Radical ideas challenge conventional thinking and inspire transformative change across various fields, from technology to social movements. Embracing radical approaches can unlock innovative solutions that traditional methods often overlook. Discover how radical concepts can reshape your perspective and impact your world in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
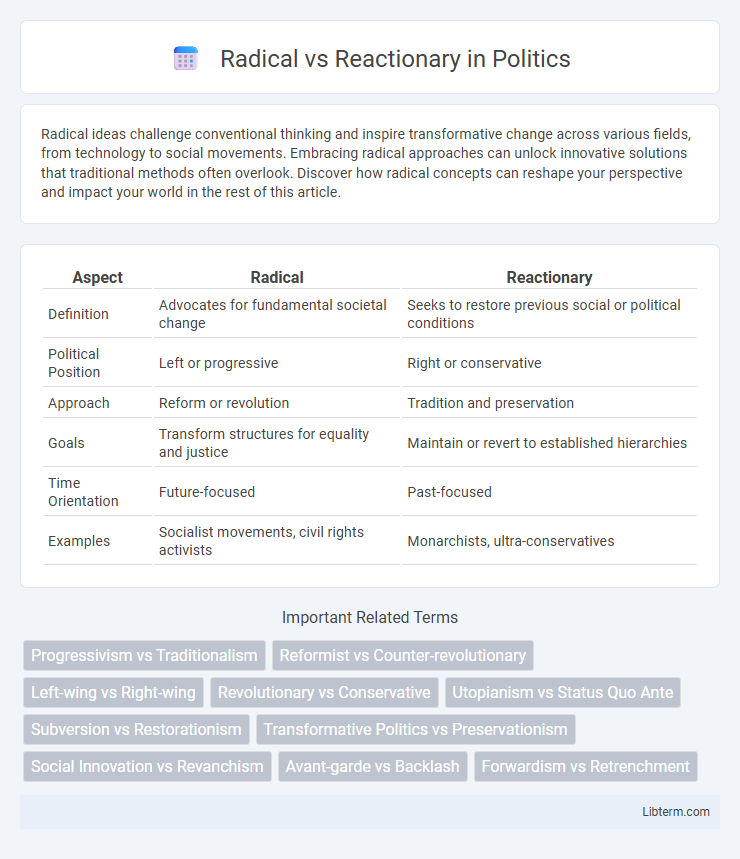
| Aspect | Radical | Reactionary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advocates for fundamental societal change | Seeks to restore previous social or political conditions |
| Political Position | Left or progressive | Right or conservative |
| Approach | Reform or revolution | Tradition and preservation |
| Goals | Transform structures for equality and justice | Maintain or revert to established hierarchies |
| Time Orientation | Future-focused | Past-focused |
| Examples | Socialist movements, civil rights activists | Monarchists, ultra-conservatives |
Understanding Radical and Reactionary Ideologies
Radical ideologies advocate for fundamental and often rapid changes to societal structures, aiming to address perceived injustices by transforming political, economic, or social systems. Reactionary ideologies emphasize a return to traditional values and established social orders, opposing modern reforms and seeking to preserve or restore previous norms. Understanding these positions involves recognizing their contrasting views on progress, stability, and the nature of change within a society.
Historical Origins of Radicalism and Reactionism
Radicalism emerged during the late 18th and early 19th centuries as a response to the inequalities and rigid social hierarchies entrenched by monarchy and aristocracy, advocating for profound political reform and expanded democratic rights. Reactionism rose as a counter-movement aimed at preserving traditional institutions, social orders, and established authority, often seeking to reverse revolutionary changes exemplified during the French Revolution and the conservative restoration in Europe. The ideological origins of radicalism are deeply intertwined with Enlightenment principles, while reactionism finds its roots in the defense of pre-revolutionary structures and conservative thought.
Core Principles of Radical Thought
Radical thought centers on profound social, political, or economic change, challenging existing power structures and advocating for a complete transformation of society. Core principles include equality, justice, and the dismantling of systemic oppression to create a more equitable world. This contrasts with reactionary perspectives, which seek to preserve or return to traditional social orders and resist progressive reforms.
Fundamental Beliefs of Reactionary Movements
Reactionary movements fundamentally believe in restoring traditional social orders and hierarchies perceived as having been lost or undermined by modern changes. They emphasize maintaining established institutions such as monarchy, religion, or class structures, viewing rapid social transformation as harmful. Their ideology often resists progressive reforms, advocating a return to past values and norms to achieve societal stability and order.
Key Differences: Radical vs Reactionary
Radicals advocate for fundamental, systemic change often embracing progressive ideals to transform society, whereas reactionaries seek to restore previous social orders and resist modern reforms. Radicals promote innovation and new political or social structures, while reactionaries emphasize tradition, hierarchy, and the reversal of recent changes. The key difference lies in radicals pushing for forward-thinking change, contrasted with reactionaries aiming to revert to past norms.
Social and Political Impacts of Both Ideologies
Radical ideologies drive rapid and fundamental social change, often challenging existing political structures to promote equality and progressive policies, which can lead to significant societal reforms or unrest. Reactionary ideologies seek to preserve or restore traditional social orders and hierarchical political institutions, frequently resisting progressive movements and fostering social stability or conflict depending on the context. The political impact of radicals often includes revolutionary movements and institutional overhaul, while reactionaries influence policy through conservative governance and preservation of established norms.
Famous Radical and Reactionary Figures
Radical figures such as Che Guevara and Malcolm X championed profound social and political reforms aimed at dismantling established power structures and promoting equality. Reactionary leaders like Joseph de Maistre and Louis XIV staunchly defended traditional hierarchies and resisted revolutionary change to preserve societal order. The ideological clash between radicals and reactionaries revolves around their opposing visions for progress and the role of authority in shaping society.
Modern Examples in Contemporary Politics
Radical movements in contemporary politics, such as the Black Lives Matter protests advocating systemic racial justice reforms, push for transformative changes challenging existing power structures. Reactionary groups, exemplified by far-right organizations opposing immigration and multicultural policies, seek to restore traditional social orders and resist progressive advancements. These modern examples highlight the ongoing ideological clash between progressive transformation and conservative restoration in global political landscapes.
Common Misconceptions about Radicals and Reactionaries
Radicals are often misunderstood as violent extremists, but they primarily seek fundamental change through progressive reforms, while reactionaries aim to restore previous social orders and resist modernization. Misconceptions also portray radicals as inherently disruptive, ignoring their commitment to addressing systemic inequalities and advocating for social justice. Reactionaries are frequently mislabeled as simply conservative, yet their ideology focuses on reversing social progress and reinstating traditional hierarchical structures.
The Future of Radical and Reactionary Movements
Radical movements, driven by progressive ideologies and calls for transformative change, are increasingly adopting technology and social media to mobilize younger generations, shaping the future political landscape. Reactionary groups, rooted in preserving traditional values and resisting change, often engage in cultural preservation and grassroots activism to maintain their influence amid rapid societal shifts. The dynamic interplay between these forces will continue to redefine governance, social norms, and public policies worldwide.
Radical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com