Merit-based selection prioritizes candidates' skills, qualifications, and performance over subjective factors, ensuring the most capable individuals are chosen. This approach promotes fairness and efficiency in recruitment, leading to better organizational outcomes. Discover how merit-based selection can transform your hiring process by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
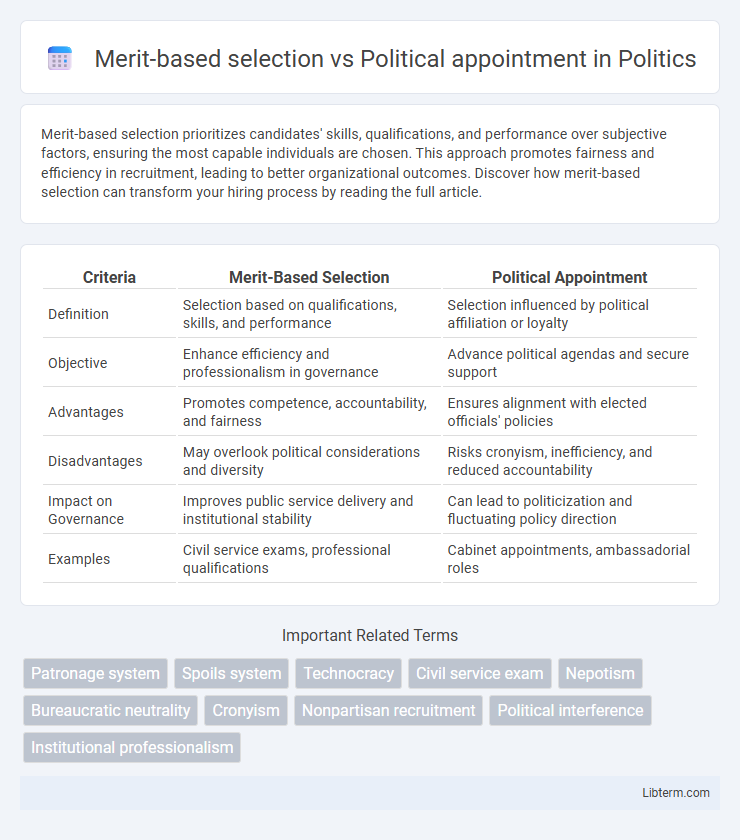
| Criteria | Merit-Based Selection | Political Appointment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Selection based on qualifications, skills, and performance | Selection influenced by political affiliation or loyalty |
| Objective | Enhance efficiency and professionalism in governance | Advance political agendas and secure support |
| Advantages | Promotes competence, accountability, and fairness | Ensures alignment with elected officials' policies |
| Disadvantages | May overlook political considerations and diversity | Risks cronyism, inefficiency, and reduced accountability |
| Impact on Governance | Improves public service delivery and institutional stability | Can lead to politicization and fluctuating policy direction |
| Examples | Civil service exams, professional qualifications | Cabinet appointments, ambassadorial roles |
Introduction to Merit-based Selection and Political Appointment
Merit-based selection emphasizes qualifications, skills, and performance as primary criteria for hiring or promotion within public service, ensuring competence and fairness in the workforce. Political appointment involves selecting individuals based on loyalty, affiliations, or alignment with political leaders, often prioritizing trust and policy alignment over technical expertise. Understanding these contrasting methods highlights the balance between professional meritocracy and political influence in government staffing decisions.
Defining Merit-based Selection
Merit-based selection refers to a system of appointment where candidates are chosen based on their qualifications, skills, and performance rather than political connections or affiliations. This approach prioritizes objective criteria such as education, experience, and competency assessments to ensure the most capable individuals fill public service positions. By emphasizing merit, organizations aim to enhance efficiency, reduce favoritism, and promote fairness in recruitment processes.
Understanding Political Appointment
Political appointment involves selecting individuals for government positions based on loyalty, connections, or political considerations rather than qualifications or merit. This process often prioritizes alignment with the appointing authority's agenda, which can influence policy implementation and governance effectiveness. Understanding political appointments requires analyzing their impact on administrative competence and potential risks of patronage or favoritism.
Historical Background of Both Systems
Merit-based selection systems trace back to ancient China's imperial examinations, designed to appoint officials based on ability and knowledge rather than birth or favoritism, influencing modern bureaucratic structures worldwide. Political appointments have roots in patronage systems, such as the spoils system in 19th-century United States, where government positions were awarded to loyal supporters and party affiliates. The Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act of 1883 marked a significant shift toward meritocracy by introducing competitive exams and reducing patronage in federal employment.
Pros and Cons of Merit-based Selection
Merit-based selection ensures qualified candidates are chosen through standardized evaluations, promoting efficiency and reducing nepotism in public service. This method enhances transparency and accountability by emphasizing skills and experience over political loyalty. However, it may limit diversity in viewpoints and slow decision-making processes due to rigid criteria and bureaucratic procedures.
Pros and Cons of Political Appointment
Political appointments enable leaders to ensure loyalty and alignment with policy goals, fostering cohesive governance and rapid decision-making. However, this approach risks favoritism, reduced meritocracy, and potential inefficiency due to selecting individuals based on political connections rather than expertise. Such appointments can undermine public trust and hinder institutional professionalism by prioritizing allegiance over qualifications.
Impact on Organizational Efficiency
Merit-based selection significantly enhances organizational efficiency by ensuring that positions are filled by qualified individuals with relevant skills and expertise, leading to higher productivity and better decision-making. Political appointments often result in placements based on loyalty rather than competence, which can decrease operational effectiveness and increase turnover. Organizations utilizing merit-based systems typically experience improved morale and streamlined workflows, fostering a culture of accountability and performance.
Implications for Public Trust and Accountability
Merit-based selection enhances public trust by promoting transparency and ensuring that qualified individuals fill key public service roles, which leads to improved accountability through performance-based evaluations. In contrast, political appointments often risk eroding public confidence due to perceptions of favoritism and potential conflicts of interest, undermining the integrity of decision-making processes. The choice between these methods significantly impacts governance quality and citizen engagement, with merit-based systems fostering a more accountable and trustworthy public sector.
Case Studies: Global Practices and Outcomes
Merit-based selection systems in global case studies, such as Singapore's Civil Service and New Zealand's State Services Commission, demonstrate higher efficiency, transparency, and public trust compared to political appointments seen in countries like Venezuela and Zimbabwe, where patronage often undermines governance quality. Empirical data reveal that meritocratic approaches correlate with improved policy implementation and reduced corruption, while political appointments tend to prioritize loyalty over competence, impacting institutional integrity. Comparative analyses emphasize the benefits of merit-based recruitment in achieving sustainable development and responsive public administration globally.
Future Trends and Recommendations
Future trends in merit-based selection emphasize the integration of advanced data analytics and AI to enhance objectivity and efficiency in evaluating candidates. Political appointments may face increasing scrutiny as public demand grows for transparency and competence, prompting hybrid models that combine merit criteria with political considerations. Recommendations include adopting standardized assessment frameworks and fostering independent oversight bodies to ensure fairness and adaptability in evolving governance environments.
Merit-based selection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com