An ordinary clause outlines the typical terms and conditions agreed upon by parties without any special or exceptional provisions. It establishes standard obligations, rights, and duties, ensuring clarity and mutual understanding in everyday agreements. Explore the rest of the article to learn how ordinary clauses impact your contracts and negotiations.
Table of Comparison
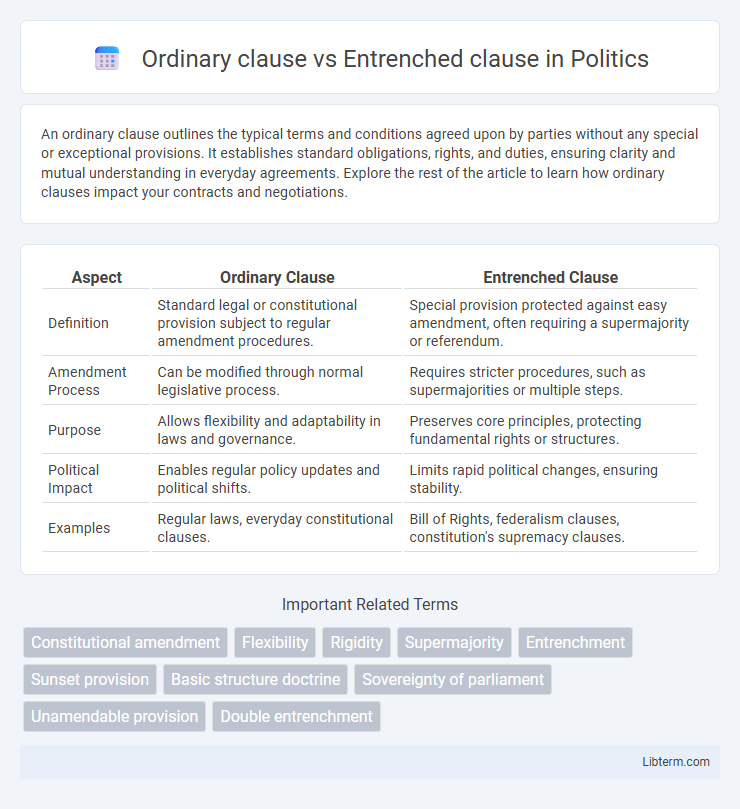
| Aspect | Ordinary Clause | Entrenched Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standard legal or constitutional provision subject to regular amendment procedures. | Special provision protected against easy amendment, often requiring a supermajority or referendum. |
| Amendment Process | Can be modified through normal legislative process. | Requires stricter procedures, such as supermajorities or multiple steps. |
| Purpose | Allows flexibility and adaptability in laws and governance. | Preserves core principles, protecting fundamental rights or structures. |
| Political Impact | Enables regular policy updates and political shifts. | Limits rapid political changes, ensuring stability. |
| Examples | Regular laws, everyday constitutional clauses. | Bill of Rights, federalism clauses, constitution's supremacy clauses. |
Introduction to Constitutional Clauses
Ordinary clauses in a constitution can be amended or repealed through the regular legislative process, reflecting the evolving needs of a society. Entrenched clauses, also known as rigid clauses, require special procedures such as supermajority votes or referendums to be altered, ensuring greater protection for fundamental principles. These distinctions safeguard constitutional stability by balancing flexibility and rigidity within the legal framework.
Defining Ordinary Clauses
Ordinary clauses are standard provisions within a constitution that can be amended through the regular legislative or constitutional amendment processes, often requiring a simple majority or specified quorum for approval. Unlike entrenched clauses, which demand more rigorous procedures to change--such as supermajority votes or referendums--ordinary clauses maintain flexibility to adapt to evolving legal and political contexts. These clauses typically govern routine governmental functions and policies that do not fundamentally alter the constitutional framework.
Understanding Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses are specific provisions in legal documents that require a more stringent process for amendment or removal, often demanding a supermajority or unanimous consent, distinguishing them from ordinary clauses. Understanding entrenched clauses is crucial for ensuring the stability and protection of fundamental rights or core governance rules within constitutions or organizational bylaws. These clauses serve as a safeguard against arbitrary changes, preserving the integrity of essential legal frameworks over time.
Key Differences Between Ordinary and Entrenched Clauses
Ordinary clauses can be amended or repealed by a simple majority vote in a legislative body, while entrenched clauses require a more rigorous process, often involving a supermajority or a referendum, to be altered. Entrenched clauses provide stronger legal protection to certain provisions, ensuring stability and preventing impulsive changes that could undermine fundamental principles. This difference highlights the legal rigidity of entrenched clauses compared to the flexible nature of ordinary clauses within constitutional and legislative contexts.
Legal Significance of Ordinary Clauses
Ordinary clauses in legal documents outline standard rights and obligations, subject to modification or removal by mutual agreement, offering flexibility in contractual relationships. These clauses lack the robust protection of entrenched clauses, which are designed to resist alteration or repeal without meeting strict procedural requirements. The legal significance of ordinary clauses lies in their adaptability, enabling parties to respond to changing circumstances but also requiring careful drafting to avoid unintended liabilities.
Legal Impact of Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses in legal documents create provisions that cannot be amended or repealed without a special procedure, which safeguards foundational legal principles from easy modification. Ordinary clauses are subject to regular legislative or procedural amendments, making them more flexible but less secure. The legal impact of entrenched clauses ensures stability and protection of core constitutional values, preventing arbitrary changes that could undermine the legal system's integrity.
Amendment Procedures: Ordinary vs Entrenched
Ordinary clauses in constitutions can be amended through standard legislative procedures, often requiring a simple or supermajority vote in the legislature, making them relatively flexible. Entrenched clauses demand more stringent amendment procedures, such as supermajorities, referenda, or approval by multiple bodies, ensuring higher protection and stability. The distinction in amendment procedures between ordinary and entrenched clauses preserves foundational principles by making entrenched clauses significantly more resistant to change.
Examples of Ordinary Clauses
Ordinary clauses in legal documents are provisions that can be amended or repealed by a simple majority vote, such as typical bylaws in corporate governance that outline procedures for meetings and elections. An example is a company's clause stating the appointment process of directors, which shareholders can easily change during annual meetings. In contrast, entrenched clauses require special procedures or higher thresholds for modification, ensuring greater protection for critical rules.
Examples of Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses, also known as "supermajority clauses" or "entrenchment provisions," require a higher threshold of approval to amend compared to ordinary clauses, commonly found in constitutions and foundational legal documents. For example, the amendment process in the United States Constitution includes entrenched clauses like Article V, which mandates a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Congress and ratification by three-fourths of the states before changes can be made. Another example is the constitution of South Africa, where certain entrenched clauses, such as those protecting human rights and the democratic order, demand a two-thirds majority in the National Assembly and a supporting vote by six of nine provinces in the National Council of Provinces.
Importance in Constitutional Law and Governance
Ordinary clauses in constitutional documents can be amended or repealed by standard legislative procedures, making them adaptable to changing political or social contexts. Entrenched clauses provide constitutional safeguards by requiring special procedures or higher thresholds for amendments, protecting fundamental principles and ensuring stability in governance. This distinction is crucial for maintaining the balance between constitutional flexibility and the preservation of core legal frameworks in constitutional law.
Ordinary clause Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com