Reaction is a fundamental concept in chemistry and biology, describing how substances interact to form new products or trigger biological responses. Understanding specific reaction mechanisms can help you predict outcomes and control processes in laboratory or real-life scenarios. Explore the article further to uncover detailed insights into different types of reactions and their practical applications.
Table of Comparison
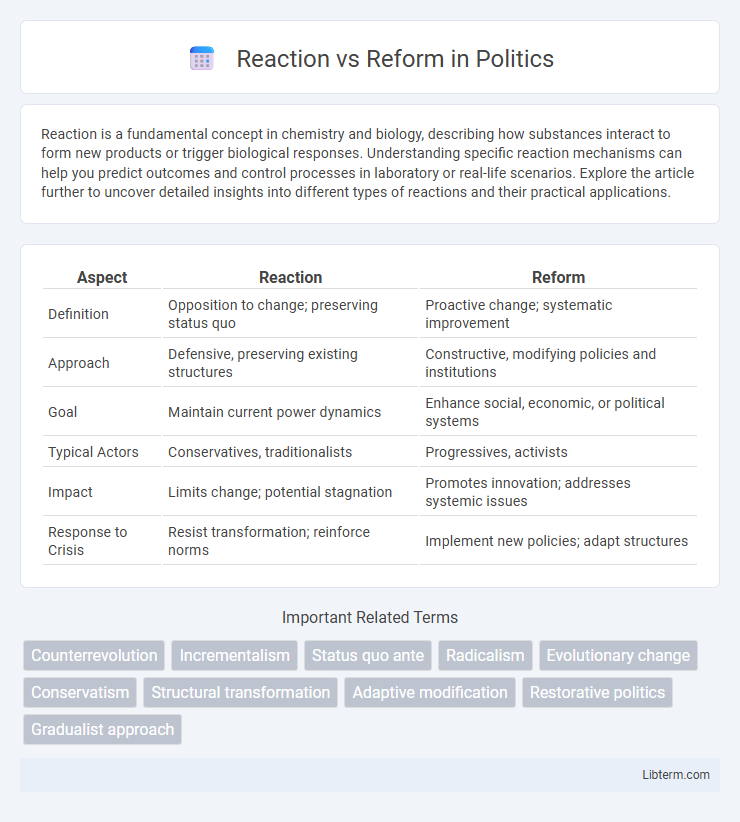
| Aspect | Reaction | Reform |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Opposition to change; preserving status quo | Proactive change; systematic improvement |
| Approach | Defensive, preserving existing structures | Constructive, modifying policies and institutions |
| Goal | Maintain current power dynamics | Enhance social, economic, or political systems |
| Typical Actors | Conservatives, traditionalists | Progressives, activists |
| Impact | Limits change; potential stagnation | Promotes innovation; addresses systemic issues |
| Response to Crisis | Resist transformation; reinforce norms | Implement new policies; adapt structures |
Understanding Reaction vs Reform
Understanding reaction versus reform highlights the contrast between resistance to change and deliberate efforts to improve systems. Reaction often involves defensive responses aimed at preserving existing structures, while reform embodies proactive strategies to address underlying issues through policy or social change. Distinguishing these concepts is essential for effective governance, organizational development, and societal progress.
Historical Context of Reactionary and Reform Movements
Reactionary movements historically arise as responses opposing rapid political or social changes, aiming to preserve traditional structures and values, often seen during periods of revolution or upheaval such as post-French Revolution Europe. Reform movements seek gradual change to improve societal conditions, emerging prominently during the 19th and 20th centuries with goals like expanding suffrage, abolishing slavery, and labor rights. The tension between these movements shapes political landscapes, exemplified by the conservative backlash to progressive reforms during the American Civil Rights era.
Key Differences Between Reaction and Reform
Reaction involves immediate responses aimed at resisting change or restoring previous conditions, often driven by emotional or defensive motives. Reform entails deliberate, structured efforts to improve systems or policies through systematic changes focused on long-term progress. Key differences include the timing, intention, and scope, where reaction is spontaneous and preservationist while reform is proactive and transformative.
Motivations Behind Reactionary Actions
Reactionary actions are primarily motivated by a desire to preserve existing social, political, or cultural structures perceived as threatened by rapid change or reform movements. These motivations stem from fear of loss, skepticism about progress, and a preference for traditional values and hierarchies. Often, reactionaries seek to restore previous norms through resistance to policies or ideologies advocating transformation.
Drivers of Reform in Society
Social inequities, economic stagnation, and public demand for justice act as powerful drivers of reform, compelling governments and institutions to implement lasting changes. Technological advancements and increased access to information empower citizens, fostering awareness and mobilizing collective action. Pressure from marginalized groups and global movements intensify efforts to challenge outdated systems, prompting policies that promote equity, transparency, and sustainability.
Political Implications of Reaction and Reform
Reaction often reinforces existing power structures by resisting change, leading to political stagnation and potential authoritarianism. Reform promotes progressive policy shifts, increasing political inclusivity and institutional adaptability. The tension between reaction and reform shapes governance dynamics and influences social stability.
Social Impacts: Reaction vs Reform
Social reaction often triggers resistance and polarization, resulting in social unrest and diminished trust within communities. In contrast, reform promotes gradual social progress and inclusivity, fostering stronger social cohesion and equitable opportunities. Empirical studies reveal that societies embracing reform experience lower inequality and higher social capital compared to those dominated by reactive responses.
Case Studies: Reactionary vs Reformist Approaches
Case studies reveal that reactionary approaches often emphasize preserving traditional values through resistance to change, as seen in movements opposing rapid technological advancements or social reforms. Reformist approaches prioritize gradual, evidence-based changes that address systemic issues, exemplified by successful public health campaigns or education system overhauls. Comparative analysis indicates reformist strategies yield more sustainable long-term outcomes, while reactionary responses may trigger social polarization or stagnation.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Paths
Reaction often faces criticism for resisting necessary change and perpetuating outdated systems, leading to stagnation and increased social tension. Reform encounters challenges such as bureaucratic inertia, limited scope, and slow implementation, which can frustrate stakeholders seeking swift transformation. Both paths struggle with balancing stability and progress, often sparking debates over effectiveness and long-term impact in political and social contexts.
Future Outlook: The Role of Reaction and Reform
The future outlook hinges on a balance between reaction and reform, where reaction addresses immediate crises and reforms pave the way for systemic change. Emphasizing reform fosters long-term resilience by implementing policies that anticipate evolving challenges in governance and society. Effective future strategies integrate reactive agility with proactive reform measures to ensure sustainable development and innovation.
Reaction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com