Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and social orders to maintain stability and continuity in society. It advocates for limited government intervention, individual responsibility, and respect for established customs that have stood the test of time. Explore the rest of the article to understand how conservatism shapes modern political and cultural landscapes.
Table of Comparison
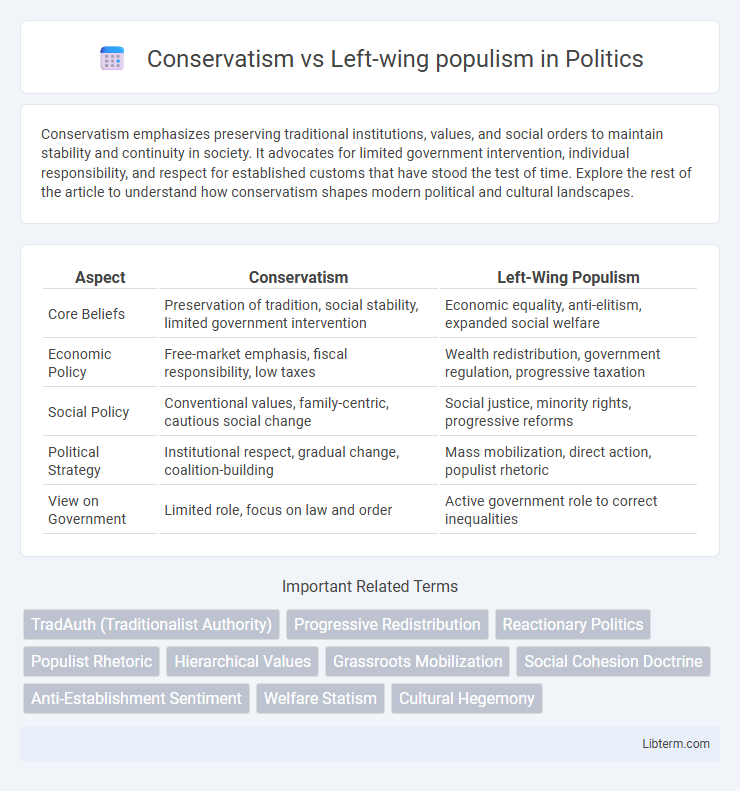
| Aspect | Conservatism | Left-Wing Populism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Beliefs | Preservation of tradition, social stability, limited government intervention | Economic equality, anti-elitism, expanded social welfare |
| Economic Policy | Free-market emphasis, fiscal responsibility, low taxes | Wealth redistribution, government regulation, progressive taxation |
| Social Policy | Conventional values, family-centric, cautious social change | Social justice, minority rights, progressive reforms |
| Political Strategy | Institutional respect, gradual change, coalition-building | Mass mobilization, direct action, populist rhetoric |
| View on Government | Limited role, focus on law and order | Active government role to correct inequalities |
Defining Conservatism and Left-Wing Populism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and social orders, often advocating for gradual change and skepticism toward radical reforms. Left-wing populism centers on mobilizing the working class against perceived elite control, promoting economic equality, and challenging capitalism through policies favoring social welfare and redistribution. Both ideologies fundamentally differ in their approach to social hierarchy, economic policies, and visions for political power distribution.
Historical Roots and Evolution
Conservatism traces its historical roots to the reaction against the French Revolution, emphasizing tradition, social order, and gradual change, as articulated by thinkers like Edmund Burke in the 18th century. Left-wing populism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, evolving from labor movements and socialist ideas that advocated for economic equality, social justice, and direct appeals to the working class. Over time, conservatism has generally sought to preserve established institutions, whereas left-wing populism has focused on mobilizing marginalized groups against perceived elite control and systemic inequalities.
Core Values and Ideologies
Conservatism emphasizes tradition, social stability, and limited government intervention, advocating for the preservation of established institutions and cultural norms. Left-wing populism centers on social justice, economic equality, and grassroots empowerment, challenging entrenched elites and promoting policies that support marginalized groups. Both ideologies prioritize different approaches to governance, with conservatism valuing order and continuity, while left-wing populism seeks radical reforms to address systemic inequalities.
Economic Perspectives and Policies
Conservatism emphasizes free-market principles, limited government intervention, and fiscal responsibility to promote economic stability and growth. Left-wing populism advocates for wealth redistribution, increased social spending, and regulation of corporations to address economic inequality and protect workers' rights. Economic policies under conservatism prioritize tax cuts and deregulation, while left-wing populism supports progressive taxation and expansive welfare programs.
Social Issues and Cultural Stances
Conservatism typically emphasizes preserving traditional social values, advocating for policies that uphold family structures, religious principles, and national identity. Left-wing populism often challenges established social norms by promoting progressive stances on issues like LGBTQ+ rights, racial equality, and inclusive immigration policies. These opposing perspectives shape debates on cultural identity, social justice, and the role of government in regulating moral and cultural matters.
Approaches to Governance and Power
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditions, institutions, and gradual change, advocating for limited government intervention and a strong rule of law to maintain social order and stability. Left-wing populism seeks to redistribute power by challenging elite control and expanding government roles to address social inequalities, promoting direct democratic participation and policies aimed at economic justice. Both approaches shape governance through contrasting views on authority: conservatism favors hierarchical structures and incremental reform, while left-wing populism endorses mass mobilization and structural transformation.
Attitudes Toward Globalization and Nationalism
Conservatism typically emphasizes protecting national sovereignty and cultural traditions, often expressing skepticism toward globalization due to concerns over economic competition and loss of national identity. Left-wing populism, while critical of corporate-driven globalization, advocates for global solidarity and inclusive economic policies that challenge inequality and advocate for social justice. Both ideologies use nationalism differently: conservatives prioritize preserving established national institutions, whereas left-wing populists promote a nationalism centered on defending the working class and marginalized groups from global neoliberal forces.
Populism: Rhetoric and Public Mobilization
Populism employs rhetoric that emphasizes direct connection between the "pure people" and a virtuous leader, often framing elites as corrupt adversaries. Left-wing populism mobilizes public support by addressing socioeconomic inequalities, advocating wealth redistribution, and challenging corporate power through inclusive, grassroots campaigns. This rhetorical strategy effectively galvanizes marginalized groups by promoting solidarity and collective political empowerment.
Major Parties and Key Figures
The Conservative Party, led by figures such as Rishi Sunak, advocates for traditional values, free-market policies, and limited government intervention. Left-wing populism is epitomized by parties like the Labour Party, with key figures including Jeremy Corbyn and currently Keir Starmer, emphasizing wealth redistribution, social justice, and expanded welfare programs. Major parties on both sides leverage their ideological bases to address economic inequality and national identity, shaping contemporary political debates.
Contemporary Impact and Future Trends
Conservatism emphasizes tradition, limited government, and free-market principles, shaping policies that prioritize economic stability and national identity in contemporary politics. Left-wing populism challenges economic inequality and corporate power, advocating for social justice reforms and expanded welfare programs, which has increased grassroots mobilization globally. Future trends suggest a dynamic interplay where conservatism may reinforce cultural preservation amid globalization, while left-wing populism could gain influence through digital activism and shifting demographics demanding socioeconomic equity.
Conservatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com