Voter suppression tactics undermine the democratic process by deliberately limiting access to the ballot through measures such as strict ID laws, reduced polling locations, and purging voter rolls. These practices disproportionately affect marginalized communities, eroding trust in the electoral system and skewing election results. Explore the rest of this article to understand the impact of voter suppression and what steps you can take to protect your voting rights.
Table of Comparison
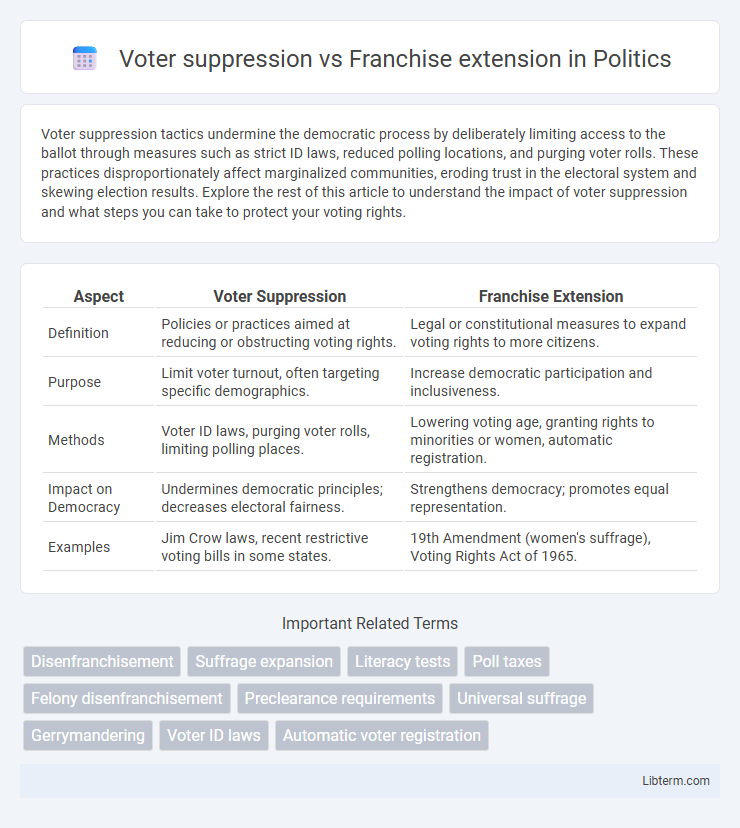
| Aspect | Voter Suppression | Franchise Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policies or practices aimed at reducing or obstructing voting rights. | Legal or constitutional measures to expand voting rights to more citizens. |
| Purpose | Limit voter turnout, often targeting specific demographics. | Increase democratic participation and inclusiveness. |
| Methods | Voter ID laws, purging voter rolls, limiting polling places. | Lowering voting age, granting rights to minorities or women, automatic registration. |
| Impact on Democracy | Undermines democratic principles; decreases electoral fairness. | Strengthens democracy; promotes equal representation. |
| Examples | Jim Crow laws, recent restrictive voting bills in some states. | 19th Amendment (women's suffrage), Voting Rights Act of 1965. |
Understanding Voter Suppression: Definition and Tactics
Voter suppression refers to strategies and tactics designed to discourage or prevent specific groups of people from voting, often targeting minorities, low-income individuals, and young voters. Common methods include strict voter ID laws, purging voter rolls, limited polling locations, and misinformation campaigns that confuse or intimidate potential voters. Understanding these tactics is essential to recognizing how they undermine democratic participation and contrast with franchise extension efforts that seek to broaden electoral inclusion.
The Evolution of Franchise Extension in Democracy
The evolution of franchise extension in democracy reflects a continuous expansion of voting rights, moving from property-based and gender-restricted systems to universal suffrage including marginalized groups such as women and minorities. Legislative milestones like the 19th Amendment in the United States and the Representation of the People Act 1918 in the UK exemplify this progression toward inclusivity. Despite these advances, voter suppression tactics--such as literacy tests, poll taxes, and gerrymandering--persistently challenge equitable participation in democratic processes.
Historical Context: Key Moments in Voter Access
Historical voter suppression tactics such as poll taxes, literacy tests, and grandfather clauses systematically disenfranchised African Americans and low-income citizens, especially in the Southern United States during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Landmark legislative acts like the Voting Rights Act of 1965 and the 24th Amendment abolished discriminatory barriers, significantly extending franchise access and protecting voting rights. Despite progress, ongoing challenges like voter ID laws and gerrymandering reflect the continuing struggle to balance voter suppression and franchise extension in American democracy.
Modern Forms of Voter Suppression
Modern forms of voter suppression include strict voter ID laws, purging of voter rolls, and limited polling locations that disproportionately affect minority and low-income voters. These tactics contrast with franchise extension efforts aimed at expanding voter access through mail-in ballots, same-day registration, and automatic voter registration. The persistent debate centers on ensuring electoral integrity while protecting the fundamental right to vote for all eligible citizens.
Legislative Efforts to Expand the Franchise
Legislative efforts to expand the franchise have historically focused on dismantling barriers such as literacy tests, poll taxes, and discriminatory registration practices that suppressed minority and low-income voters. Key laws like the Voting Rights Act of 1965 and the 26th Amendment, which lowered the voting age to 18, significantly broadened voter participation by legally prohibiting disenfranchisement tactics. Ongoing legislative initiatives continue to target voter suppression through measures like automatic voter registration and expanded early voting access, aiming to ensure equitable electoral participation.
Impact of Voter ID Laws on Electoral Participation
Voter ID laws have been linked to decreased voter turnout, particularly among minority, low-income, and elderly populations who face challenges obtaining acceptable identification. These laws contribute to voter suppression by creating barriers that disproportionately affect marginalized communities, undermining efforts to extend the franchise to broader voter demographics. Research indicates that states with stringent voter ID requirements experience statistically significant reductions in electoral participation compared to states with more inclusive voting policies.
Demographic Groups Most Affected by Voting Policies
Voter suppression disproportionately impacts minority groups such as African Americans, Latinx, and Native Americans through measures like strict ID laws, purging voter rolls, and limited polling locations. Conversely, franchise extension policies aim to increase electoral participation by removing barriers for marginalized populations, including young voters, low-income individuals, and persons with disabilities. These contrasting approaches significantly influence voter turnout and representation among historically underrepresented demographic groups.
Legal Battles Shaping Voter Rights
Legal battles shaping voter rights have centered on the tension between voter suppression tactics and franchise extension efforts, with landmark cases such as Shelby County v. Holder redefining the enforcement of the Voting Rights Act. Courts have frequently addressed issues like voter ID laws, purging of voter rolls, and restrictions on early voting, assessing their impact on minority enfranchisement. Key legislation and judicial decisions continue to influence the balance between preventing fraud and ensuring equal access to the ballot.
Technology’s Role in Voter Suppression and Inclusion
Technology plays a critical role in both voter suppression and franchise extension by shaping access and barriers to voting. Advanced data analytics, biometric systems, and digital ID verification can be manipulated to disenfranchise marginalized groups through targeted purging and restrictive identification requirements. Conversely, innovations like online voter registration, mobile voting apps, and electronic poll books enhance voter inclusion by simplifying participation and expanding outreach to underserved communities.
Future Directions: Balancing Election Integrity and Accessibility
Future directions in election policy emphasize integrating advanced voter identification technologies with expanded access methods such as mail-in and early voting to enhance both election integrity and accessibility. Legislative efforts focus on harmonizing strict security protocols with inclusive measures like automatic voter registration and expanded polling locations to reduce disenfranchisement. Emerging data analytics and blockchain applications promise transparent, secure election processes that safeguard voter rights while minimizing fraud risks.
Voter suppression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com