Democratic socialism advocates for a political and economic system where both democracy and social ownership coexist, aiming to reduce income inequality and provide universal access to essential services like healthcare and education. It emphasizes collective decision-making through elected representatives and policies that prioritize social welfare without abolishing capitalism entirely. Discover how democratic socialism shapes modern governance and impacts Your society by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
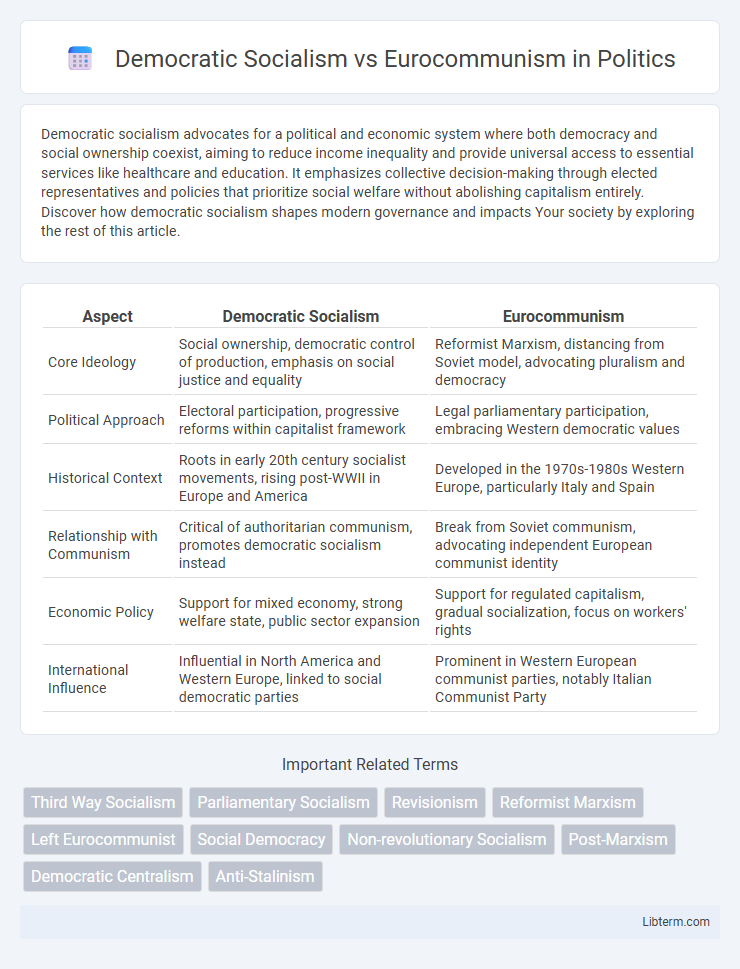
| Aspect | Democratic Socialism | Eurocommunism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Ideology | Social ownership, democratic control of production, emphasis on social justice and equality | Reformist Marxism, distancing from Soviet model, advocating pluralism and democracy |
| Political Approach | Electoral participation, progressive reforms within capitalist framework | Legal parliamentary participation, embracing Western democratic values |
| Historical Context | Roots in early 20th century socialist movements, rising post-WWII in Europe and America | Developed in the 1970s-1980s Western Europe, particularly Italy and Spain |
| Relationship with Communism | Critical of authoritarian communism, promotes democratic socialism instead | Break from Soviet communism, advocating independent European communist identity |
| Economic Policy | Support for mixed economy, strong welfare state, public sector expansion | Support for regulated capitalism, gradual socialization, focus on workers' rights |
| International Influence | Influential in North America and Western Europe, linked to social democratic parties | Prominent in Western European communist parties, notably Italian Communist Party |
Introduction to Democratic Socialism and Eurocommunism
Democratic Socialism advocates for a political system combining democratic governance with social ownership of the means of production, aiming to reduce economic inequality through progressive policies and social welfare programs. Eurocommunism emerged in the 1970s as a revisionist trend within Western European communist parties, seeking to distance itself from Soviet-style authoritarianism by promoting political pluralism, civil liberties, and democratic socialism. Both ideologies emphasize democratic engagement but differ in their approach to socialism, with Democratic Socialism prioritizing gradual reform within existing democratic frameworks and Eurocommunism focusing on ideological independence from traditional Marxist-Leninist doctrines.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Democratic Socialism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a movement advocating for political democracy alongside social ownership of the means of production, rooted in the labor movements of Western Europe. Eurocommunism developed in the 1970s as a revisionist trend within Western European communist parties, distancing itself from Soviet orthodoxy by promoting parliamentary democracy and pluralism. The historical evolution of Democratic Socialism is marked by its influence on social democratic parties, while Eurocommunism represented a strategic adaptation to Cold War realities, emphasizing independence from Moscow and integration within European political frameworks.
Core Ideological Differences
Democratic Socialism prioritizes social ownership and democratic control of the economy alongside political democracy, emphasizing gradual reform within existing political frameworks to achieve social justice and economic equality. Eurocommunism diverges by advocating for a break from Soviet-style centralized control, promoting pluralism, political autonomy, and alliances with other progressive forces within Western democracies. The core ideological difference lies in Democratic Socialism's emphasis on democratic economic redistribution versus Eurocommunism's insistence on political reform and adaptability to Western parliamentary systems.
Key Political Figures and Movements
Democratic socialism is prominently associated with figures like Bernie Sanders and Jeremy Corbyn, who advocate for social ownership and expanded welfare within pluralistic democratic frameworks. Eurocommunism emerged in the 1970s with leaders such as Enrico Berlinguer of Italy's Italian Communist Party and Santiago Carrillo of Spain's Communist Party, emphasizing independence from Soviet influence and adapting communist ideology to Western European parliamentary systems. Both movements significantly influenced left-wing politics by promoting democratic principles, yet they diverged in their approach to socialism and relations with the Soviet Union.
Economic Policies and Approaches
Democratic Socialism emphasizes extensive welfare states, progressive taxation, and public ownership of key industries to reduce inequality and ensure universal access to healthcare and education. Eurocommunism advocates for a mixed economy where market mechanisms coexist with strong labor rights and social welfare programs, promoting gradual reform through parliamentary democracy rather than revolutionary means. Both approaches prioritize social justice but differ in their reliance on state intervention versus market compatibility to achieve economic equity.
Attitudes Toward Capitalism and Markets
Democratic Socialism advocates for social ownership and extensive regulation of capital, aiming to reduce inequalities while maintaining democratic institutions and market mechanisms under strong government oversight. Eurocommunism, emerging in the 1970s, presents a more critical stance toward capitalism, emphasizing a break from Soviet-style communism and advocating for a mixed economy with limited reliance on markets, focusing on political pluralism and gradual reform. Both ideologies seek to challenge capitalist dominance, but Democratic Socialism integrates market dynamics with social welfare, whereas Eurocommunism prioritizes political democracy and worker control over the means of production.
Strategies for Achieving Social Change
Democratic Socialism emphasizes gradual reform through electoral processes and the expansion of social welfare programs to achieve social change, advocating for a robust welfare state and public ownership in key sectors. Eurocommunism prioritizes political pluralism and coalition-building within parliamentary frameworks, distancing itself from authoritarian models while promoting democratic governance and civil rights. Both strategies underscore the importance of democratic institutions but differ in their approaches to state intervention and party alliances.
Relations with Traditional Marxism-Leninism
Democratic Socialism emphasizes achieving socialism through democratic means, rejecting the authoritarianism associated with traditional Marxism-Leninism, while Eurocommunism seeks to adapt communist principles within a democratic framework, distancing itself from Soviet-style bureaucratic control. Both ideologies critique the centralized, vanguard-party model of Marxism-Leninism but diverge in their approaches to party organization and the role of the state, with Eurocommunism often advocating for parliamentary participation and pluralism. Their relationships with traditional Marxism-Leninism highlight a shift from revolutionary overthrow toward reformist and democratic pathways to socialism.
Influence on Contemporary European Politics
Democratic socialism has significantly shaped welfare state policies across Northern and Western Europe by promoting social justice through electoral democracy and public ownership. Eurocommunism, emerging in the 1970s, influenced Southern and Western European leftist parties by advocating for a democratic path distinct from Soviet-style communism, emphasizing pluralism and civil liberties. Both ideologies contributed to the broadening of the European left's appeal, impacting labor rights, social policies, and the redefinition of socialism in many European political landscapes.
Future Prospects and Global Impact
Democratic Socialism emphasizes gradual reform within democratic frameworks, aiming for social equity and sustainable economic policies, which positions it favorably in evolving pluralistic societies worldwide. Eurocommunism, marked by its rejection of Soviet-style authoritarianism and embrace of parliamentary democracy, influenced leftist movements in Western Europe, but faces challenges adapting to contemporary geopolitical shifts. The future prospects of Democratic Socialism hinge on its ability to address climate change and economic inequality globally, while Eurocommunism's legacy informs debates on democratic governance and socialist strategies in a multipolar world.
Democratic Socialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com