Economic power shapes global influence by determining a nation's ability to control resources, trade, and financial systems. It directly impacts your country's political leverage and development opportunities on the world stage. Explore the rest of the article to understand how economic strength transforms international relations and individual prosperity.
Table of Comparison
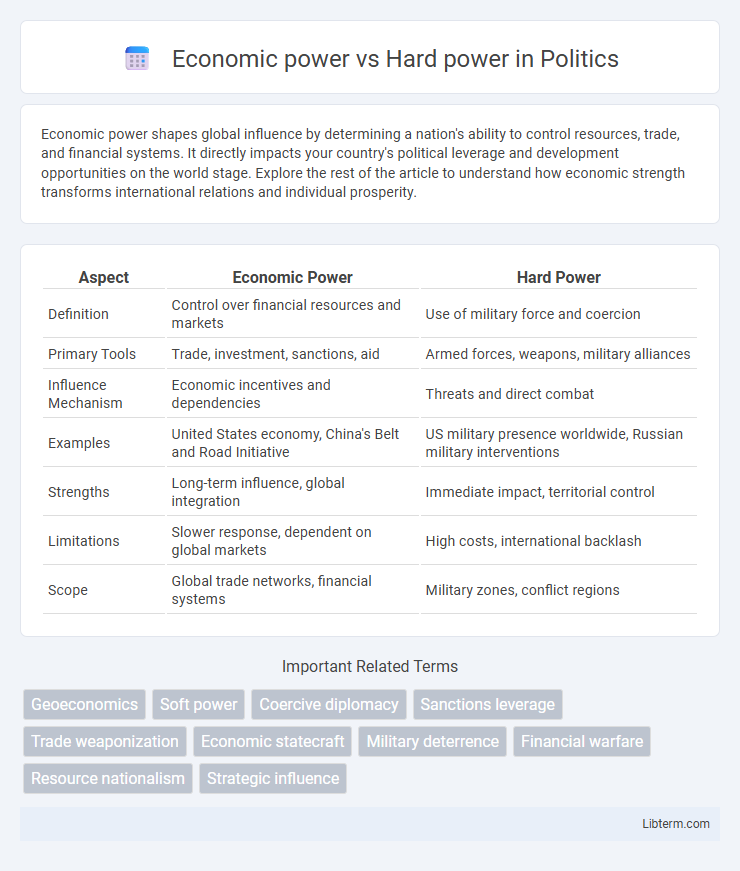
| Aspect | Economic Power | Hard Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control over financial resources and markets | Use of military force and coercion |
| Primary Tools | Trade, investment, sanctions, aid | Armed forces, weapons, military alliances |
| Influence Mechanism | Economic incentives and dependencies | Threats and direct combat |
| Examples | United States economy, China's Belt and Road Initiative | US military presence worldwide, Russian military interventions |
| Strengths | Long-term influence, global integration | Immediate impact, territorial control |
| Limitations | Slower response, dependent on global markets | High costs, international backlash |
| Scope | Global trade networks, financial systems | Military zones, conflict regions |
Defining Economic Power and Hard Power
Economic power refers to a nation's ability to influence other countries through control over resources, trade, financial markets, and economic policies that drive global wealth distribution. Hard power involves the use of military force, coercion, and physical threats to achieve geopolitical objectives and enforce national interests. While economic power shapes international relations through financial leverage and sanctions, hard power relies on tangible military capabilities and strategic defense systems.
Historical Context of Power Dynamics
Throughout history, economic power has often underpinned military strength, with empires like Rome and Britain leveraging wealth to build formidable armies and navies. The Industrial Revolution marked a shift where economic capacity became a crucial determinant of hard power, enabling rapid mobilization and technological advancements in warfare. Modern global influence balances economic dominance, exemplified by the U.S. and China, alongside hard power capabilities such as military alliances and technological defense systems.
Key Instruments of Economic Power
Economic power harnesses key instruments such as trade policies, financial markets, and technological innovation to influence global dynamics and shape international relations. Control over strategic resources, foreign direct investment, and economic aid further amplifies a nation's ability to exert influence without resorting to military force. Leveraging sanctions and currency strength also plays a crucial role in compelling compliance and shaping geopolitical outcomes effectively.
Military Might: The Essence of Hard Power
Military might remains the core of hard power, enabling nations to exert influence through defense capabilities, strategic deployments, and advanced weaponry. Economic power fuels military strength by funding technological advancements, maintaining armed forces, and supporting defense infrastructure. Despite the rising significance of economic influence, the essence of hard power lies in a country's ability to project military force decisively and effectively.
Case Studies: Nations Balancing Both Powers
China exemplifies the strategic balance between economic power and hard power by leveraging its vast economic resources to fund military modernization and assert influence through projects like the Belt and Road Initiative. The United States maintains its global dominance by combining robust economic strength with advanced military capabilities, enabling rapid deployment and strategic alliances worldwide. Russia utilizes hard power to project influence regionally while facing economic sanctions that challenge its economic stability, highlighting the complex interplay between both power types in modern geopolitics.
Impact of Globalization on Power Structures
Economic power reshapes global influence by enabling nations to exert control through trade, investment, and financial markets, surpassing traditional hard power based on military force. Globalization amplifies economic interdependence, weakening unilateral hard power strategies and promoting multilateral cooperation and soft diplomacy. The shift in power structures favors countries with robust economies and technological innovation, challenging the dominance of conventional military superpowers.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Economic Influence
Measuring the effectiveness of economic influence involves analyzing metrics such as trade volume, investment flows, and financial sanctions compliance, which reflect a nation's capacity to shape global behavior without military force. Indicators like GDP share in global trade, control over critical resources, and participation in international financial institutions quantify economic power's reach and impact. Success in achieving policy goals through sanctions enforcement or bilateral agreements demonstrates economic influence as a strategic tool contrasted with traditional hard power.
Limitations and Risks of Hard Power
Hard power, characterized by military force and coercion, faces significant limitations such as high economic costs and international backlash, which can undermine long-term strategic goals. The use of hard power often escalates conflicts, risking loss of life, infrastructure damage, and regional instability, thereby reducing its effectiveness in securing lasting peace. Moreover, reliance on military might may alienate allies and fuel anti-state sentiments, ultimately weakening a nation's global influence compared to economic power's capacity for sustainable influence through trade, investment, and diplomacy.
The Shift Toward Economic Statecraft
The shift toward economic statecraft highlights how nations increasingly leverage economic tools such as trade policies, sanctions, and investment controls to achieve geopolitical objectives without resorting to military force. Economic power now plays a crucial role in shaping global influence, complementing or even substituting traditional hard power mechanisms like military interventions and defense capabilities. This strategic emphasis on economic instruments reflects a broader trend where global interconnectedness and economic interdependence become central to national security and international diplomacy.
Future Trends: Blending Economic and Hard Power
Future trends indicate a strategic blend of economic power and hard power will shape global influence, with nations increasingly leveraging economic sanctions alongside military capabilities to achieve geopolitical objectives. The rise of integrated tools such as cyber warfare combined with financial warfare exemplifies this fusion, highlighting the necessity for multifaceted national security strategies. Countries like China and the United States exemplify this trend by deploying economic initiatives like the Belt and Road alongside military presence, signaling a new era of hybrid power projection.
Economic power Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com