An elected representative serves as a voice for their community, advocating for the needs and interests of their constituents in legislative or governmental bodies. Their role involves decision-making, policy development, and ensuring transparency and accountability in governance. Discover how your elected representative impacts daily life and what you can do to engage effectively by reading the rest of this article.
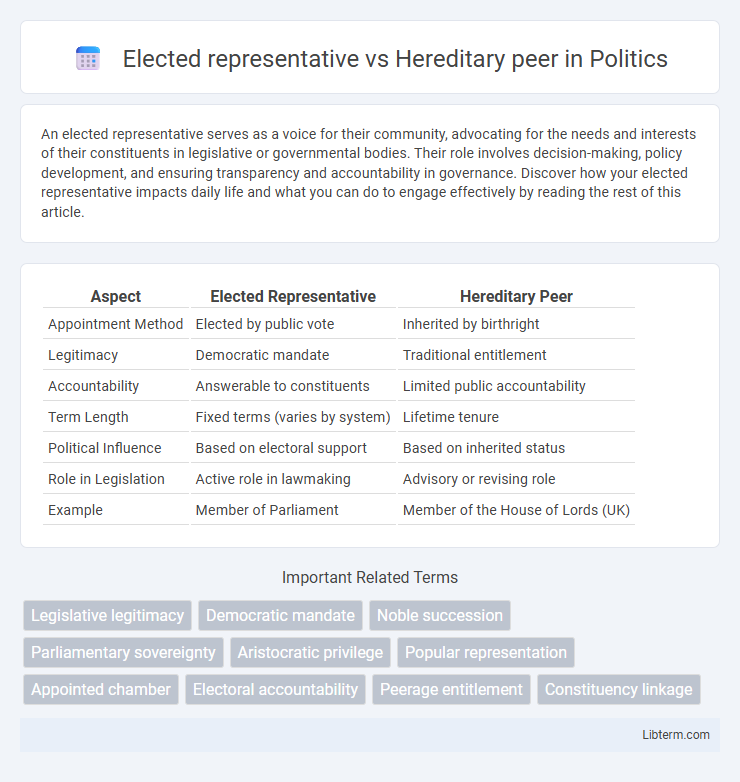
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Elected Representative | Hereditary Peer |
|---|---|---|
| Appointment Method | Elected by public vote | Inherited by birthright |
| Legitimacy | Democratic mandate | Traditional entitlement |
| Accountability | Answerable to constituents | Limited public accountability |
| Term Length | Fixed terms (varies by system) | Lifetime tenure |
| Political Influence | Based on electoral support | Based on inherited status |
| Role in Legislation | Active role in lawmaking | Advisory or revising role |
| Example | Member of Parliament | Member of the House of Lords (UK) |
Introduction: Defining Elected Representatives and Hereditary Peers
Elected representatives are individuals chosen by voters through democratic elections to serve in legislative bodies and create laws reflecting public interests. Hereditary peers inherit their titles and parliamentary positions based on family lineage, traditionally holding seats in the House of Lords without public electoral input. The contrasting legitimacy of elected representatives versus hereditary peers highlights fundamental differences in democratic accountability and governance structures.
Historical Origins of Hereditary Peerage
Hereditary peerage originates from medieval feudal systems where titles and lands were passed down through noble families, establishing a rigid aristocratic hierarchy in the United Kingdom. Unlike elected representatives, who gain political authority through popular vote or appointment based on merit, hereditary peers inherited legislative privileges based on lineage, often holding seats in the House of Lords by virtue of birthright. This system, deeply rooted in historical notions of hereditary rule and social class, contrasts with modern democratic principles that emphasize representation and accountability.
Evolution of Elected Representation in Governance
Elected representation has evolved as a fundamental principle in modern governance, emphasizing accountability and public participation compared to hereditary peerage, which relies on inherited titles and positions. The transition from hereditary peers holding legislative power to elected representatives reflects a broader democratization trend, enabling citizens to influence policy through voting. Legislative bodies worldwide increasingly favor elected officials to ensure legitimacy, responsiveness, and transparency in decision-making processes.
Selection Process: Elections vs Inheritance
Elected representatives gain their positions through a democratic voting process where citizens or designated groups cast ballots to choose candidates based on policies or qualifications. Hereditary peers inherit their titles and seats automatically through family lineage, often tied to aristocratic tradition without public input. While elections emphasize public participation and merit-based selection, hereditary positions rely on ancestral rights and continuity of noble bloodlines.
Legitimacy and Public Accountability
Elected representatives derive legitimacy from the democratic process, reflecting the voice and consent of the electorate through regular, free, and fair elections. Hereditary peers hold positions based on inherited titles, lacking direct public endorsement, which often raises questions about their legitimacy in modern governance. Public accountability is stronger for elected officials who are answerable to voters and can be removed through elections, while hereditary peers are generally insulated from direct public scrutiny and electoral mechanisms.
Role in Modern Legislative Systems
Elected representatives serve in modern legislative systems as accountable lawmakers chosen by the public through democratic elections, ensuring representation reflects current societal interests. Hereditary peers, by contrast, hold legislative positions based on inherited titles, limiting their influence primarily to traditional or advisory roles in contemporary parliaments where democratic legitimacy is prioritized. The shift towards elected officials underscores a broader commitment to representative democracy and legislative transparency in modern governance.
Power Dynamics and Influence
Elected representatives derive their power and influence directly from voters, enabling greater accountability and responsiveness in governance, which often limits their tenure to electoral cycles. Hereditary peers hold power inherited through family lineage, granting them entrenched influence and long-term positions that can shape legislation without direct public mandate. This dynamic creates a tension between democratic legitimacy and traditional authority, impacting policy decisions and institutional control within political systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Elected representatives ensure democratic legitimacy by being chosen directly by the public, promoting accountability and responsiveness to constituents, but can face short-term political pressures and partisanship. Hereditary peers provide continuity and institutional memory, often bringing long-term perspectives and non-partisan expertise, yet lack democratic legitimacy and may perpetuate elitism and unrepresentative interests. The elected system fosters dynamic political engagement, while hereditary peers offer stability, highlighting a trade-off between democratic representation and historical tradition.
Public Opinion and Democratic Values
Public opinion strongly favors elected representatives as they embody democratic values by being directly accountable to voters, ensuring governance reflects the electorate's will. In contrast, hereditary peers, appointed by virtue of birthright, often face criticism for lacking legitimacy and undermining democratic inclusivity. The democratic ethos prioritizes merit-based selection over inherited privilege, reinforcing the preference for elected officials in modern governance.
Future Trends: Reform and Relevance
Future trends indicate increasing pressure to reform hereditary peerage within legislative bodies, emphasizing democratic legitimacy and accountability. Elected representatives are gaining prominence due to their direct mandate from voters, aligning with contemporary demands for transparency and inclusivity in governance. Efforts to balance tradition with modernization suggest potential hybrid models or phased reductions in hereditary influence to enhance political relevance.
Elected representative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com