Political rivalry shapes the dynamics of governance, influencing policy decisions and power distribution within nations. Intense competition between parties or leaders often drives innovation but can also lead to polarization and social unrest. Explore the complexities of political rivalry and its impact on your society in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
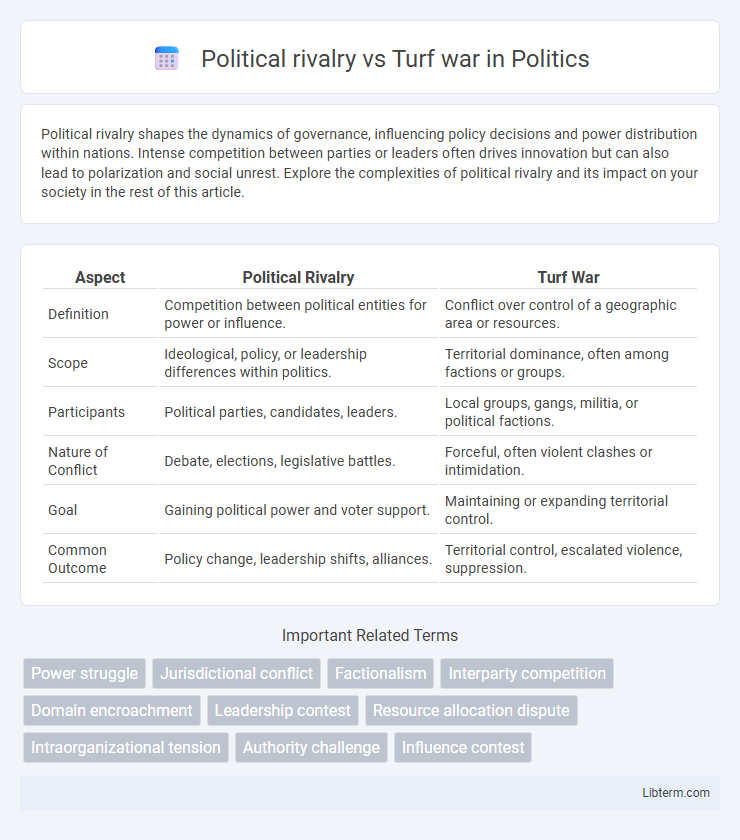
| Aspect | Political Rivalry | Turf War |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Competition between political entities for power or influence. | Conflict over control of a geographic area or resources. |
| Scope | Ideological, policy, or leadership differences within politics. | Territorial dominance, often among factions or groups. |
| Participants | Political parties, candidates, leaders. | Local groups, gangs, militia, or political factions. |
| Nature of Conflict | Debate, elections, legislative battles. | Forceful, often violent clashes or intimidation. |
| Goal | Gaining political power and voter support. | Maintaining or expanding territorial control. |
| Common Outcome | Policy change, leadership shifts, alliances. | Territorial control, escalated violence, suppression. |
Defining Political Rivalry and Turf War
Political rivalry denotes ongoing competition between individuals or parties aiming for power, influence, or control within governmental or organizational settings. Turf war refers to conflicts where groups aggressively defend or expand their territorial boundaries or domains, often in non-political contexts like gangs or corporate sectors. Defining these terms highlights that political rivalry centers on ideological or power struggles, while turf wars emphasize physical or territorial dominance.
Historical Contexts of Political Rivalry
Historical contexts of political rivalry often involve power struggles between competing factions or leaders within a state, such as the conflicts between the Roman Senate and Julius Caesar or the intense competition among feudal lords during medieval Europe. These rivalries are typically driven by ideological differences, quests for legitimacy, or control over governance institutions, distinguishing them from turf wars that are primarily territorial and resource-based. Political rivalries shape the formation of political systems, alliances, and revolutions, highlighting the strategic maneuvering that defines statecraft throughout history.
Turf Wars: Origins and Impacts
Turf wars originate from conflicts over territorial control, often fueled by resource competition, power struggles, and identity assertions within communities or organizations. These disputes significantly impact social cohesion, escalate violence, and disrupt economic activities by creating entrenched divisions and insecurity in affected areas. Understanding the roots of turf wars is essential for developing conflict resolution strategies that address underlying causes rather than merely managing symptoms.
Key Differences Between Political Rivalry and Turf War
Political rivalry centers on competition for power, influence, and leadership within governmental or organizational structures, whereas turf wars involve disputes over control of physical or operational territories, often between informal groups or factions. Political rivalry typically manifests through strategic alliances, policy debates, and electoral contests, while turf wars are more likely to involve direct confrontation, territorial defense, and resource dominance. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for analyzing conflicts in political science and organizational behavior contexts.
Motivations Behind Political Conflicts
Political rivalry often stems from the pursuit of power, influence, and policy control within established institutions, driven by ideological differences or ambitions for leadership. Turf wars arise from territorial control, resource allocation, and dominance over specific areas or market segments, motivated by economic gains and protecting vested interests. Both conflicts share a core motivation of securing authority but differ in arenas and tactics used to consolidate control.
Influence of Power Dynamics in Rivalries
Political rivalry often centers on competing ideologies and the pursuit of influence within established institutions, shaping policies and governance. Turf wars primarily involve control over specific areas or resources, emphasizing territorial dominance and operational authority. Power dynamics critically influence both, as the balance of authority, strategic alliances, and resource control determine the intensity and outcomes of rivalries.
Manifestations of Turf Wars in Modern Politics
Turf wars in modern politics often manifest through intense competition over jurisdictional authority, control of party resources, and influence within governmental institutions. These conflicts can lead to legislative gridlock, partisan factionalism, and the marginalization of dissenting voices, undermining effective governance. Evidence of turf wars is prevalent in disputes over committee assignments, budget allocations, and leadership positions, reflecting deep-rooted struggles for power among political actors.
Consequences for Governance and Policy
Political rivalry often leads to polarized decision-making, slowing legislative processes and undermining effective governance, while turf wars result in fragmented authority and inefficient resource allocation, disrupting policy implementation. Rivalries can create entrenched factions that prioritize power over public interest, diminishing accountability and transparency in government operations. Turf wars typically generate overlapping responsibilities and conflicting agendas among agencies, weakening institutional cohesion and reducing policy effectiveness.
Notable Examples from Global Politics
Political rivalry often manifests in high-stakes electoral battles like the intense competition between the United States' Democratic and Republican parties, where ideological differences shape national policy directions. Turf wars emerge more distinctly within factional disputes such as the power struggle between China's Communist Party leaders Xi Jinping and his rivals, reflecting conflicts over control rather than policy. Notable global examples highlight that political rivalry centers on competing governance approaches, whereas turf wars revolve around dominance over specific political territories or institutions.
Strategies for Conflict Resolution and Prevention
Political rivalry often involves strategic negotiation, coalition-building, and communication channels to de-escalate tensions and resolve conflicts through formal mechanisms like mediation or diplomacy. Turf wars typically require clearly defined boundaries, conflict management protocols, and third-party arbitration to prevent disputes over resources or control, emphasizing proactive engagement and mutual agreements. Effective conflict resolution in both contexts hinges on transparency, trust-building, and establishing shared goals to reduce competition and promote cooperation.
Political rivalry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com