Sincere voting reflects genuine preferences without strategic manipulation, ensuring election outcomes truly represent voter intentions. Understanding the impact of sincere voting can enhance Your confidence in democratic processes and the legitimacy of elected representatives. Dive deeper into the article to explore how sincere voting shapes political landscapes and voter satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
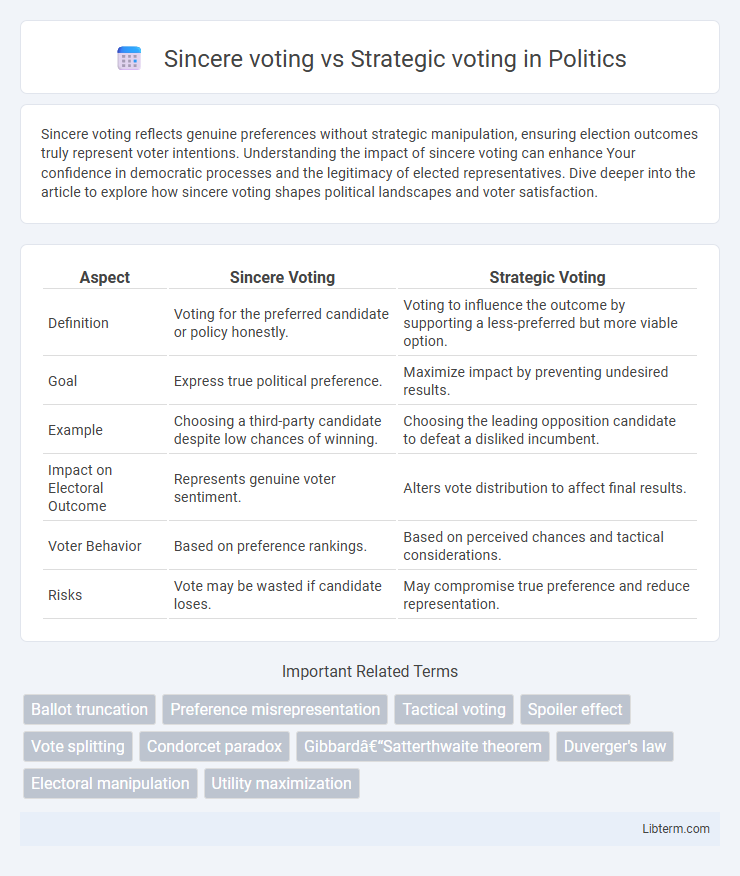
| Aspect | Sincere Voting | Strategic Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting for the preferred candidate or policy honestly. | Voting to influence the outcome by supporting a less-preferred but more viable option. |
| Goal | Express true political preference. | Maximize impact by preventing undesired results. |
| Example | Choosing a third-party candidate despite low chances of winning. | Choosing the leading opposition candidate to defeat a disliked incumbent. |
| Impact on Electoral Outcome | Represents genuine voter sentiment. | Alters vote distribution to affect final results. |
| Voter Behavior | Based on preference rankings. | Based on perceived chances and tactical considerations. |
| Risks | Vote may be wasted if candidate loses. | May compromise true preference and reduce representation. |
Understanding Sincere Voting
Sincere voting involves casting a ballot for the candidate or option that genuinely reflects a voter's true preference, without concern for the candidate's likelihood of winning. This behavior contrasts with strategic voting, where voters might select a less-preferred but more viable option to influence the election outcome. Understanding sincere voting helps clarify voter motivations and the expression of authentic political preferences in democratic processes.
Defining Strategic Voting
Strategic voting occurs when voters cast their ballots not for their preferred candidate but for a less favored candidate who has a better chance of winning, aiming to prevent an undesirable outcome. This behavior often arises in plurality voting systems where vote splitting can disadvantage similar candidates. In contrast, sincere voting involves selecting the candidate that genuinely aligns with a voter's preferences, regardless of their electability.
Key Differences Between Sincere and Strategic Voting
Sincere voting involves casting a ballot for the candidate or option that truly reflects a voter's preferences, prioritizing honest expression over electoral outcomes. Strategic voting occurs when voters choose a less-preferred candidate to prevent an undesirable candidate's victory, often influenced by poll standings and perceived viability. Key differences include motivation--sincere voting is preference-driven, while strategic voting is outcome-driven--and impact on election dynamics, where strategic voting can alter results by consolidating votes around frontrunners.
Motivations Behind Sincere Voting
Motivations behind sincere voting often stem from a desire to express genuine political preferences without distortion, reflecting voters' true support for a candidate or policy. This form of voting emphasizes trust in the electoral process and the belief that honest choices contribute to democratic legitimacy. Voters motivated by sincerity typically prioritize policy alignment and ideological consistency over tactical considerations or perceived electability.
Why Voters Choose Strategic Voting
Voters choose strategic voting to maximize the impact of their vote in elections where their preferred candidate has little chance of winning, preventing the election of a less desired candidate. Strategic voting helps avoid vote splitting among similar candidates, ensuring that support consolidates behind a more viable contender. This approach is common in plurality electoral systems, encouraging voters to weigh both candidate preferences and electability.
Impacts on Election Outcomes
Sincere voting, where voters select their genuinely preferred candidate, can lead to a more accurate reflection of public opinion but risks vote splitting among similar candidates, potentially allowing less popular options to win. Strategic voting, involving voters choosing less-preferred but more viable candidates to prevent undesired outcomes, often influences election results by consolidating support and altering the final winner. The dynamic between these voting behaviors significantly impacts election outcomes, shaping which candidates gain office and affecting overall political representation.
Psychological Factors Influencing Voting Choices
Psychological factors influencing voting choices reveal that sincere voting aligns with voters' true preferences and values, fostering emotional satisfaction and perceived authenticity. Strategic voting involves voters anticipating election outcomes and casting ballots to maximize impact, often driven by cognitive biases like risk aversion and outcome uncertainty. Social identity theory and perceived group membership further shape whether individuals prioritize sincere expression or pragmatic calculations in their voting behavior.
Sincere vs. Strategic Voting in Different Electoral Systems
Sincere voting involves casting a ballot for the candidate or party that best matches a voter's true preferences, whereas strategic voting occurs when voters support a less-preferred candidate to prevent an undesirable outcome. In plurality or first-past-the-post (FPTP) systems, strategic voting is more prevalent due to the fear of "wasting" votes on less viable candidates. Proportional representation (PR) systems reduce the incentive for strategic voting by allowing votes to contribute directly to seat allocation, enabling more sincere voting behavior.
Ethical Implications of Strategic Voting
Strategic voting raises ethical concerns as it involves voters casting ballots not for their true preferences but to influence election outcomes, potentially undermining democratic sincerity. This behavior can distort representation by prioritizing tactical advantage over genuine policy support, challenging the integrity of the electoral process. Ethical debates center on whether compromising honest expression compromises voter autonomy and the legitimacy of elected officials.
Encouraging Informed and Authentic Participation
Sincere voting reflects an individual's genuine preferences, promoting authentic participation grounded in voters' true priorities. Strategic voting involves casting ballots to influence electoral outcomes, often prioritizing practicality over personal preference to prevent undesired results. Encouraging informed voting behaviors enhances democratic legitimacy by fostering choices that accurately represent voters' intentions while maintaining pragmatic considerations.
Sincere voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com