Effective customer support ensures prompt resolution of issues and enhances overall satisfaction, boosting your brand's reputation and customer loyalty. Leveraging multiple support channels, such as live chat, email, and phone, caters to diverse preferences and maximizes accessibility. Explore this article to discover strategies that can elevate your support services and transform your customer experience.
Table of Comparison
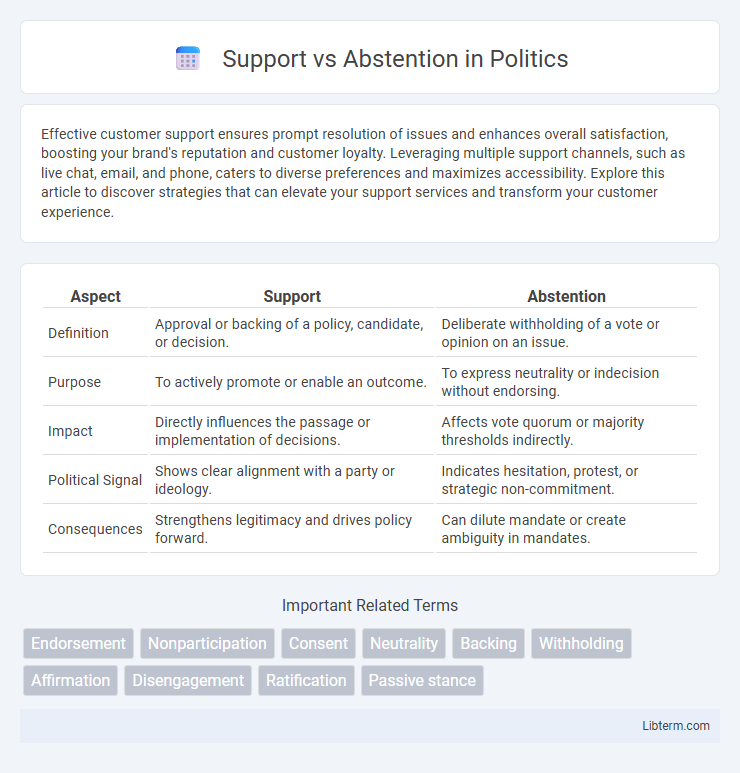
| Aspect | Support | Abstention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Approval or backing of a policy, candidate, or decision. | Deliberate withholding of a vote or opinion on an issue. |
| Purpose | To actively promote or enable an outcome. | To express neutrality or indecision without endorsing. |
| Impact | Directly influences the passage or implementation of decisions. | Affects vote quorum or majority thresholds indirectly. |
| Political Signal | Shows clear alignment with a party or ideology. | Indicates hesitation, protest, or strategic non-commitment. |
| Consequences | Strengthens legitimacy and drives policy forward. | Can dilute mandate or create ambiguity in mandates. |
Understanding Support vs Abstention: Key Differences
Support involves actively endorsing or backing a particular decision, policy, or candidate, demonstrating agreement and commitment to its success. Abstention refers to the deliberate choice to refrain from voting or expressing a preference, often due to neutrality, indecision, or conflict of interest. Understanding the distinction helps clarify voter intentions and the impact on decision-making processes in elections or organizational votes.
Historical Contexts of Support and Abstention
Historical contexts of support and abstention reveal patterns of political and social alignment during critical events such as wars, elections, and referendums. Support often manifested through active participation in movements, military alliances, or voting behaviors that aligned with dominant ideologies or interests, while abstention reflected dissent, disillusionment, or strategic neutrality within populations. Key examples include voter abstention in early 20th-century European elections as a response to political instability and widespread support for resistance movements during World War II.
Motivations Behind Supporting or Abstaining
Support often stems from alignment with shared goals, values, or perceived benefits, driving individuals or groups to actively endorse an initiative or decision. Abstention, however, may arise from uncertainty, ethical dilemmas, or strategic neutrality, reflecting hesitation to commit due to incomplete information or conflicting interests. Understanding these motivations is crucial for predicting stakeholder behavior and tailoring engagement strategies effectively.
Political Implications of Support and Abstention Votes
Support votes reinforce the legitimacy and strength of government policies, often signaling political alignment and consensus within legislative bodies. Abstention votes can indicate political ambivalence or strategic neutrality, affecting the perceived mandate without directly opposing or endorsing a proposal. The political implications of abstentions often include signaling dissent or caution, influencing coalition dynamics and public perception without altering vote outcomes.
Case Studies: Support and Abstention in International Organizations
Case studies of support and abstention in international organizations reveal strategic diplomatic behaviors influencing decision-making outcomes and coalition formations. Support often signals alignment with prevailing norms or policies, while abstention can reflect nuanced positions, signaling neutrality or dissent without direct opposition, impacting legitimacy and consensus-building. Instances from the United Nations General Assembly highlight how abstention serves as a tool for states balancing geopolitical interests and maintaining flexible foreign policy stances.
Social Dynamics Influencing Support vs Abstention
Social dynamics influencing support vs abstention often revolve around group identity, peer pressure, and perceived social norms, which can significantly sway individual participation in voting or activism. Trust in leadership and collective efficacy shape whether individuals feel their support will create meaningful impact or if abstention is a safer social stance. The presence of social networks and communal dialogues frequently amplifies mobilization by reinforcing shared values and reducing uncertainty about the consequences of active support.
Strategic Considerations: When to Support or Abstain
Strategic support is often chosen when aligning with allies can influence key outcomes or strengthen long-term partnerships, especially in contentious political or organizational decisions. Abstention may be preferred to maintain neutrality, avoid alienating stakeholders, or signal reservations without outright opposition, preserving flexibility for future negotiations. Evaluating the potential risks and benefits, including power dynamics and public perception, guides the choice between supporting or abstaining in critical strategic scenarios.
Impact of Abstention on Decision-Making Outcomes
Abstention in decision-making processes can significantly alter outcomes by reducing the total number of votes cast, thereby lowering the threshold needed for a decision to pass or fail. The impact of abstention depends on the voting rules, where high abstention rates may enable minority groups to exert disproportionate influence or lead to less representative results. Understanding abstention patterns is essential for analyzing the legitimacy and effectiveness of collective choices in political, corporate, or organizational contexts.
Public Perception: Support vs Abstention Explained
Public perception of support versus abstention significantly influences political outcomes and social movements. Support conveys approval and active participation, often leading to strengthened legitimacy for policies or candidates, while abstention signals neutrality or indecision, which can skew the perceived consensus and complicate interpretation of public opinion. Understanding the nuanced implications of abstention rates is crucial for accurately assessing electoral mandates and gauging the true level of public engagement.
Navigating Ethical Dilemmas: Support and Abstention Choices
Navigating ethical dilemmas often involves choosing between support and abstention, each carrying distinct moral implications. Providing support can affirm ethical principles and promote justice, while abstention may prevent complicity in unethical actions and preserve personal integrity. Understanding the context and potential outcomes enables more conscientious decision-making in complex moral situations.
Support Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com