The war cabinet played a critical role in strategic decision-making during times of conflict, consolidating military, political, and economic resources to ensure efficient governance. Understanding its structure and functions reveals how leaders balanced complex challenges to maintain national security. Explore the rest of the article to discover how the war cabinet influenced pivotal moments in history and shaped your nation's wartime policies.
Table of Comparison
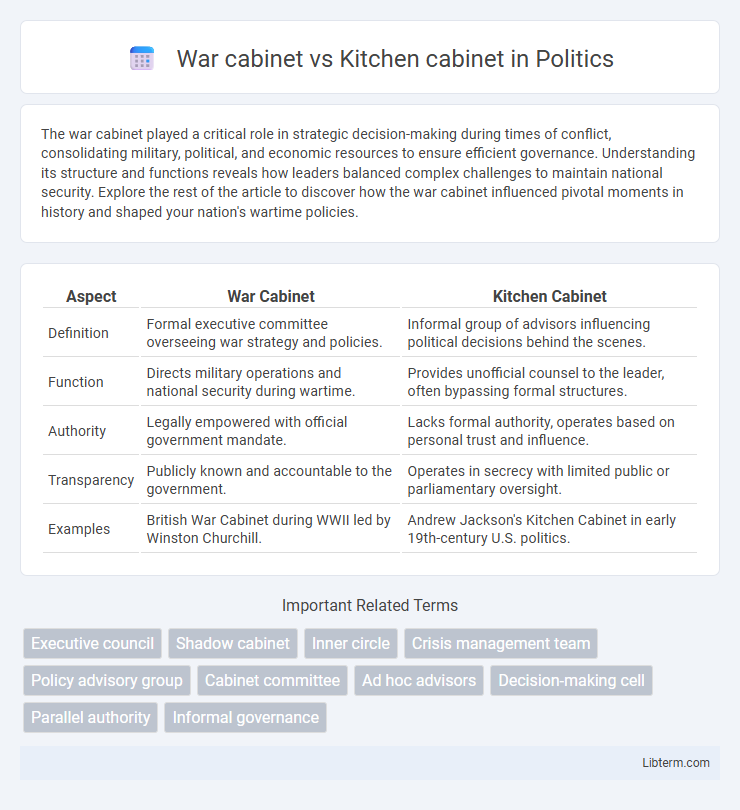
| Aspect | War Cabinet | Kitchen Cabinet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal executive committee overseeing war strategy and policies. | Informal group of advisors influencing political decisions behind the scenes. |
| Function | Directs military operations and national security during wartime. | Provides unofficial counsel to the leader, often bypassing formal structures. |
| Authority | Legally empowered with official government mandate. | Lacks formal authority, operates based on personal trust and influence. |
| Transparency | Publicly known and accountable to the government. | Operates in secrecy with limited public or parliamentary oversight. |
| Examples | British War Cabinet during WWII led by Winston Churchill. | Andrew Jackson's Kitchen Cabinet in early 19th-century U.S. politics. |
Introduction to War Cabinet and Kitchen Cabinet
The War Cabinet refers to a formal group of senior government officials and military leaders established during wartime to coordinate strategy and decision-making at the highest level. It operates with official authority and meets regularly to address urgent national security issues, often excluding the broader cabinet. In contrast, the Kitchen Cabinet is an informal advisory group consisting of trusted friends or unofficial advisors who influence a leader's decisions behind the scenes without official status or formal structure.
Historical Origins of the War Cabinet
The War Cabinet originated during World War I as a smaller, more focused group within the British government to streamline decision-making on military and strategic matters, contrasting with the larger traditional cabinet. It was first established by Prime Minister David Lloyd George in 1916 to increase efficiency and secrecy in wartime governance. The term "Kitchen Cabinet," in contrast, refers to an informal group of advisors outside the official cabinet, notably used during Andrew Jackson's presidency in the United States, emphasizing close personal influence rather than formal war-related responsibilities.
Evolution of the Kitchen Cabinet Concept
The concept of the kitchen cabinet evolved from informal advisory groups, contrasting with the formal structure of the War Cabinet established during wartime for strategic decision-making. Unlike the War Cabinet's official status and defined responsibilities, the Kitchen Cabinet emerged as a private circle of trusted political advisors influencing policy behind the scenes. This evolution reflects a shift toward personalized governance, where informal consultations supplement formal political frameworks.
Composition and Structure: War Cabinet vs Kitchen Cabinet
The War Cabinet is a formal group usually composed of senior government ministers, military leaders, and key advisors, structured to make strategic decisions during wartime. The Kitchen Cabinet refers to an informal group of trusted advisors or friends who influence the leader outside official channels, lacking a defined composition or formal structure. The War Cabinet operates through official meetings with documented agendas, while the Kitchen Cabinet relies on private, informal consultations without formal procedures.
Roles and Functions in Governance
The War Cabinet, primarily established during wartime, concentrates on strategic military decisions and national security policies, enabling swift, focused, and confidential governance in crisis situations. The Kitchen Cabinet, an informal advisory group, influences broader political strategies and executive decisions through close personal relationships with the leader, often bypassing official cabinet channels. While the War Cabinet maintains a formal, crisis-driven role focused on defense governance, the Kitchen Cabinet operates behind the scenes, shaping policy and political tactics in peacetime governance.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
War cabinets centralize decision-making authority within a small, officially appointed group of key government and military leaders to ensure swift, coordinated responses during national crises. Kitchen cabinets consist of informal advisors who influence decisions through personal relationships rather than formal appointments, often leading to less transparent and unstructured decision processes. The war cabinet's structured approach enhances accountability and strategic clarity, while the kitchen cabinet's informal nature can result in flexible but inconsistent policy guidance.
Influence on National Policy
The War Cabinet, established during times of crisis such as World War II, held formal authority with direct influence on national policy through official government channels, shaping military strategy and critical wartime decisions. In contrast, the Kitchen Cabinet consisted of informal advisors who influenced national policy through personal relationships and behind-the-scenes counsel, often affecting political decisions without official mandates. While the War Cabinet's role was institutionalized and transparent, the Kitchen Cabinet wielded its power through discreet persuasion, impacting domestic and foreign policy in less visible but significant ways.
Notable Examples in Political History
The War Cabinet of Winston Churchill during World War II is a notable example of a formal, high-level decision-making body exclusively handling wartime strategy, including key figures like Clement Attlee and Anthony Eden. In contrast, the Kitchen Cabinet refers to President Andrew Jackson's informal group of advisors who influenced policy outside traditional government channels, with members such as Martin Van Buren and Amos Kendall. These examples illustrate differences in official authority and the role of informal influence within political leadership structures.
Advantages and Criticisms of Both Cabinets
War cabinets concentrate decision-making among a small group, ensuring swift and unified responses during crises, which enhances operational efficiency and security. Kitchen cabinets, as informal advisory groups, offer flexibility and diverse perspectives but often face criticism for lack of transparency, accountability, and potential bypassing of formal governmental processes. Both frameworks reflect trade-offs between centralized authority and broad-based consultation, affecting governance effectiveness and public trust.
Contemporary Relevance and Impact
The contemporary relevance of the War Cabinet lies in its ability to centralize decision-making during crises, ensuring coordinated military and political strategies critical in global conflict scenarios. In contrast, the Kitchen Cabinet represents informal advisory influence, often shaping executive decisions through trusted personal relationships rather than official institutional frameworks. Both structures impact governance by balancing formal authority with flexible advisory input, affecting policy effectiveness and public accountability in modern administrations.
War cabinet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com