Undecided voters hold significant power in elections as their final choice can sway outcomes in closely contested races. Understanding the motivations and concerns that influence these voters is crucial for political campaigns aiming to secure their support. Discover how undecided voters impact election results and what factors shape their decisions by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
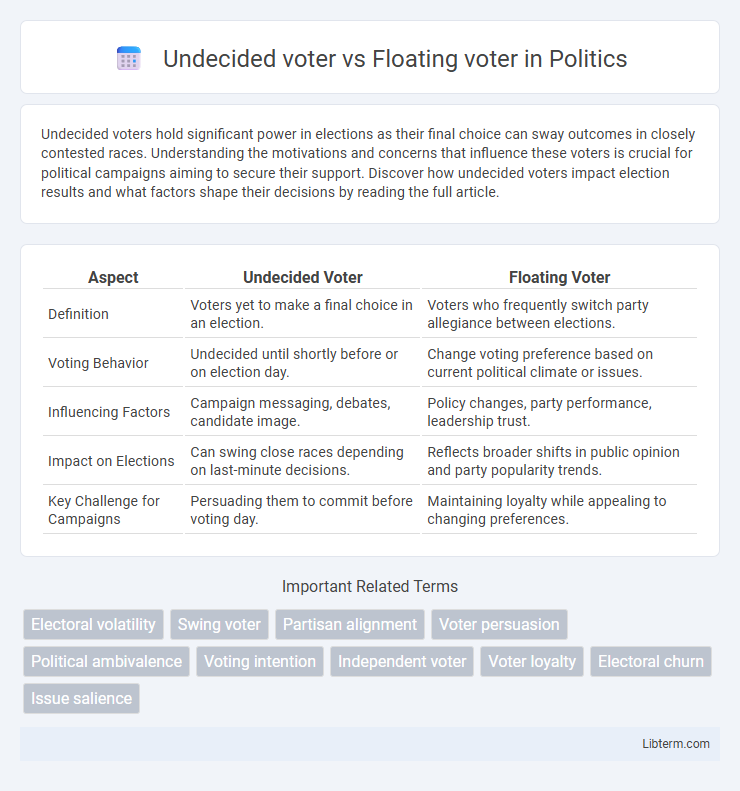
| Aspect | Undecided Voter | Floating Voter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voters yet to make a final choice in an election. | Voters who frequently switch party allegiance between elections. |
| Voting Behavior | Undecided until shortly before or on election day. | Change voting preference based on current political climate or issues. |
| Influencing Factors | Campaign messaging, debates, candidate image. | Policy changes, party performance, leadership trust. |
| Impact on Elections | Can swing close races depending on last-minute decisions. | Reflects broader shifts in public opinion and party popularity trends. |
| Key Challenge for Campaigns | Persuading them to commit before voting day. | Maintaining loyalty while appealing to changing preferences. |
Understanding the Concepts: Undecided Voter vs Floating Voter
Undecided voters have not yet made a firm choice between candidates or parties, often seeking more information before deciding, whereas floating voters may have a preference but switch their vote between elections or candidates based on issues or campaign influence. Understanding the distinction is critical for political strategists aiming to target communications, as undecided voters represent open opportunities while floating voters indicate shifting loyalties. Data from electoral studies shows that floating voters can significantly sway election outcomes, requiring tailored messaging that addresses their specific concerns and motivations.
Defining Undecided Voters: Who Are They?
Undecided voters are individuals who have not yet committed to a specific candidate or political party during an election cycle, often due to insufficient information or conflicting preferences. These voters differ from floating voters, who may switch allegiance between candidates or parties based on campaign dynamics or current issues. Understanding the characteristics and motivations of undecided voters is crucial for political strategists aiming to influence election outcomes.
Characteristics of Floating Voters
Floating voters exhibit high electoral volatility, frequently shifting support between parties based on campaign issues and candidate appeal. Unlike undecided voters who have yet to form a preference, floating voters possess prior voting experience but remain open to persuasion. Their decisive role often influences tight races due to their unpredictable allegiance and sensitivity to political dynamics.
Key Differences Between Undecided and Floating Voters
Undecided voters have not formed a clear preference for any candidate or party, while floating voters have previously supported a candidate but remain open to switching their vote. The key difference lies in voter commitment: undecided voters lack initial allegiance, whereas floating voters exhibit fluctuating loyalty based on campaign events or issues. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for targeted political strategies and predicting electoral outcomes.
Why Voters Remain Undecided: Major Factors
Voters remain undecided primarily due to insufficient information about candidates and policies, leading to uncertainty in making an informed choice. Psychological factors such as ambivalence toward party ideologies and lack of strong partisan loyalty contribute to their indecision. External influences like shifting campaign dynamics, negative media coverage, and conflicting social pressures further perpetuate the undecided voter status compared to floating voters who exhibit more transient electoral preferences.
The Behavior of Floating Voters in Elections
Floating voters exhibit variable electoral behavior characterized by their lack of party allegiance and susceptibility to campaign influences, media narratives, and candidate appeal. Unlike undecided voters who remain neutral until late in the voting process, floating voters actively shift support between parties or candidates across different election cycles, impacting electoral volatility. Their behavior often reflects strategic voting patterns influenced by immediate political contexts, making them critical targets for campaign strategies aiming to sway electoral outcomes.
Impacts on Election Outcomes: Undecided vs. Floating Voters
Undecided voters, who have not committed to any candidate or party, can significantly sway election outcomes as their eventual choice may reflect last-minute shifts influenced by campaign efforts or current events. Floating voters, often characterized by low party loyalty, frequently change preferences across elections, increasing electoral unpredictability and compelling candidates to address diverse, evolving concerns. Both voter types amplify the importance of targeted campaign strategies and real-time voter sentiment analysis in determining electoral success.
Campaign Strategies to Target Undecided and Floating Voters
Campaign strategies targeting undecided and floating voters prioritize personalized messaging and micro-targeting using data analytics to identify voter preferences and concerns. Campaigns deploy tailored communication through digital platforms, emphasizing issue-based outreach and persuasive narratives to address voter skepticism and information gaps. Mobilization efforts include engagement events and direct voter contact to build trust and convert these pivotal groups into committed supporters.
Trends and Statistics: Undecided and Floating Voters Worldwide
Undecided voters, who have not committed to any candidate or party, typically account for 10-20% of the electorate in major democracies, reflecting uncertainty or disengagement in political choices. Floating voters, often numbered between 15-30% in electoral studies, switch allegiances between parties from one election to another, indicating volatility and the impact of campaign strategies. Recent global trends show a gradual decrease in undecided voters due to increased access to information, while floating voter percentages remain significant, especially in emerging democracies and closely contested elections.
Future Implications for Political Parties and Elections
Undecided voters, who have yet to form a firm preference for any candidate or party, represent a crucial demographic for political parties aiming to expand their support base and influence election outcomes. Floating voters, characterized by their shifting allegiances between elections, create volatility in electoral dynamics, prompting parties to continuously adapt strategies and policy platforms to capture their votes. Both groups necessitate targeted engagement efforts and data-driven campaign tactics to secure electoral advantages and shape future political landscapes.
Undecided voter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com