parties unite temporarily to achieve specific goals despite lacking deep ideological alignment, contrasting with a traditional coalition government built on shared policy agendas for stable governance. This pragmatic alliance often emerges during crises or to pass urgent legislation, prioritizing immediate benefits over long-term cohesion. Understanding this concept highlights the tactical nature of political cooperation driven by convenience rather than commitment.
Historical Origins of Coalition Formations
Coalition governments emerged prominently in early 20th-century parliamentary systems as diverse political parties joined forces to achieve stable governance during periods of fragmentation, such as post-World War I Europe. In contrast, coalitions of convenience often arise from short-term interests or tactical alignments without shared ideological foundations, frequently seen in transitional or crisis contexts. The historical origins of formal coalition governments trace back to nations like Belgium and Sweden, where proportional representation systems encouraged collaboration, whereas coalitions of convenience can be observed in varied political landscapes where expedient alliances override long-term policy coherence.
Key Motivations Behind Political Alliances
Coalition governments form through strategic partnerships among political parties to achieve majority rule and implement shared policy goals, often motivated by ideological alignment and long-term governance stability. Coalitions of convenience emerge primarily from short-term tactical interests, such as overcoming political deadlock or opposing a common adversary, without deep policy consensus. The key motivations behind political alliances involve balancing power dynamics, enhancing parliamentary influence, and addressing electoral demands while navigating competing party priorities.
Structural Differences Between Coalitions
A coalition government is a formal alliance of political parties that collaboratively shares power and decision-making authority within a legislative framework, often with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. In contrast, a coalition of convenience is a temporary, strategic partnership formed to achieve specific objectives, lacking stable institutional structures or long-term commitment. Structural differences lie in the permanence, legal recognition, and internal organization, with coalition governments exhibiting stable, rule-based cooperation, whereas coalitions of convenience operate on flexible, ad hoc agreements.
Impact on Governance and Policy Stability
Coalition governments often promote broader representation and encourage policy stability by fostering compromise among diverse political parties, while coalitions of convenience prioritize short-term power gains, leading to fragile alliances and frequent policy shifts. The impact on governance is significant as stable coalitions create consistent policy frameworks, enhancing investor confidence and public trust, whereas coalitions of convenience risk legislative paralysis and governance inefficiency. Empirical studies link coalition government durability with higher policy coherence, contrasting with the volatility observed in coalitions formed solely for electoral advantage.
Advantages of Coalition Governments
Coalition governments enhance political stability by bringing together diverse parties that represent a broad spectrum of public interests, fostering inclusive decision-making. They facilitate policy continuity and compromise, enabling legislation that balances competing priorities and reduces polarization. This cooperative approach often leads to increased voter representation and stronger democratic legitimacy in governance.
Challenges Posed by Coalitions of Convenience
Coalitions of convenience often face challenges such as ideological conflicts and lack of long-term commitment, leading to unstable governance and frequent policy reversals. These coalitions struggle with trust issues among member parties, resulting in difficulties in decision-making and coherent policy implementation. The instability caused by opportunistic alliances can undermine public confidence and hinder effective government performance.
Case Studies: Global Examples
Coalition governments, such as Germany's CDU-SPD alliance, demonstrate long-term political cooperation based on shared governance goals, whereas coalitions of convenience, like the temporary NAZI-Communist pacts in the Weimar Republic, are formed for short-term tactical advantages without ideological alignment. In India, coalition governments led by the United Progressive Alliance have shown sustained policy-making through stable alliances, contrasting with Venezuela's shifting coalitions of convenience driven by immediate political gains. These global case studies highlight how coalition governments often prioritize governance stability, while coalitions of convenience serve transient, situational needs.
Future Trends in Coalition Politics
Future trends in coalition politics indicate a rise in both coalition governments and coalitions of convenience as political fragmentation increases globally. Coalition governments aim for long-term partnership and policy coherence, while coalitions of convenience prioritize short-term strategic gains often resulting in unstable governance. Advances in data analytics and real-time voter sentiment monitoring may enhance coalition negotiation strategies, potentially reshaping alliance durability and effectiveness.
Coalition government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com