A judicial panel comprises a group of judges assigned to hear and decide cases collectively, ensuring fair and balanced judgments. These panels are vital in appellate courts where multiple judges review lower court decisions to maintain consistency in the legal system. Explore the rest of the article to understand how judicial panels influence legal outcomes and your rights.
Table of Comparison
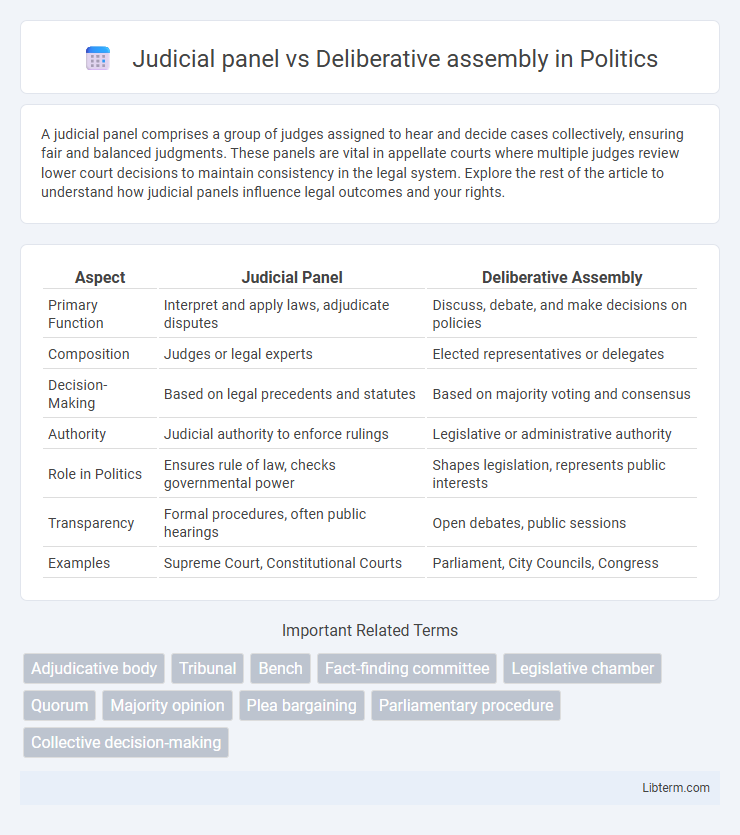
| Aspect | Judicial Panel | Deliberative Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Interpret and apply laws, adjudicate disputes | Discuss, debate, and make decisions on policies |
| Composition | Judges or legal experts | Elected representatives or delegates |
| Decision-Making | Based on legal precedents and statutes | Based on majority voting and consensus |
| Authority | Judicial authority to enforce rulings | Legislative or administrative authority |
| Role in Politics | Ensures rule of law, checks governmental power | Shapes legislation, represents public interests |
| Transparency | Formal procedures, often public hearings | Open debates, public sessions |
| Examples | Supreme Court, Constitutional Courts | Parliament, City Councils, Congress |
Introduction to Judicial Panels and Deliberative Assemblies
Judicial panels consist of a group of judges or appointed officials who review cases, interpret laws, and render decisions based on legal evidence and statutes, ensuring justice is administered according to established legal principles. Deliberative assemblies are structured groups of members who engage in discussion and decision-making on organizational or legislative matters, emphasizing democratic participation and majority rule in determining policies or resolutions. Both entities play crucial roles in governance, with judicial panels focusing on legal adjudication and deliberative assemblies on collective decision-making.
Defining Judicial Panels: Structure and Purpose
Judicial panels consist of a group of judges or legal experts tasked with adjudicating specific cases, ensuring impartiality and adherence to legal standards. Their structure typically includes three or more members, collaboratively reviewing evidence and legal arguments to render a binding decision. The primary purpose of judicial panels is to deliver fair judgments in complex legal matters while maintaining consistency across similar cases.
Understanding Deliberative Assemblies: Roles and Functions
Deliberative assemblies serve as decision-making bodies where members engage in structured discussions to reach consensus or majority decisions on organizational matters. These assemblies prioritize open debate, member participation, and the use of parliamentary procedures to ensure fair and transparent governance. Unlike judicial panels focused on legal adjudication, deliberative assemblies emphasize collaborative policy development and collective decision-making within groups such as legislatures, boards, or committees.
Key Differences Between Judicial Panels and Deliberative Assemblies
Judicial panels consist of judges or legal experts who evaluate evidence and interpret laws to make binding legal decisions, whereas deliberative assemblies are groups of members who discuss, debate, and decide on policies or organizational matters through voting. Judicial panels operate under strict procedural rules and legal standards to ensure fairness and compliance with the law, while deliberative assemblies focus on consensus-building and representation within organizations or governments. The primary distinction lies in judicial panels' authoritative, legally enforceable rulings versus deliberative assemblies' role in democratic decision-making processes.
Composition and Membership Criteria
A judicial panel typically consists of appointed or elected judges with legal expertise and qualifications, often requiring formal legal education and experience in the judiciary. In contrast, a deliberative assembly comprises elected representatives or members from a specific community or organization, selected based on criteria such as electoral mandates or membership status. The membership criteria for a judicial panel emphasize legal competency, while deliberative assemblies prioritize representational legitimacy and inclusivity.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Judicial panels rely on structured procedures and legal standards to ensure fair and consistent decision-making, emphasizing evidence evaluation and adherence to statutes. Deliberative assemblies prioritize consensus-building through discussion and voting, allowing members to influence outcomes based on majority rule and debate. The decision-making process in judicial panels is typically formal and rule-bound, whereas deliberative assemblies operate with flexible procedures aimed at collective agreement and representation of diverse viewpoints.
Authority and Jurisdiction: Legal vs. Legislative
Judicial panels possess authority grounded in legal jurisdiction, adjudicating disputes based on statutory laws and precedents within defined courts. Deliberative assemblies hold legislative authority, empowered to enact, amend, or repeal laws through collective decision-making processes in bodies such as parliaments or councils. The jurisdiction of judicial panels is confined to interpreting laws and ensuring legal compliance, whereas deliberative assemblies create and shape legislation impacting governance and public policy.
Impact on Policy and Society
Judicial panels influence policy by interpreting laws and setting legal precedents that shape societal norms and government actions, ensuring accountability and protection of rights. Deliberative assemblies impact policy through collective decision-making processes that reflect social, economic, and political interests, enabling representation and inclusive governance. Both institutions play crucial roles in balancing power, with judicial panels providing legal oversight and deliberative assemblies driving democratic participation and policy formulation.
Examples in Practice: Case Studies and Institutions
Judicial panels, such as the U.S. Court of Appeals and the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia, serve as specialized bodies adjudicating legal disputes through formal hearings and evidence evaluation. Deliberative assemblies, exemplified by the United Nations General Assembly and the U.S. Senate, function as representative forums where members debate policies, draft legislation, and make collective decisions. Case studies reveal that judicial panels emphasize impartial rule application, while deliberative assemblies prioritize inclusive discussion and consensus-building among diverse stakeholders.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Forum for Decision-Making
Selecting the appropriate forum for decision-making depends on the nature and complexity of the issues involved; judicial panels offer legally binding resolutions backed by formal procedures and expertise in law, making them ideal for disputes requiring authoritative judgments. Deliberative assemblies emphasize participatory discussion and consensus-building, suitable for organizational decisions where member input and democratic processes are prioritized. Understanding the forum's procedural framework and intended outcomes ensures effective governance and conflict resolution aligned with the stakeholders' needs.
Judicial panel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com