Public diplomacy shapes international relationships by promoting cultural exchange, dialogue, and mutual understanding between nations. It enhances a country's image while influencing foreign publics to support its policies and values. Discover how public diplomacy can impact global affairs and why it matters to Your nation's strategic success in the full article.
Table of Comparison
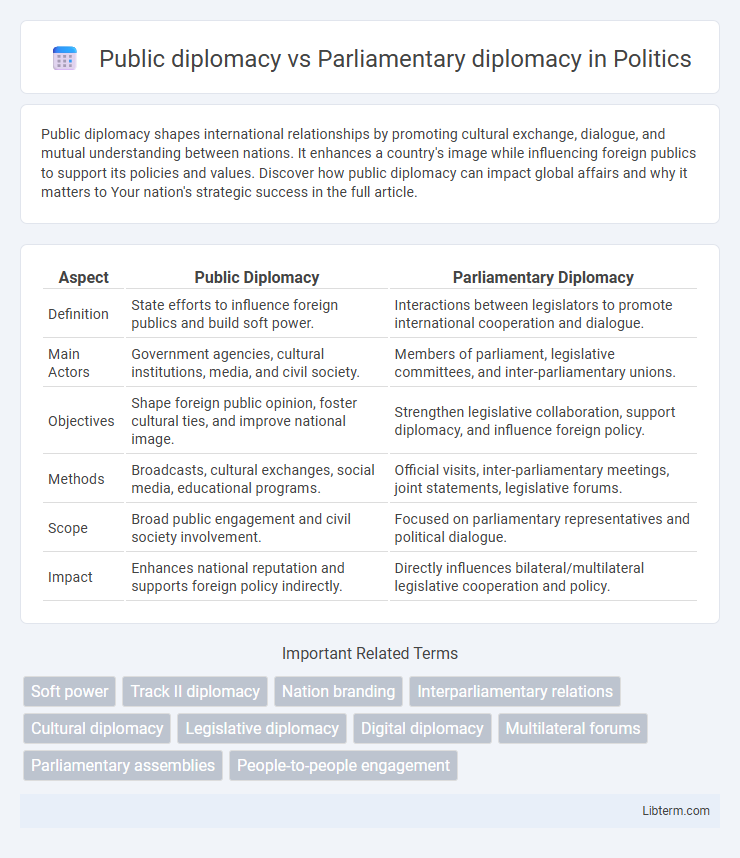
| Aspect | Public Diplomacy | Parliamentary Diplomacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State efforts to influence foreign publics and build soft power. | Interactions between legislators to promote international cooperation and dialogue. |
| Main Actors | Government agencies, cultural institutions, media, and civil society. | Members of parliament, legislative committees, and inter-parliamentary unions. |
| Objectives | Shape foreign public opinion, foster cultural ties, and improve national image. | Strengthen legislative collaboration, support diplomacy, and influence foreign policy. |
| Methods | Broadcasts, cultural exchanges, social media, educational programs. | Official visits, inter-parliamentary meetings, joint statements, legislative forums. |
| Scope | Broad public engagement and civil society involvement. | Focused on parliamentary representatives and political dialogue. |
| Impact | Enhances national reputation and supports foreign policy indirectly. | Directly influences bilateral/multilateral legislative cooperation and policy. |
Understanding Public Diplomacy: Definition and Scope
Public diplomacy involves government efforts to communicate and build relationships with foreign publics to influence public opinion and promote national interests, emphasizing cultural exchange, media outreach, and educational programs. It operates beyond official government channels, engaging directly with global audiences to foster mutual understanding and goodwill. Parliamentary diplomacy, by contrast, entails interactions between legislators and parliamentary bodies to enhance cooperation and dialogue at the governmental and intergovernmental levels.
Parliamentary Diplomacy: Concept and Significance
Parliamentary diplomacy refers to the formal and informal interactions between legislators from different countries aimed at fostering dialogue, cooperation, and mutual understanding on global issues. This form of diplomacy plays a significant role in shaping international policies by complementing traditional executive-focused diplomacy through legislative engagement and oversight. Parliamentary diplomacy enhances transparency, accountability, and peaceful conflict resolution by promoting dialogue among diverse political groups within and across nations.
Historical Evolution of Diplomatic Practices
Public diplomacy evolved significantly after World War II, emphasizing state-to-citizen communication to influence foreign publics, shaped by technological advances and global media expansion. Parliamentary diplomacy emerged more prominently in the late 20th century, involving legislative bodies in international negotiations and fostering inter-parliamentary cooperation to complement traditional executive diplomacy. Both forms reflect a shift from exclusive state-centric diplomacy towards inclusive, multi-actor diplomatic practices influenced by democratization and globalization trends.
Key Objectives: Public vs Parliamentary Diplomacy
Public diplomacy aims to influence foreign publics and foster mutual understanding through cultural exchanges, media outreach, and educational programs, enhancing a nation's soft power globally. Parliamentary diplomacy focuses on building inter-parliamentary cooperation, promoting legislative dialogue, and strengthening diplomatic relations through official visits and joint decision-making processes. Both approaches seek to advance national interests, but public diplomacy targets wider societal engagement while parliamentary diplomacy emphasizes governmental and legislative collaboration.
Stakeholders and Actors Involved
Public diplomacy primarily involves government agencies, media outlets, cultural institutions, and the general populace as key stakeholders, aiming to influence foreign public opinion and foster mutual understanding. Parliamentary diplomacy centers on legislators, parliamentary committees, and inter-parliamentary organizations such as the Inter-Parliamentary Union, focusing on dialogue, cooperation, and conflict resolution between national parliaments. Both forms engage diplomats and policymakers, but parliamentary diplomacy uniquely empowers elected representatives in shaping legislative collaboration and soft power across nations.
Methods and Tools of Engagement
Public diplomacy employs mass media campaigns, cultural exchanges, social media platforms, and international broadcasting to influence foreign publics and shape global perceptions. Parliamentary diplomacy relies on inter-parliamentary meetings, legislative forums, bilateral parliamentary visits, and joint committees to foster dialogue and collaboration among representatives. Both methods use targeted communication tools designed to build trust, facilitate negotiation, and advance national interests through soft power.
Influence on Foreign Policy Decision-Making
Public diplomacy directly shapes foreign policy decision-making by engaging foreign publics to build favorable perceptions and influence government actions through cultural exchanges, media, and information campaigns. Parliamentary diplomacy involves legislators' interactions across borders, facilitating cooperation and dialogue that inform and sometimes constrain executive foreign policy decisions through legislative oversight and international parliamentary unions. Both forms of diplomacy serve complementary roles in shaping foreign policy, with public diplomacy fostering grassroots influence and parliamentary diplomacy exerting formal institutional pressure.
Challenges and Limitations
Public diplomacy faces challenges such as managing diverse international audiences, overcoming misinformation, and ensuring message consistency across multiple platforms. Parliamentary diplomacy struggles with limitations including slower decision-making processes, varying national legislative priorities, and difficulties in achieving unified consensus among parliamentarians. Both forms often encounter obstacles related to transparency, accountability, and the balancing of domestic and foreign policy interests.
Case Studies: Successful Applications
Public diplomacy effectively shaped global perceptions during the Cold War through initiatives like America's Voice of America broadcasts, enhancing U.S. cultural influence abroad. Parliamentary diplomacy demonstrated success in the Nordic region, where inter-parliamentary cooperation fostered regional stability and consensus on environmental policies. Both approaches leverage distinct channels--public diplomacy targeting foreign publics, while parliamentary diplomacy engages legislators directly--to achieve international cooperation and conflict resolution.
Future Trends in Global Diplomacy
Future trends in global diplomacy emphasize the growing importance of digital platforms in public diplomacy, enabling governments to engage broader audiences through social media, virtual forums, and global information campaigns. Parliamentary diplomacy is expected to evolve with increased inter-parliamentary coalitions and regional legislative collaborations that enhance transparency, promote legislative exchanges, and support conflict resolution. Integrating artificial intelligence and data analytics will optimize both public and parliamentary diplomacy efforts by providing real-time insights and fostering adaptive, evidence-based decision-making.
Public diplomacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com