A censure motion serves as a formal expression of disapproval against a public official or member of an organization for misconduct or failure to meet obligations. It typically involves a parliamentary or corporate procedure that condemns the action without removing the individual from their position. Discover the detailed process and implications of a censure motion to understand how it may affect Your role or interest in governance.
Table of Comparison
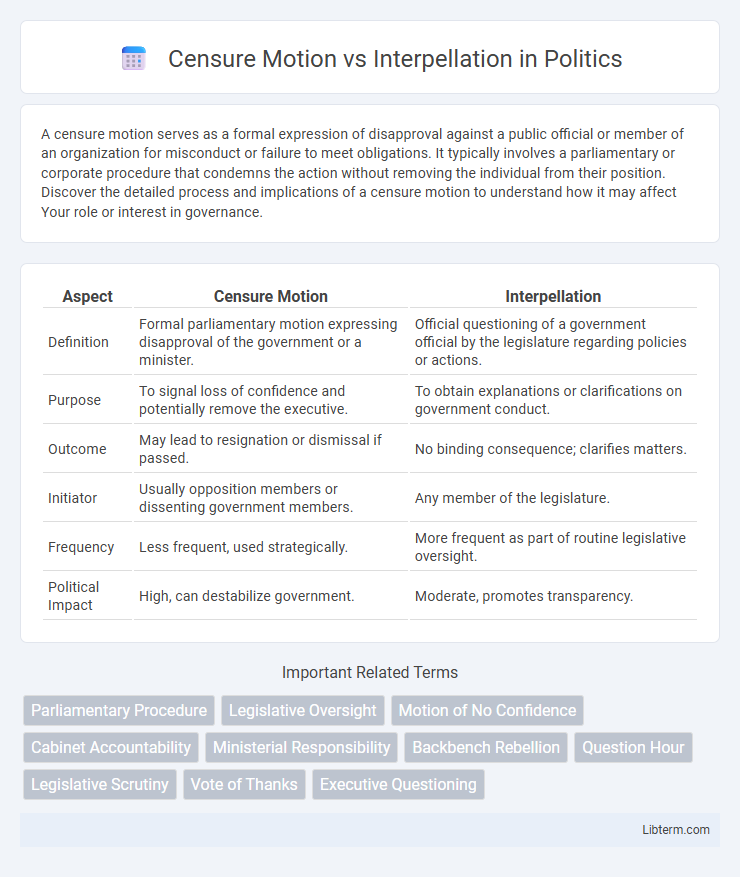
| Aspect | Censure Motion | Interpellation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal parliamentary motion expressing disapproval of the government or a minister. | Official questioning of a government official by the legislature regarding policies or actions. |
| Purpose | To signal loss of confidence and potentially remove the executive. | To obtain explanations or clarifications on government conduct. |
| Outcome | May lead to resignation or dismissal if passed. | No binding consequence; clarifies matters. |
| Initiator | Usually opposition members or dissenting government members. | Any member of the legislature. |
| Frequency | Less frequent, used strategically. | More frequent as part of routine legislative oversight. |
| Political Impact | High, can destabilize government. | Moderate, promotes transparency. |
Introduction to Parliamentary Oversight Mechanisms
Censure Motion and Interpellation are key parliamentary oversight mechanisms enabling legislatures to hold the executive accountable. A Censure Motion formally expresses disapproval of a government official's actions, potentially leading to resignation or dismissal. Interpellation involves questioning government members to obtain information or explanations, fostering transparency and informed decision-making.
Defining Censure Motion
A censure motion is a formal parliamentary procedure used to express strong disapproval or condemnation of a government official's actions or policies. It directly targets the individual's conduct and requires a majority vote to pass, which may lead to consequences such as resignation or loss of confidence. Unlike interpellation, which primarily seeks detailed explanations or clarifications from a minister, a censure motion functions as a political reprimand and vote of no confidence.
Defining Interpellation
Interpellation is a parliamentary procedure that allows legislators to formally question government officials, typically ministers, regarding their policies or administrative actions. This mechanism ensures executive accountability by compelling detailed explanations and clarifications within a specified timeframe. Unlike a censure motion, which directly challenges the confidence in a government official or body, interpellation functions primarily as an investigative tool to scrutinize decisions and promote transparency in governance.
Key Objectives: Censure Motion vs Interpellation
A Censure Motion aims to formally express disapproval or condemnation of a government official's actions, often leading to political consequences such as resignation or removal from office. Interpellation is a parliamentary procedure designed to question and seek explanations from government officials regarding specific policies or administrative actions, promoting transparency and accountability. Both mechanisms serve as tools for legislative oversight but differ in their focus: Censure motions emphasize punitive measures, while interpellations prioritize information gathering and clarification.
Legal Basis and Procedures
A Censure Motion is a formal resolution passed by a legislative body to express strong disapproval of a government official's conduct, grounded in parliamentary rules such as the Rules of Procedure of the House of Representatives or Senate. Its procedure typically involves filing the motion, notification to the concerned official, and a plenary vote requiring a majority to adopt the censure. Interpellation, governed by similar legislative rules, entails a formal process where legislators question a government official or agency to obtain information or explanations, initiated by a written request followed by a specified period for response and subsequent debates.
Differences in Implementation
Censure motion is a formal process where the legislature expresses strong disapproval of a government official's actions, often leading to potential removal from office, while interpellation involves questioning a government member to clarify policies or decisions without immediate punitive consequences. Censure motions require a majority vote and are typically triggered by misconduct or serious policy disagreements, whereas interpellations serve as tools for accountability and transparency through direct questioning during parliamentary sessions. The timing and procedural rules differ; censure motions follow strict parliamentary protocols with possible debates before voting, whereas interpellations allow for dialogue and explanatory responses within a fixed timeframe.
Impact on Government Stability
A Censure Motion directly challenges the government's legitimacy by expressing formal disapproval, potentially leading to the resignation of ministers or the entire cabinet, thereby destabilizing the ruling administration. Interpellation involves questioning government officials about policies or decisions without necessarily threatening their position, serving more as a tool for accountability than immediate government upheaval. While both mechanisms hold the government accountable, a Censure Motion carries a higher risk of triggering political instability due to its binding consequences.
Case Studies: Censure Motion and Interpellation in Action
In the Philippine House of Representatives, the 2018 censure motion against Defense Secretary Delfin Lorenzana illustrated how this tool publicly reprimands officials for alleged misconduct, though it lacks binding consequences. In contrast, the 2019 interpellation of the Department of Budget and Management highlighted the process of detailed questioning and accountability through legislative sessions, often influencing policy decisions. These cases demonstrate censure motions serve as formal denunciations, while interpellations function as investigative dialogues promoting transparency and responsiveness.
Pros and Cons of Each Mechanism
Censure Motion allows legislators to formally express disapproval of a government official, promoting accountability but potentially leading to political instability or partisan conflicts. Interpellation requires officials to respond to specific questions, fostering transparency and detailed scrutiny yet may result in prolonged debates and delay legislative processes. Both mechanisms serve as tools for oversight, but balancing their use is essential to maintain effective governance and avoid excessive governmental disruption.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Oversight Tool
Selecting the appropriate oversight tool depends on the gravity of the issue and the desired impact. Censure Motion serves as a formal reprimand that holds officials accountable, while Interpellation facilitates thorough questioning and information gathering. Effective governance requires balancing these mechanisms to ensure transparency and uphold institutional integrity.
Censure Motion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com