Alternative vote, also known as ranked-choice voting, allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference instead of selecting just one. This voting system ensures that the winning candidate has broad support by redistributing votes from the least popular candidates until a majority is achieved. Discover how adopting alternative vote can enhance your democratic participation by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
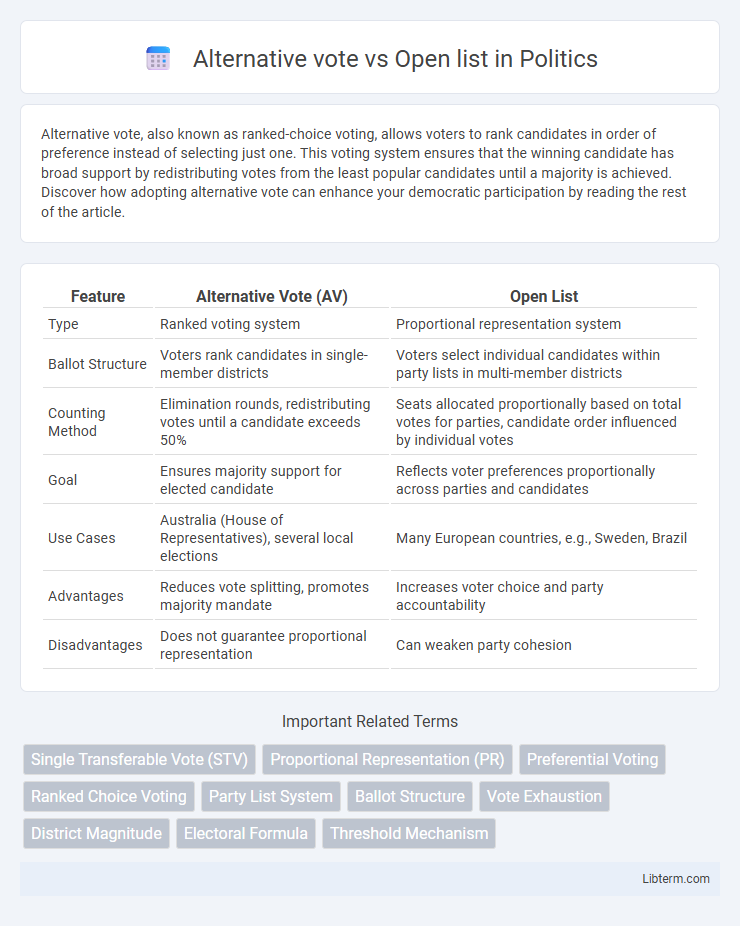
| Feature | Alternative Vote (AV) | Open List |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Ranked voting system | Proportional representation system |
| Ballot Structure | Voters rank candidates in single-member districts | Voters select individual candidates within party lists in multi-member districts |
| Counting Method | Elimination rounds, redistributing votes until a candidate exceeds 50% | Seats allocated proportionally based on total votes for parties, candidate order influenced by individual votes |
| Goal | Ensures majority support for elected candidate | Reflects voter preferences proportionally across parties and candidates |
| Use Cases | Australia (House of Representatives), several local elections | Many European countries, e.g., Sweden, Brazil |
| Advantages | Reduces vote splitting, promotes majority mandate | Increases voter choice and party accountability |
| Disadvantages | Does not guarantee proportional representation | Can weaken party cohesion |
Introduction to Alternative Vote and Open List
Alternative Vote (AV) is a ranked voting system where voters rank candidates by preference, and votes are redistributed until a candidate achieves a majority, ensuring broader support. Open List proportional representation allows voters to select individual candidates within party lists, influencing which candidates win seats based on personal preference and party vote share. Both systems enhance voter choice but differ in candidate selection and vote counting processes.
Core Principles of Alternative Vote
The Alternative Vote (AV) system is designed to ensure majority support by allowing voters to rank candidates in order of preference, thereby minimizing wasted votes and promoting majority consensus. This preferential voting method enhances representation by enabling vote transfers when no candidate achieves an initial majority, contrasting with the Open List system where voters select individual candidates within party lists, emphasizing proportional representation. Core principles of the Alternative Vote include promoting majority legitimacy, reducing strategic voting, and providing voters with greater influence over candidate selection through ranked preferences.
Key Features of Open List Voting
Open list voting allows voters to influence the order of candidates on a party's list, giving them the power to select individual representatives rather than just choosing a party. This system enhances voter choice by enabling preference votes, which directly affect which candidates win seats based on personal popularity within the party. Unlike the alternative vote system, which is a ranked choice method for single-winner elections, open list voting is typically used in proportional representation systems to allocate seats among multiple candidates.
Representation and Voter Choice
The Alternative Vote (AV) system enhances voter choice by allowing ranked preferences, ensuring that elected candidates represent a broader consensus within single-member districts. In contrast, the Open List system offers greater representation diversity by enabling voters to select individual candidates within party lists, promoting proportional outcomes in multi-member constituencies. Both systems balance representation and voter choice differently: AV emphasizes majority support for a single candidate, while Open List fosters proportional representation and intra-party competition.
Ballot Design and Voting Process
The Alternative Vote (AV) system features a ranked-choice ballot where voters rank candidates by preference, streamlining vote counting through instant runoff rounds that eliminate the lowest-ranked candidates until one attains a majority. Open List proportional representation uses a ballot where voters select individual candidates within party lists, allowing preference votes to influence candidate order and seat allocation, reflecting voter priorities within the party framework. AV emphasizes preference ranking of individual candidates for majority support in single-member districts, while Open List prioritizes voter impact on party candidate selection in multi-member districts.
Impact on Political Parties
The Alternative Vote system enhances the presence of moderate candidates by allowing voters to rank preferences, which often benefits centrist political parties and encourages coalition-building. In contrast, the Open List proportional representation system empowers voters to select individual candidates within party lists, strengthening party accountability and internal competition. While Alternative Vote tends to consolidate party options, Open List promotes diverse representation within parties, affecting party cohesion and electoral strategy.
Proportionality of Election Results
The Alternative Vote system often results in less proportional election outcomes due to its single-member district setup, which favors major parties and can distort representation. In contrast, the Open List system enhances proportionality by allowing voters to select individual candidates within party lists, ensuring seat allocation closely matches the total vote share each party receives. Empirical studies demonstrate that Open List voting leads to more accurate reflections of voter preferences, benefiting smaller parties and increasing overall electoral fairness.
Advantages of Alternative Vote
The Alternative Vote system enhances voter choice by allowing ranked preferences, which reduces the likelihood of vote splitting and promotes majority support for elected candidates. This method encourages candidates to appeal to a broader electorate, fostering more moderate and consensus-driven politics. Compared to Open List systems, Alternative Vote often leads to greater voter satisfaction by ensuring the winner has broader acceptance rather than simply the highest plurality.
Strengths of Open List Systems
Open list systems empower voters to influence candidate selection within party lists, enhancing voter choice and accountability. They often promote greater intra-party competition and encourage candidates to engage directly with constituents, leading to stronger voter representation. This system also increases proportionality by allowing popular candidates to receive more personal votes, improving the reflection of voter preferences in the final election outcome.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Electoral System
Selecting the right electoral system hinges on the values a society prioritizes, such as representation, simplicity, and voter empowerment. Alternative vote promotes majority support and reduces vote splitting by allowing ranking preferences, while open list enhances proportionality and voter influence on candidate selection within parties. Decision-makers must weigh the trade-offs between majoritarian clarity and proportional inclusivity to align the system with democratic goals.
Alternative vote Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com