Opposition plays a crucial role in shaping political landscapes by challenging governmental policies and holding leaders accountable. Effective opposition fosters democratic debate, ensuring diverse perspectives are represented and preventing abuse of power. Discover how understanding opposition can empower your awareness of political processes in the full article.
Table of Comparison
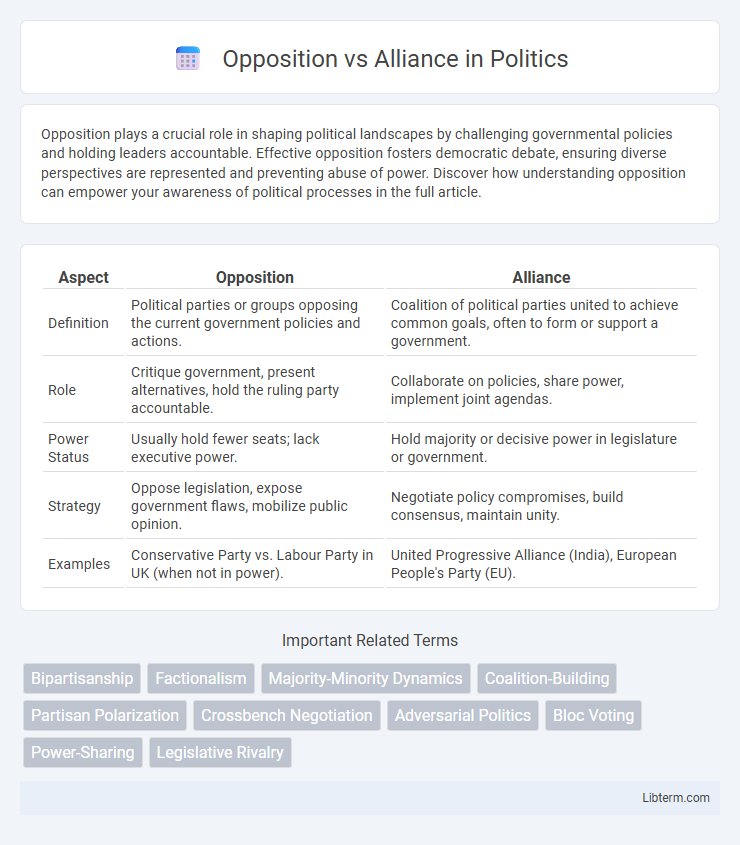
| Aspect | Opposition | Alliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political parties or groups opposing the current government policies and actions. | Coalition of political parties united to achieve common goals, often to form or support a government. |
| Role | Critique government, present alternatives, hold the ruling party accountable. | Collaborate on policies, share power, implement joint agendas. |
| Power Status | Usually hold fewer seats; lack executive power. | Hold majority or decisive power in legislature or government. |
| Strategy | Oppose legislation, expose government flaws, mobilize public opinion. | Negotiate policy compromises, build consensus, maintain unity. |
| Examples | Conservative Party vs. Labour Party in UK (when not in power). | United Progressive Alliance (India), European People's Party (EU). |
Understanding Opposition and Alliance: Key Definitions
Opposition refers to groups or individuals actively resisting or challenging prevailing policies, ideologies, or authorities, often driven by contrasting goals or values, while alliance denotes a formal or informal agreement between parties to collaborate for mutual benefit or shared objectives. Opposition emphasizes conflict, dissent, and competition, whereas alliance highlights cooperation, unity, and strategic partnership. Understanding these key definitions is crucial for analyzing political dynamics, social movements, and organizational strategies where power relations and collective actions shape outcomes.
Historical Context: Opposition vs Alliance in Politics
Opposition and alliance in politics have historically shaped power dynamics, with opposition representing dissent or resistance to ruling parties, while alliances form through agreements for mutual benefit or common goals. Notable examples include the Cold War era, where the opposition between capitalist and communist blocs defined global alliances and conflicts. Understanding these roles highlights how political strategies and ideological divides influence governance and policy-making.
Core Differences Between Opposition and Alliance
Opposition involves groups or entities actively challenging or resisting each other's goals, often resulting in conflict and competition for dominance. Alliance refers to a cooperative relationship where parties share common interests and work together to achieve mutual objectives, enhancing collective strength. The core difference lies in opposition's adversarial stance versus alliance's collaborative approach, impacting strategies, trust levels, and long-term outcomes in political, social, or organizational contexts.
Motivations Behind Forming Oppositions and Alliances
Oppositions often form to challenge existing power structures, driven by motivations such as ideological differences, competition for resources, or pursuit of political influence. Alliances emerge to consolidate strengths, combining resources and strategic advantages to achieve shared goals or counter common adversaries. Both oppositions and alliances are fundamentally motivated by the desire to maximize influence, security, and access to opportunities within a given political or social context.
Impact on Governance: Opposition vs Alliance Dynamics
Opposition forces often play a critical role in governance by providing checks and balances, holding ruling parties accountable, and fostering transparency in policy-making. In contrast, alliances can streamline decision-making processes and enhance government stability but may also lead to compromised policy positions due to coalition negotiations. The dynamic between opposition and alliance shapes legislative effectiveness, influencing the balance of power and the quality of democratic governance in parliamentary or multiparty systems.
Strategies Employed by Oppositions and Alliances
Oppositions often employ strategies such as grassroots mobilization, targeted campaigns, and leveraging social media to challenge incumbent power while highlighting governance flaws. Alliances focus on consolidating resources, coordinating policy platforms, and negotiating power-sharing agreements to present a united front and increase electoral competitiveness. Both employ strategic communication and coalition-building to maximize influence and voter support in political landscapes.
Benefits and Challenges of Alliances Compared to Oppositions
Alliances offer benefits such as pooled resources, shared expertise, and increased influence, enabling members to achieve common goals more effectively than acting alone. Challenges include potential conflicts of interest, coordination difficulties, and the need for compromise among diverse parties. In contrast, opposition groups retain more independence and flexibility but often face limitations in resources and reduced collective impact.
Case Studies: Successful Oppositions and Alliances
Case studies of successful oppositions and alliances reveal contrasting strategies that drive impactful social and political change. The Civil Rights Movement exemplifies a powerful opposition, effectively using nonviolent protests and legal challenges to dismantle segregation laws. In contrast, the European Union represents a successful alliance, uniting diverse nations through shared economic policies and political cooperation to maintain regional stability and growth.
Role of Public Opinion in Opposition and Alliance Movements
Public opinion plays a crucial role in shaping the effectiveness of both opposition and alliance movements by influencing legitimacy and mobilization capacity. Opposition movements often rely on public discontent and widespread support to challenge prevailing power structures and advocate for change. Alliance movements harness diverse public sentiments to build coalitions, enhance collective bargaining power, and promulgate shared goals in political, social, or economic contexts.
Future Trends: Evolving Nature of Opposition vs Alliance
Future trends indicate that the nature of opposition and alliance is becoming increasingly fluid, driven by technological advancements and geopolitical shifts. Emerging digital platforms enable more dynamic and complex coalition-building, often transcending traditional boundaries and ideologies. Data analytics and AI tools are playing a pivotal role in identifying potential allies and adversaries, reshaping strategic decision-making processes.
Opposition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com