Subpoena power grants legal authorities the ability to compel individuals or organizations to provide testimony or produce evidence crucial to investigations or court cases. This mechanism ensures the enforcement of justice by preventing withholding of information essential for legal proceedings. Explore the rest of the article to understand how subpoena power impacts your rights and legal responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
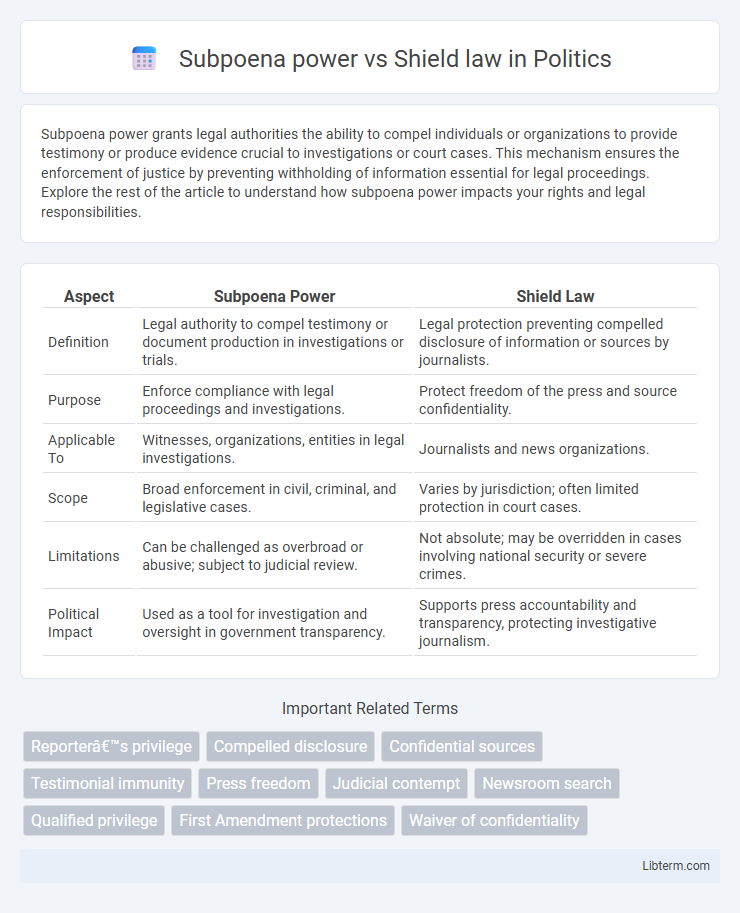
| Aspect | Subpoena Power | Shield Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal authority to compel testimony or document production in investigations or trials. | Legal protection preventing compelled disclosure of information or sources by journalists. |
| Purpose | Enforce compliance with legal proceedings and investigations. | Protect freedom of the press and source confidentiality. |
| Applicable To | Witnesses, organizations, entities in legal investigations. | Journalists and news organizations. |
| Scope | Broad enforcement in civil, criminal, and legislative cases. | Varies by jurisdiction; often limited protection in court cases. |
| Limitations | Can be challenged as overbroad or abusive; subject to judicial review. | Not absolute; may be overridden in cases involving national security or severe crimes. |
| Political Impact | Used as a tool for investigation and oversight in government transparency. | Supports press accountability and transparency, protecting investigative journalism. |
Introduction to Subpoena Power and Shield Laws
Subpoena power grants legal authorities the ability to compel individuals or entities to provide testimony, documents, or evidence relevant to an investigation or trial. Shield laws protect journalists from being forced to disclose confidential sources or unpublished information in legal proceedings, ensuring press freedom and safeguarding the flow of information. Balancing subpoena power with shield laws involves navigating the tension between law enforcement interests and the protection of journalistic integrity.
Historical Background of Subpoena Power
The historical background of subpoena power traces back to English common law, where courts developed the authority to compel testimony and documents essential for judicial proceedings. This power evolved to ensure the enforcement of legal processes by requiring individuals to appear or produce evidence under penalty of contempt. Over time, subpoena power became a fundamental tool in the American legal system for maintaining the integrity of judicial investigations and trials.
The Evolution of Shield Laws in Journalism
The evolution of shield laws in journalism highlights growing legal protections that journalists possess against subpoenas demanding source disclosures. Shield laws, varying by state, aim to balance the subpoena power of courts with reporters' rights to maintain confidentiality, fostering investigative journalism. As courts increasingly recognize the critical role of press freedom, shield laws have expanded, reinforcing journalists' ability to resist subpoenas and safeguard anonymous sources.
Legal Definitions: Subpoena Power vs Shield Law
Subpoena power refers to the legal authority to compel individuals or organizations to provide testimony, documents, or evidence in judicial or legislative proceedings. Shield laws protect journalists from being compelled to reveal confidential sources or unpublished information in legal cases, serving as a legal defense against subpoenas. The key distinction lies in subpoena power enforcing disclosure, while shield laws limit disclosure to preserve press freedom and confidentiality.
Key Differences Between Subpoena Power and Shield Law
Subpoena power authorizes courts or government agencies to compel individuals or organizations to produce evidence or testify, often used in legal investigations and trials. Shield law protects journalists from being forced to disclose confidential sources or unpublished information, ensuring press freedom and safeguarding source anonymity. The key difference lies in subpoena power enforcing disclosure for legal proceedings, while shield law limits this enforcement to protect journalistic privilege.
Landmark Court Cases Shaping Both Doctrines
The landmark court cases of Branzburg v. Hayes (1972) and New York Times Co. v. United States (1971) significantly shaped subpoena power and shield laws in the United States. Branzburg v. Hayes affirmed the government's subpoena power over journalists, emphasizing the need for testimony in criminal investigations, while shield laws, inspired by cases like Cohen v. Cowles Media Co. (1991), protect journalists from revealing confidential sources, balancing press freedom and legal obligations. These pivotal rulings continue to influence the ongoing legal dialogue regarding the limits of subpoena power and the scope of shield law protections in contemporary media law.
Constitutional Implications: First Amendment Perspectives
Subpoena power grants legal authority to compel individuals or entities to provide evidence or testimony, potentially conflicting with First Amendment protections of free speech and press. Shield laws exist to protect journalists from being forced to disclose confidential sources, serving as a critical safeguard for press freedom and informed public discourse under constitutional principles. Balancing subpoena power against shield laws remains a complex constitutional issue, as courts strive to uphold both government interests and the fundamental rights guaranteed by the First Amendment.
Balancing Press Freedom and Legal Accountability
Subpoena power enables courts to compel journalists to disclose information or testify, aiming to uphold legal accountability and justice. Shield laws protect reporters from being forced to reveal confidential sources or unpublished material, preserving press freedom and confidentiality. Balancing these forces requires nuanced legal frameworks that safeguard the public's right to know while ensuring that journalistic privilege does not obstruct legitimate legal processes.
Challenges Journalists Face Under Subpoena Power
Journalists face significant challenges under subpoena power, as it compels the disclosure of confidential sources and unpublished materials, undermining press freedom and source protection. Shield laws, designed to protect journalists from revealing such information, vary widely across jurisdictions, offering inconsistent safeguards. This legal tension creates a precarious environment where reporters risk legal penalties or loss of critical sources, affecting investigative journalism's efficacy.
The Future of Journalistic Protections and Legal Demands
Subpoena power grants courts the authority to compel journalists to disclose sources or unpublished materials, posing significant challenges to press freedom and investigative integrity. Shield laws, enacted in various jurisdictions, provide journalists with legal protection against such demands, aiming to balance the public interest in press disclosure with the necessity of confidential reporting. The future of journalistic protections may depend on expanding comprehensive shield laws and clarifying the limits of subpoena power to safeguard press independence amid evolving digital and legal landscapes.
Subpoena power Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com