Redistricting is the process of redrawing electoral district boundaries to reflect changes in population and maintain equal representation. This practice ensures that political districts are fairly apportioned, influencing election outcomes and political power distribution. Discover more about how redistricting impacts your voting rights and the political landscape in the full article.
Table of Comparison
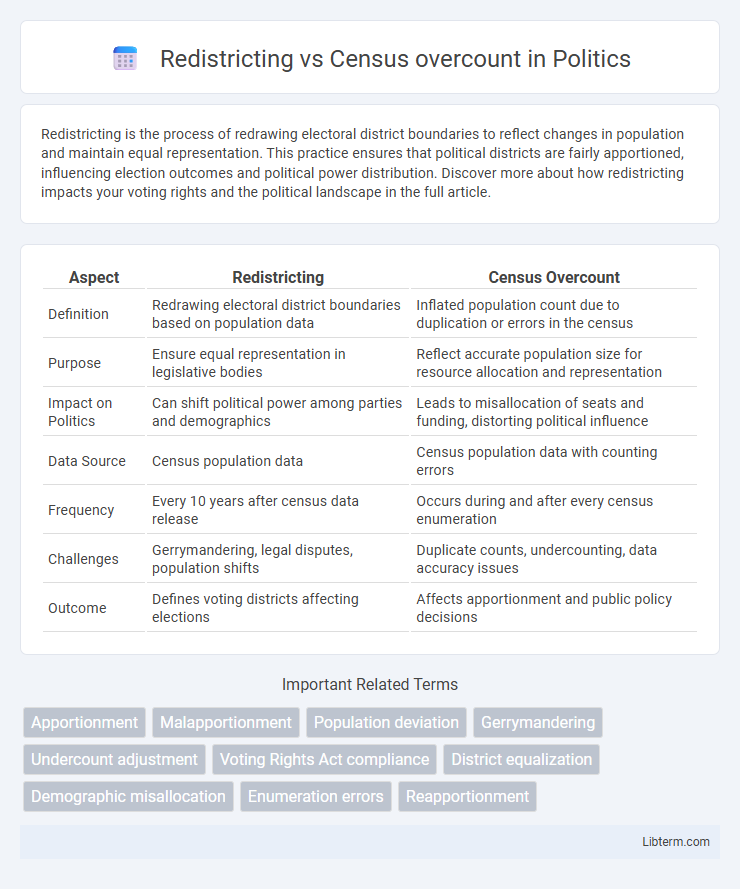
| Aspect | Redistricting | Census Overcount |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Redrawing electoral district boundaries based on population data | Inflated population count due to duplication or errors in the census |
| Purpose | Ensure equal representation in legislative bodies | Reflect accurate population size for resource allocation and representation |
| Impact on Politics | Can shift political power among parties and demographics | Leads to misallocation of seats and funding, distorting political influence |
| Data Source | Census population data | Census population data with counting errors |
| Frequency | Every 10 years after census data release | Occurs during and after every census enumeration |
| Challenges | Gerrymandering, legal disputes, population shifts | Duplicate counts, undercounting, data accuracy issues |
| Outcome | Defines voting districts affecting elections | Affects apportionment and public policy decisions |
Understanding Redistricting: A Foundational Overview
Redistricting involves redrawing electoral district boundaries based on population data collected from the decennial census, ensuring equal representation in legislative bodies. Census overcounts can distort this process by inflating population figures, potentially skewing district lines and affecting political power distribution. Accurate census data is essential for fair redistricting, making the interplay between these elements crucial for maintaining democratic integrity.
What Is Census Overcount? Key Definitions Explained
Census overcount occurs when individuals are counted more than once or included erroneously in the population data during the decennial census, leading to inflated population figures. This inaccuracy can impact redistricting by skewing the allocation of legislative seats and federal funding, as districts may appear to have more residents than actually exist. Understanding census overcount is essential for ensuring fair political representation and precise demographic analysis in the redistricting process.
The Interconnection Between Redistricting and Census Data
Redistricting relies heavily on accurate census data to ensure fair political representation and equitable resource allocation. Census overcounts can lead to distorted population figures, resulting in redistricting plans that misrepresent community sizes and demographics. Ensuring precise census counts is critical to maintaining the integrity of the redistricting process and upholding democratic principles.
Causes and Consequences of Census Overcounts
Census overcounts often result from duplication of individuals, such as counting people at both their home and college address or including deceased persons due to outdated records. These overcounts can lead to distorted population data, impacting redistricting by inflating representation in certain districts and skewing the allocation of federal funds. Consequently, overcounts undermine the principle of equal representation, potentially causing legal challenges and misallocation of public resources.
Impact of Census Overcount on Political Representation
Census overcount can distort redistricting by inflating population figures, leading to unequal representation in legislative districts. When certain areas are overcounted, those districts may receive more political power and resources than warranted, undermining fair representation. Accurate population data from the decennial census is critical to ensure balanced redistricting that reflects true demographic distribution and maintains political equity.
How Redistricting Relies on Accurate Census Results
Redistricting depends heavily on precise census data to ensure equitable representation by accurately reflecting population shifts and demographic changes within jurisdictions. Inaccurate census counts, such as overcounts, can distort district boundaries, leading to unequal voter representation and potential legal challenges. Accurate census results are critical for creating fair electoral districts that uphold the principle of "one person, one vote.
Legal Challenges: Redistricting and Census Miscounts
Legal challenges surrounding redistricting often arise due to allegations of census overcounts or undercounts, which can distort population data critical for equitable district mapping. Courts scrutinize claims that miscounts infringe on the principle of "one person, one vote," impacting political representation and federal resource allocation. Litigation typically involves federal statutes like the Voting Rights Act and constitutional provisions to address census-related inaccuracies affecting redistricting outcomes.
Historical Examples: Redistricting Affected by Census Overcount
Historical examples illustrate how census overcounts have significantly influenced redistricting decisions, notably the 1990 U.S. Census, where overcounts in states like California led to delayed and contentious redistricting processes. The overcount inflated population figures, resulting in misapportioned legislative districts and challenges in achieving equitable representation. These cases underscore the critical impact of accurate census data on the legitimacy and fairness of redistricting outcomes.
Policy Solutions for Minimizing Census Overcount
Policy solutions for minimizing census overcount include implementing advanced address canvassing techniques, enhancing outreach in hard-to-count communities, and utilizing administrative records to verify and cross-check census data. Improved training for enumerators and investment in real-time data monitoring systems can further reduce duplicate counting. Legislators often support funding for independent oversight bodies to audit census methods and ensure accuracy in redistricting processes based on reliable population counts.
Future Implications: Redistricting Amid Census Accuracy Concerns
Redistricting processes increasingly face challenges due to potential census overcounts, which threaten the equitable allocation of legislative districts. Inaccurate census data can distort population representation, leading to skewed political power and resource distribution for the next decade. Future redistricting efforts must incorporate advanced demographic analysis and independent verification methods to mitigate these risks and uphold electoral fairness.
Redistricting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com