Voting is a fundamental democratic process that empowers citizens to influence government decisions and shape public policies. By participating in elections, you contribute to the selection of leaders who represent your interests and uphold your rights. Explore the rest of this article to discover how voting impacts society and ways to engage effectively in the electoral process.
Table of Comparison
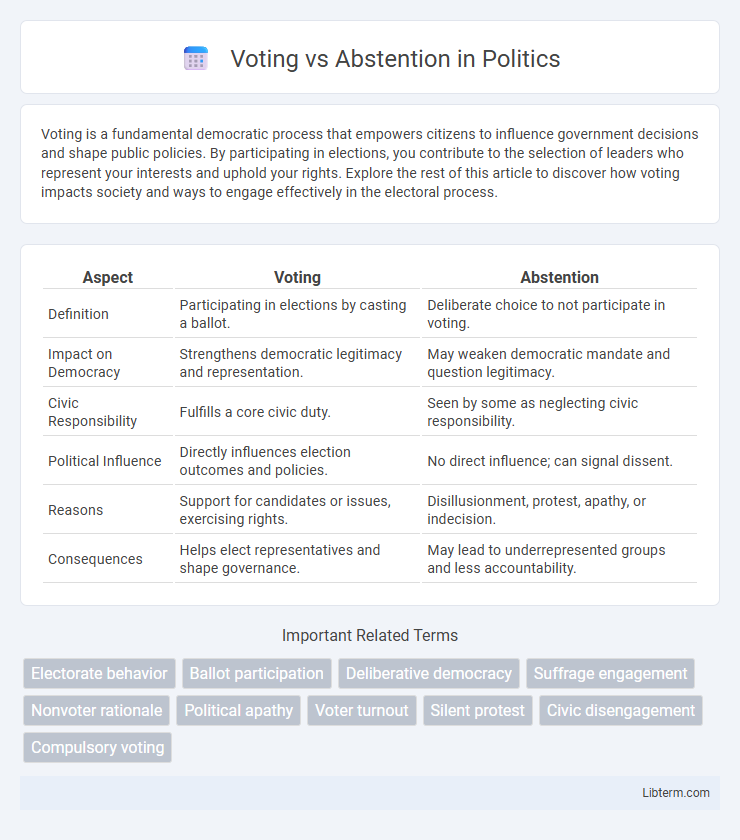
| Aspect | Voting | Abstention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Participating in elections by casting a ballot. | Deliberate choice to not participate in voting. |
| Impact on Democracy | Strengthens democratic legitimacy and representation. | May weaken democratic mandate and question legitimacy. |
| Civic Responsibility | Fulfills a core civic duty. | Seen by some as neglecting civic responsibility. |
| Political Influence | Directly influences election outcomes and policies. | No direct influence; can signal dissent. |
| Reasons | Support for candidates or issues, exercising rights. | Disillusionment, protest, apathy, or indecision. |
| Consequences | Helps elect representatives and shape governance. | May lead to underrepresented groups and less accountability. |
Understanding Voting: Definition and Importance
Voting is the process by which eligible citizens express their preferences in elections to select representatives or decide on public policies. It is a fundamental mechanism in democratic systems that ensures government legitimacy, accountability, and citizen participation in decision-making. High voter turnout strengthens the representative nature of governance and promotes social equity by reflecting diverse public interests.
What is Abstention? Meaning and Context
Abstention refers to the deliberate choice of a voter to neither support nor oppose a proposal or candidate during an election or decision-making process. In political contexts, abstention can signal neutrality, protest, or indecision, influencing the perceived legitimacy and outcome of votes. Understanding abstention is crucial in analyzing voter behavior and interpreting election results within democratic systems.
Historical Trends in Voting and Abstention
Historical trends in voting and abstention reveal fluctuating participation rates influenced by social, political, and economic factors across different eras. Voter turnout peaked during landmark elections such as the 1960s civil rights movement in the United States but declined notably during periods of political disenchantment in the late 20th century. Abstention rates often rise in contexts of voter suppression, disenfranchisement, or perceived electoral inefficacy, highlighting the complex relationship between citizen engagement and democratic health.
Motivations Behind Casting a Vote
Voters are motivated by a sense of civic duty, the desire to influence political outcomes, and the belief that their participation can lead to social change. Psychological factors such as political efficacy, where individuals feel their vote matters, significantly impact voter turnout. External motivations include responses to candidate appeal, party loyalty, and key issues that resonate with voters' values and interests.
Reasons People Choose to Abstain
Many individuals choose to abstain from voting due to dissatisfaction with available candidates, perceiving a lack of representation or meaningful choice in elections. Concerns about the integrity of the voting process, such as fears of fraud or systemic bias, also contribute to voter abstention. Additionally, some abstain due to apathy, political disengagement, or logistical barriers like registration issues and inconvenient polling locations.
Impact of Voting on Democratic Processes
Voting serves as the cornerstone of democratic processes by enabling citizens to directly influence government decisions and policy outcomes. High voter turnout enhances the legitimacy of elected representatives and strengthens accountability within political institutions. Abstention can weaken democratic functions by skewing representation and diminishing the responsiveness of governments to public needs.
Consequences of Widespread Abstention
Widespread abstention in elections can significantly undermine the legitimacy of elected officials, leading to decreased public trust in democratic institutions. Low voter turnout often skews representation, favoring groups with higher participation rates and resulting in policies that may not reflect the broader population's interests. Persistent abstention can also encourage political apathy, weakening civic engagement and the accountability mechanisms essential for a healthy democracy.
Social and Psychological Factors Influencing Participation
Social identity and group norms significantly impact voting behavior, as individuals often vote to affirm belonging to a community or social class. Psychological factors such as perceived efficacy and political interest determine the likelihood of participation, with lower motivation leading to abstention. Social pressure and fear of social exclusion also drive voting, while feelings of alienation and distrust in political systems contribute to abstention rates.
Strategies to Encourage Voter Turnout
Implementing targeted voter education campaigns increases awareness of election importance and reduces voter apathy, boosting turnout rates significantly. Utilizing convenient voting methods such as mail-in ballots and extended early voting periods removes logistical barriers and encourages participation. Engaging community leaders and leveraging social media platforms create personalized outreach that motivates hesitant voters to cast their ballots rather than abstain.
Balancing Civic Duty: Voting Rights vs Freedom to Abstain
Voting embodies a fundamental civic duty, empowering citizens to influence governance and uphold democratic principles, while abstention represents a deliberate exercise of individual freedom, signaling dissent or disengagement without coercion. Balancing voting rights and the freedom to abstain safeguards democratic integrity by respecting personal autonomy and encouraging informed participation. Ensuring accessible voting mechanisms alongside protecting abstention choices strengthens a resilient and inclusive electoral framework.
Voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com