Left-wing coalitions unite diverse progressive parties to promote social justice, economic equality, and environmental sustainability. These alliances leverage shared goals to influence policy and drive political reforms that prioritize the needs of marginalized communities. Discover how your support can shape the future of left-wing coalitions in the full article.
Table of Comparison
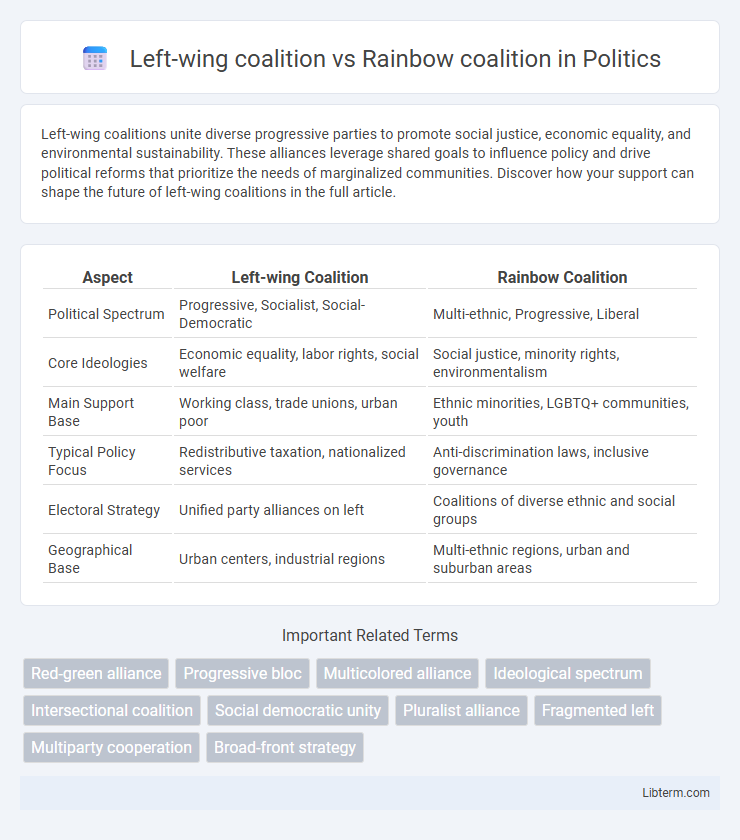
| Aspect | Left-wing Coalition | Rainbow Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Political Spectrum | Progressive, Socialist, Social-Democratic | Multi-ethnic, Progressive, Liberal |
| Core Ideologies | Economic equality, labor rights, social welfare | Social justice, minority rights, environmentalism |
| Main Support Base | Working class, trade unions, urban poor | Ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ communities, youth |
| Typical Policy Focus | Redistributive taxation, nationalized services | Anti-discrimination laws, inclusive governance |
| Electoral Strategy | Unified party alliances on left | Coalitions of diverse ethnic and social groups |
| Geographical Base | Urban centers, industrial regions | Multi-ethnic regions, urban and suburban areas |
Overview of Left-Wing and Rainbow Coalitions
Left-wing coalitions consist of political parties and groups united by progressive ideologies emphasizing social equality, economic justice, and expanded government intervention in welfare. The Rainbow Coalition, originally formed in the United States during the 1980s, brings together diverse ethnic and social groups including African Americans, Latinos, and labor unions to address systemic inequalities. Both coalitions prioritize inclusive policies but differ in composition, with Left-wing coalitions emphasizing ideological alignment and Rainbow coalitions focusing on multicultural and cross-group solidarity.
Historical Background and Evolution
The Left-wing coalition emerged in the early 20th century as a unification of socialist, communist, and labor parties aiming to address workers' rights and social equality, shaped by industrialization and class struggles. The Rainbow coalition, popularized in the late 20th century, broadened this framework by incorporating diverse ethnic, racial, and minority groups alongside traditional leftist elements, reflecting evolving social dynamics and multiculturalism. Both coalitions evolved through political realignments and social movements, yet the Rainbow coalition represents a more inclusive approach to coalition-building in contemporary politics.
Key Ideological Differences
The Left-wing coalition primarily centers on socialist and progressive economic policies emphasizing wealth redistribution, labor rights, and expanded social welfare. The Rainbow coalition, while also embracing social justice, places stronger emphasis on multiculturalism, civil rights, and broad inclusivity across racial and ethnic groups. Key ideological differences include the Left-wing coalition's focus on economic class struggle versus the Rainbow coalition's prioritization of identity politics and intersectional solidarity.
Core Parties and Member Groups
The Left-wing coalition primarily consists of socialist and progressive parties such as the Democratic Socialists of America and the Green Party, emphasizing labor rights and social justice issues. The Rainbow coalition brings together a more diverse group of member groups, including civil rights organizations like the NAACP, labor unions such as the AFL-CIO, and minority advocacy groups spanning ethnic and LGBTQ+ communities. Both coalitions focus on progressive policies but differ in their core party structure and the breadth of constituent groups represented.
Policy Objectives and Priorities
Left-wing coalitions prioritize social justice, wealth redistribution, and expansive welfare programs aimed at reducing economic inequality and protecting workers' rights. Rainbow coalitions emphasize broad inclusivity and civil rights, uniting diverse racial, ethnic, and marginalized groups to advance policies on anti-discrimination, immigration reform, and social equity. Both coalitions advocate progressive taxation and environmental sustainability but differ in focus: left-wing coalitions center predominantly on economic reforms, while rainbow coalitions champion multicultural representation and social integration.
Governing Strategies and Coalition Dynamics
Left-wing coalitions prioritize progressive policies such as social welfare expansion, labor rights, and environmental reforms, often requiring consensus-building among diverse party ideologies to maintain unity. Rainbow coalitions integrate a broader spectrum of interest groups, including racial, ethnic, and social minorities, emphasizing inclusion and representation through power-sharing arrangements and negotiated policy platforms. Both coalition types rely on strategic compromise and coalition discipline to sustain governance, yet rainbow coalitions typically face more complex dynamics due to their heterogeneous membership and intersectional focus.
Electoral Performance and Voter Base
The Left-wing coalition demonstrates strong electoral performance by appealing primarily to progressive voters, labor unions, and younger demographics, often securing significant seats in urban and industrial regions. The Rainbow coalition, characterized by its diverse multi-ethnic and multicultural voter base, achieves success by uniting marginalized communities and fostering cross-cultural solidarity, which broadens its appeal across various social strata. Both coalitions capitalize on social justice and equality themes, but the Left-wing coalition tends to dominate in working-class districts while the Rainbow coalition garners support in ethnically diverse, metropolitan areas.
Challenges and Internal Conflicts
Left-wing coalitions often face challenges such as ideological disparities among socialist, communist, and social-democratic members, leading to internal conflicts over policy priorities and governance strategies. Rainbow coalitions, typically comprising diverse racial, ethnic, and progressive groups, encounter difficulties managing varied cultural perspectives and conflicting social justice agendas, which can strain unity and decision-making. Both coalition types struggle with balancing inclusive representation and effective cohesion, often resulting in factionalism and weakened political influence.
Impact on National Politics
Left-wing coalitions often unify progressive parties to influence national policies on social welfare, labor rights, and environmental reforms, shaping legislative agendas significantly. Rainbow coalitions, characterized by diverse groups across ethnic, social, and political spectra, drive inclusive policymaking and promote social equity, impacting national political dynamics through broader representation. Both coalitions reshape power structures by mobilizing marginalized voices and altering legislative priorities within national governance.
Future Prospects and Emerging Trends
The Left-wing coalition is expected to emphasize progressive economic reforms and environmental policies, leveraging growing public demand for social justice and climate action. The Rainbow coalition, known for its broader inclusivity across racial, ethnic, and social groups, is likely to advance intersectional policies that reflect demographic shifts and increasing calls for representation. Emerging trends indicate both coalitions will harness digital activism and youth engagement to shape policy discourse and electoral strategies moving forward.
Left-wing coalition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com