Swing voters hold the balance of power in closely contested elections by shifting their support between parties based on candidates and issues. Understanding the motivations and concerns of these undecided voters is crucial for crafting effective campaign strategies. Explore how swing voters influence election outcomes and what this means for Your political engagement in the full article.
Table of Comparison
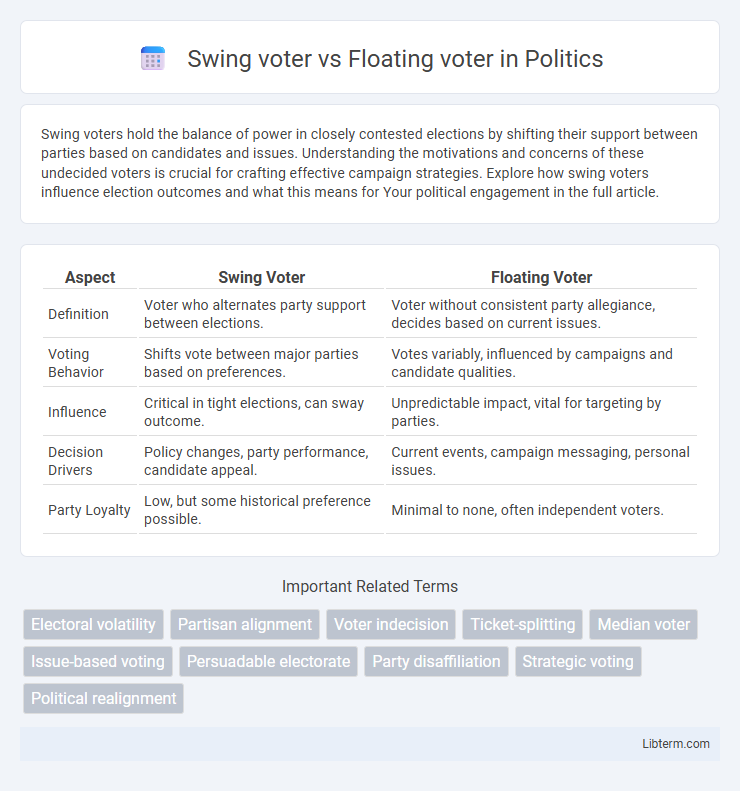
| Aspect | Swing Voter | Floating Voter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voter who alternates party support between elections. | Voter without consistent party allegiance, decides based on current issues. |
| Voting Behavior | Shifts vote between major parties based on preferences. | Votes variably, influenced by campaigns and candidate qualities. |
| Influence | Critical in tight elections, can sway outcome. | Unpredictable impact, vital for targeting by parties. |
| Decision Drivers | Policy changes, party performance, candidate appeal. | Current events, campaign messaging, personal issues. |
| Party Loyalty | Low, but some historical preference possible. | Minimal to none, often independent voters. |
Definition of Swing Voter
A swing voter is an individual who does not have a consistent allegiance to a single political party and can be persuaded to vote for different candidates or parties in different elections based on issues, candidates, or current events. Floating voters share similarities with swing voters but are often characterized by a lack of strong political opinions or commitment, making their voting behavior more unpredictable. Understanding the distinction between swing and floating voters is crucial for political campaigns aiming to target undecided or persuadable electorates.
Definition of Floating Voter
Floating voters are individuals who do not have a consistent party affiliation and can shift their support between different political parties or candidates in each election. These voters are influenced by current issues, candidate appeal, and campaign strategies rather than ideological loyalty. In contrast, swing voters also lack fixed party loyalty but are specifically targeted as they often decide the outcome in closely contested elections.
Key Differences Between Swing and Floating Voters
Swing voters are individuals who switch their support between major political parties based on candidates' policies and campaign effectiveness, often influencing election outcomes in closely contested regions. Floating voters lack strong party allegiance and may vote unpredictably, driven by current events or immediate issues rather than long-term political preferences. The key difference lies in swing voters' potential to sway tightly contested elections, while floating voters reflect a more volatile and less predictable electorate segment.
Historical Significance of Swing Voters
Swing voters have played a crucial role in shaping election outcomes throughout history, often determining the balance of power in closely contested political races. Their shifting allegiances reflect changing social, economic, and political climates, making them a focal point in campaign strategies since at least the early 20th century. Key examples include the 1960 U.S. presidential election and the Brexit referendum, where swing voters' decisions significantly impacted the final results.
The Role of Floating Voters in Elections
Floating voters play a crucial role in elections by acting as the unpredictable segment of the electorate who have no fixed party allegiance, often deciding the outcome in closely contested races. Their voting behavior is influenced by current issues, campaign strategies, and candidate appeal rather than long-term loyalty to political parties. Understanding the preferences and concerns of floating voters enables political campaigns to tailor messages effectively, making them a pivotal target for winning elections.
Demographic Profiles: Swing vs. Floating Voters
Swing voters typically belong to middle-income brackets and often include suburban families with moderate education levels, showing a historical tendency to shift between major political parties based on policy impact. Floating voters are frequently younger, highly mobile individuals with diverse educational backgrounds, often less politically engaged and more influenced by current events and media narratives. Both groups play crucial roles in elections, but swing voters usually have more consistent voting patterns, while floating voters can be more unpredictable.
Factors Influencing Swing Voters
Swing voters are influenced by campaign messaging, current events, and candidate charisma, making their decisions highly responsive to persuasive communication and emotional appeal. Economic conditions, social issues, and media coverage heavily impact their voting behavior, as they seek stability and alignment with personal values. Unlike floating voters, swing voters exhibit more informed and deliberate consideration, often weighing past performance and policy proposals before deciding.
Factors Influencing Floating Voters
Floating voters, characterized by their lack of allegiance to any political party, are influenced by factors such as candidate appeal, current political issues, and campaign effectiveness. Economic conditions, media coverage, and social influences also play significant roles in shaping their voting decisions. Unlike swing voters who may have a history of party preference but switch allegiance, floating voters remain unpredictable until the moment of choice.
Impact on Election Outcomes
Swing voters, who shift their support between parties from one election to another, significantly influence election outcomes by creating unpredictable vote distributions and often determining the margin of victory. Floating voters, lacking strong party loyalty and easily swayed by campaigns or current issues, can alter the direction of an election by responding to candidate performance and policy appeals in real-time. Both groups increase electoral volatility, compelling candidates to prioritize targeted messaging and dynamic strategies to capture their decisive support.
Strategies to Target Swing and Floating Voters
Effective strategies to target swing voters involve personalized messaging that addresses their core concerns and emphasizes policy differences between candidates, leveraging data analytics to identify key issues and demographic trends. For floating voters, campaigns prioritize clear, consistent communication and emotional appeals to build trust and reduce uncertainty, often utilizing social media and grassroots outreach to engage and influence their decision-making process. Tailored voter segmentation combined with targeted advertisements enhances the ability to sway both swing and floating voters in competitive electoral districts.
Swing voter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com