The treasury bench is the seating area in a parliamentary or legislative assembly reserved for members of the ruling government, including the prime minister and key ministers. It plays a crucial role in policy-making and legislative debates, reflecting the executive's stance on various issues. Discover how the treasury bench influences parliamentary proceedings and shapes national governance in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
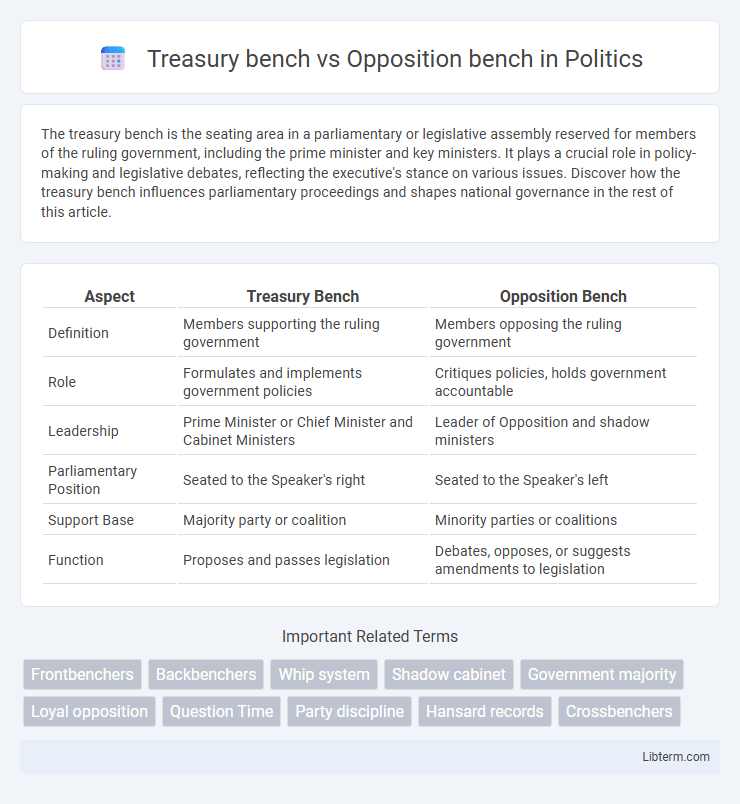
| Aspect | Treasury Bench | Opposition Bench |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Members supporting the ruling government | Members opposing the ruling government |
| Role | Formulates and implements government policies | Critiques policies, holds government accountable |
| Leadership | Prime Minister or Chief Minister and Cabinet Ministers | Leader of Opposition and shadow ministers |
| Parliamentary Position | Seated to the Speaker's right | Seated to the Speaker's left |
| Support Base | Majority party or coalition | Minority parties or coalitions |
| Function | Proposes and passes legislation | Debates, opposes, or suggests amendments to legislation |
Introduction to Treasury and Opposition Benches
The Treasury bench refers to the seats occupied by government ministers and ruling party members responsible for proposing and implementing policies in the legislature. The Opposition bench consists of members from political parties not in power, tasked with scrutinizing government actions and offering alternative policies. Both benches play crucial roles in democratic governance, ensuring balanced debate and accountability in parliamentary proceedings.
Historical Origins of Parliamentary Benches
The Treasury Bench and the Opposition Bench trace their origins to the British Parliament, where the seating arrangement physically represents the government's executive and opposing parties. Historically, the Treasury Bench held members of the ruling party including the Prime Minister and key ministers, reflecting direct governance responsibility, while the Opposition Bench housed leaders and members tasked with scrutinizing government policies. This division emerged from the evolution of constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy in the UK, influencing numerous Commonwealth legislatures worldwide.
Composition and Roles of the Treasury Bench
The Treasury Bench comprises members of the ruling party or coalition, including key government officials such as the Prime Minister and Cabinet Ministers responsible for policy formulation and administration. Their primary roles include proposing legislation, defending government policies, and managing the state's executive functions. In contrast, the Opposition Bench consists of members from opposition parties tasked with scrutinizing government actions and holding the Treasury Bench accountable.
Key Functions of the Opposition Bench
The Opposition bench plays a crucial role in a parliamentary democracy by holding the government accountable through questioning policies, scrutinizing legislation, and representing alternative viewpoints. Members of the Opposition actively participate in debates, propose amendments, and ensure transparency in governance. Their key functions also include safeguarding democratic principles and voicing public concerns to balance the power of the Treasury bench.
Institutional Powers: Treasury vs Opposition
The Treasury bench holds institutional powers including the formulation and execution of government policies, control over the financial budget, and the authority to administer public administration. The Opposition bench exercises crucial institutional powers by scrutinizing government actions, holding the executive accountable through questioning and debates, and providing alternative policy perspectives. Both benches play essential roles in parliamentary democracy, with the Treasury driving governance and the Opposition ensuring transparency and checks on power.
Debate Dynamics Between Both Benches
The Treasury bench, representing the ruling government, drives legislative agendas and employs strategic rhetoric to justify policies, emphasizing governance and development. The Opposition bench counters by scrutinizing government actions, raising dissent, and highlighting policy flaws to hold the government accountable. Debate dynamics between both benches intensify parliamentary proceedings, fostering robust discussions essential for democratic decision-making.
Policy Formulation: Government vs Scrutiny
The Treasury bench, representing the ruling government, takes primary responsibility for policy formulation and legislative agenda setting, driving national development priorities through proposed laws and budget allocations. The Opposition bench plays a critical role in scrutiny, rigorously analyzing government policies, debating their implications, and holding the administration accountable to ensure transparency and prevent misuse of power. This dynamic balance between proactive governance and vigilant oversight sustains democratic decision-making and effective public administration.
Influence on Legislative Outcomes
The Treasury bench, comprising government members, wields significant influence on legislative outcomes through agenda control and majority voting power, often steering bills toward approval. The Opposition bench provides critical scrutiny and debate, influencing amendments and public opinion to shape legislation. Effective interplay between these benches determines the balance of policy direction and democratic accountability in parliamentary decisions.
Challenges Facing Both Benches
The Treasury bench grapples with the challenge of effectively implementing government policies while managing public expectations and ensuring legislative compliance. The Opposition bench faces obstacles in holding the government accountable, maintaining cohesive party strategy, and effectively voicing dissent within parliamentary procedures. Both benches must navigate the complexities of political negotiation, media scrutiny, and public opinion to influence legislative outcomes.
Conclusion: Balancing Power in Parliament
The dynamic between the Treasury bench and Opposition bench is crucial for maintaining a functional parliamentary democracy by ensuring a balance of power. The Treasury bench, comprising government ministers, drives legislation and policy execution, while the Opposition bench provides critical scrutiny and accountability. This interplay fosters transparency, prevents authoritarian rule, and upholds the democratic principle of checks and balances.
Treasury bench Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com