Constitutional constraints serve as fundamental limits on the powers of government, ensuring that authorities operate within the bounds of established laws and protect individual rights. These constraints help maintain a balance between different branches of government and prevent any single entity from gaining unchecked authority. Discover how constitutional constraints shape governance and safeguard your freedoms in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
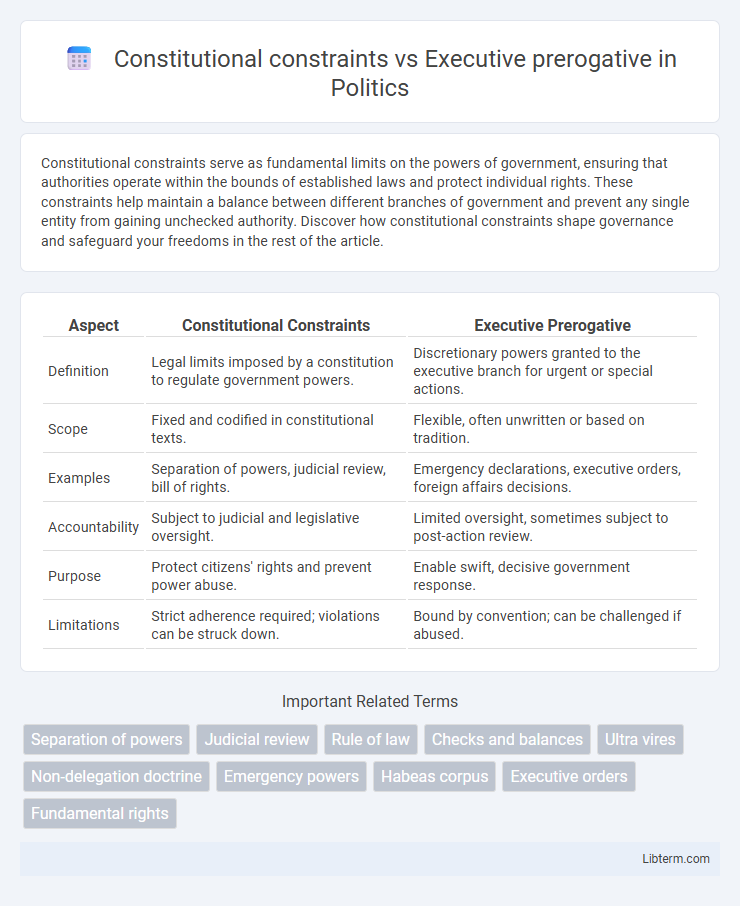
| Aspect | Constitutional Constraints | Executive Prerogative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal limits imposed by a constitution to regulate government powers. | Discretionary powers granted to the executive branch for urgent or special actions. |
| Scope | Fixed and codified in constitutional texts. | Flexible, often unwritten or based on tradition. |
| Examples | Separation of powers, judicial review, bill of rights. | Emergency declarations, executive orders, foreign affairs decisions. |
| Accountability | Subject to judicial and legislative oversight. | Limited oversight, sometimes subject to post-action review. |
| Purpose | Protect citizens' rights and prevent power abuse. | Enable swift, decisive government response. |
| Limitations | Strict adherence required; violations can be struck down. | Bound by convention; can be challenged if abused. |
Understanding Constitutional Constraints
Constitutional constraints limit executive powers by establishing clear legal boundaries, ensuring actions comply with fundamental laws and rights enshrined in the constitution. These constraints safeguard democratic principles by enabling judicial review and legislative oversight, preventing arbitrary use of executive authority. Understanding these limitations is essential for maintaining the balance of power and protecting citizens from potential abuses within governance frameworks.
Defining Executive Prerogative
Executive prerogative refers to the discretionary powers exercised by the head of state or government, often rooted in common law, allowing unilateral decisions without prior legislative approval. These powers encompass actions like foreign diplomacy, national security measures, and emergency responses, which are constitutionally recognized yet not explicitly codified. Constitutional constraints limit executive prerogative by mandating legal boundaries, checks and balances, and adherence to statutory laws to prevent abuse of authority.
Historical Context of Executive Powers
The historical context of executive powers reveals a tension between constitutional constraints and executive prerogative, where early constitutional frameworks sought to limit unilateral presidential actions to prevent authoritarian rule. Landmark cases such as Youngstown Sheet & Tube Co. v. Sawyer (1952) illustrate judiciary efforts to delineate the boundaries of executive authority during national emergencies. This evolving balance reflects ongoing debates about the scope of presidential powers in response to shifting political and social challenges.
Constitutional Checks and Balances
Constitutional constraints limit executive prerogative by establishing a framework of checks and balances that ensures no single branch of government wields excessive power. The separation of powers doctrine empowers the legislature and judiciary to review, restrict, or override executive actions through mechanisms like judicial review and legislative oversight. These constitutional checks maintain democratic governance by preventing arbitrary use of executive authority and safeguarding individual rights.
Judicial Oversight of Executive Actions
Judicial oversight of executive actions ensures constitutional constraints limit executive prerogative by interpreting the constitutionality of decisions, preventing arbitrary use of power. Courts play a critical role in reviewing executive orders, enforcing legality, and protecting fundamental rights under constitutional law. This balance upholds the rule of law by holding the executive accountable within the framework of constitutional provisions.
Tensions Between Security and Liberty
Constitutional constraints limit executive prerogative by embedding checks and balances that protect civil liberties even during national security threats. Tensions between security and liberty arise as governments invoke executive powers to address emergencies, often challenging constitutional protections like due process and free speech. Courts frequently mediate these conflicts, balancing the necessity of security measures against the preservation of fundamental rights.
Notable Case Studies and Precedents
Notable case studies such as United States v. Nixon (1974) and the Marbury v. Madison (1803) firmly delineate constitutional constraints on executive prerogatives by affirming judicial review and limiting absolute executive privilege. In the United Kingdom, the Case of Proclamations (1611) and R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the European Union (2017) reinforce parliamentary sovereignty and the requirement for explicit legislative authorization before the executive can exercise prerogative powers. These precedents underscore the judiciary's critical role in balancing executive actions within the bounds of constitutional law, ensuring accountability and preventing overreach.
Impact on Democratic Governance
Constitutional constraints establish clear legal limits on executive power, ensuring accountability and protecting democratic institutions from autocratic rule. Executive prerogative allows leaders discretionary authority in urgent or unforeseen circumstances, potentially bypassing legislative oversight and risking democratic erosion. The balance between these forces critically shapes the robustness and responsiveness of democratic governance.
Modern Challenges in Balancing Powers
Modern challenges in balancing powers highlight the tension between constitutional constraints and executive prerogative, particularly in contexts of national security and emergency powers. Judicial review increasingly scrutinizes executive actions to ensure adherence to constitutional limits, reflecting evolving interpretations of separation of powers. The rise of digital surveillance and rapid crisis response demands accentuates debates on executive authority versus legislative oversight and civil liberties protection.
Future Trends in Executive-Constitutional Relations
Future trends in executive-constitutional relations indicate a growing tension between constitutional constraints and executive prerogative, driven by an increasing reliance on emergency powers and national security measures. Courts are progressively scrutinizing executive actions to ensure adherence to constitutional principles while balancing the need for swift decision-making in crises. Technological advancements and geopolitical shifts also demand a re-evaluation of traditional boundaries, prompting legal reforms aimed at clarifying the scope of executive authority within constitutional limits.
Constitutional constraints Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com