Open primaries allow voters to participate in any party's primary election without declaring party affiliation, increasing voter inclusivity and influence in candidate selection. This system can lead to more moderate candidates by encouraging broader voter participation across the political spectrum. Explore the article to understand how open primaries could impact your voting experience and the political landscape.
Table of Comparison
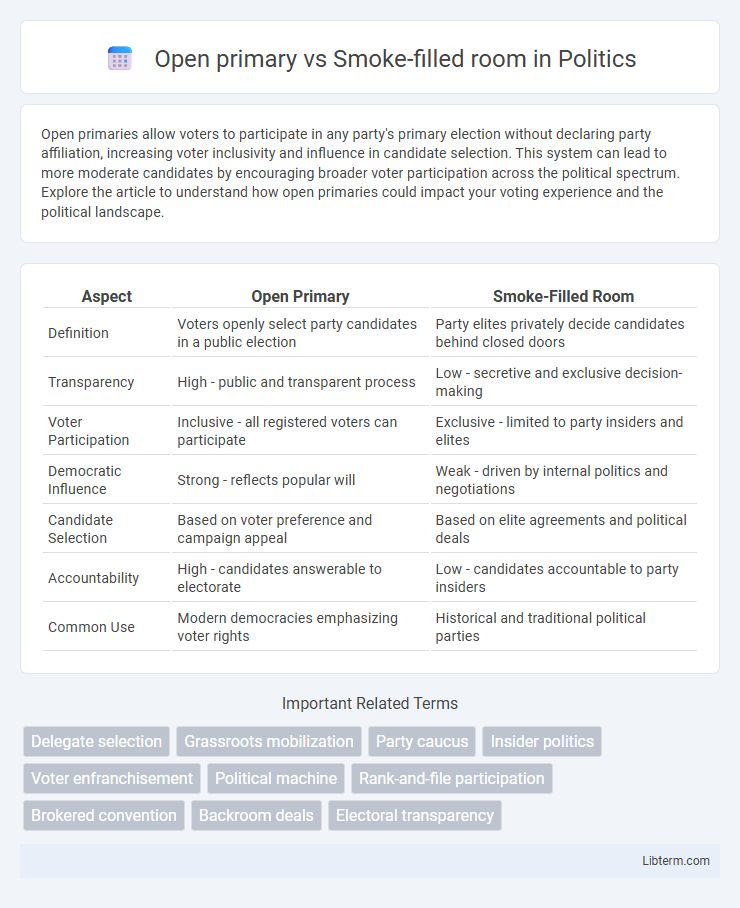
| Aspect | Open Primary | Smoke-Filled Room |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voters openly select party candidates in a public election | Party elites privately decide candidates behind closed doors |
| Transparency | High - public and transparent process | Low - secretive and exclusive decision-making |
| Voter Participation | Inclusive - all registered voters can participate | Exclusive - limited to party insiders and elites |
| Democratic Influence | Strong - reflects popular will | Weak - driven by internal politics and negotiations |
| Candidate Selection | Based on voter preference and campaign appeal | Based on elite agreements and political deals |
| Accountability | High - candidates answerable to electorate | Low - candidates accountable to party insiders |
| Common Use | Modern democracies emphasizing voter rights | Historical and traditional political parties |
Introduction to Primary Election Systems
Open primary election systems allow all registered voters to participate in selecting party candidates regardless of their own party affiliation, promoting broader voter engagement and candidate diversity. In contrast, the smoke-filled room refers to informal, behind-the-scenes decision-making by party elites that often excludes wider voter input in candidate selection. Understanding these contrasting methods highlights the shift from exclusive, centralized control toward more transparent and democratic primary election processes.
What is an Open Primary?
An Open Primary allows voters to participate in any party's primary regardless of their registered party affiliation, promoting broader voter engagement and inclusivity. This system contrasts with closed primaries, where only registered party members can vote, and avoids the exclusivity of decisions made behind closed doors in a Smoke-filled Room, where party leaders select candidates without direct voter input. Open Primaries enhance transparency and democratic participation by empowering a wider electorate to influence candidate selection.
Defining the Smoke-Filled Room Approach
The smoke-filled room approach refers to a secretive, closed-door decision-making process where political leaders or party elites select candidates without public input, contrasting sharply with the open primary system that allows registered voters to choose nominees. This method emphasizes concentrated power among a few influential insiders, often leading to less transparency and diminished democratic participation. Historically, the smoke-filled room symbolizes backroom deals and elite control in candidate selection, undermining broad-based electoral engagement.
Historical Background of Both Systems
Open primaries emerged in the early 20th century as a reform to increase voter participation and transparency in candidate selection, contrasting with the traditional smoke-filled room system prevalent in the late 19th and early 20th centuries where party leaders decided nominees behind closed doors. The smoke-filled room metaphor originated from elite political gatherings, especially within the Republican and Democratic parties, characterized by closed negotiations and elite control over nominations. Open primaries represent a shift toward democratic inclusivity by allowing a broader electorate to influence candidate selection, reflecting Progressive Era efforts to reduce corruption and insider control in American politics.
Key Differences: Open Primary vs Smoke-Filled Room
Open primary elections promote transparency by allowing registered voters to participate in candidate selection, reflecting broader public preference. Smoke-filled rooms, in contrast, involve closed-door decisions by party elites, prioritizing insider influence over voter input. This fundamental difference highlights the democratic openness of primaries versus the secretive, elite-driven nature of smoke-filled room selections.
Advantages of Open Primaries
Open primaries enhance democratic participation by allowing all registered voters, regardless of party affiliation, to select candidates, which increases voter turnout and engagement. These primaries promote transparency and reduce the influence of party elites, limiting backroom deals and ensuring that candidates better reflect the broader electorate's preferences. Open primaries also encourage moderate candidates to emerge, as they must appeal to a wider range of voters beyond party loyalists.
Drawbacks of the Smoke-Filled Room System
The smoke-filled room system suffers from a lack of transparency, as decisions are made behind closed doors by a select few, excluding broader party members and voters. This approach often leads to cronyism and favoritism, diminishing the democratic legitimacy of candidate selection. Voters and grassroots activists have minimal influence, reducing accountability and increasing the risk of corrupt practices within political parties.
Case Studies: Examples in Political History
The 1968 Democratic presidential primary exemplifies the impact of open primaries, where voter participation in multiple states influenced the nomination process more democratically compared to the smoke-filled room tactics used in earlier 20th-century conventions such as the 1924 Democratic National Convention, which was dominated by party elites making decisions behind closed doors. The 1912 Republican presidential primary also demonstrates the transition from smoke-filled room maneuvering, as Theodore Roosevelt challenged the party establishment through voter-driven primaries. These case studies highlight the evolving mechanisms of candidate selection, contrasting transparent voter-involved systems with secretive elite negotiations.
Impact on Voter Participation and Representation
Open primaries significantly increase voter participation by allowing all registered voters, regardless of party affiliation, to select candidates, thus broadening democratic engagement. Smoke-filled rooms, where party elites make decisions in secretive settings, restrict voter involvement and often lead to unrepresentative outcomes that favor insiders. Consequently, open primaries promote transparency and inclusivity, enhancing representation by reflecting a wider array of voter preferences.
Future Trends in Candidate Selection Methods
Open primaries are gaining momentum as future trends in candidate selection emphasize transparency and wider voter participation, enabling broader democratic engagement beyond party lines. In contrast, smoke-filled room practices, characterized by closed-door decisionmaking among party elites, face increasing criticism for lack of inclusiveness and potential bias. Emerging digital platforms and data-driven analytics forecast a shift toward more open, participatory, and technology-enabled candidate selection processes, diminishing the influence of traditional insider negotiations.
Open primary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com